
(a)
Interpretation:
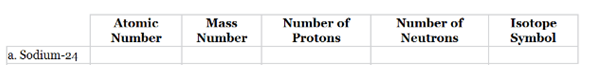
The following table of isotopes should be completed:
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same
To write an isotope symbol atomic number (Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass (A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.28P
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| Sodium-24 | 11 | 24 | 11 | 13 |
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number is equal to the number of protons in an element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
The atomic number for sodium is 11 and the mass number is 24.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the number of protons in sodium is 11 and the number of neutrons in sodium can be calculated by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Sodium is
(b)
Interpretation:
The following table of isotopes should be completed:

Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number (Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass (A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.28P
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| b. Strotium-89 | 38 | 89 | 38 | 51 |
Explanation of Solution
The formula to determine the mass number is:
Rearranging:
Substituting the values:
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the element with atomic number 38 is strontium, Sr.
Therefore, the isotope symbol for strontium is
(c)
Interpretation:
The following table of isotopes should be completed:

Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.28P
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| c. Iron-59 | 26 | 59 | 26 | 33 |
Explanation of Solution
The mass number of element is 59.
Since atomic number = number of protons
So, the atomic number of the isotope is 26 thus, the element is iron, Fe.
Thus, the number of protons for this element is 26 and the number of neutrons in iron can be calculated by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for iron is
(d)
Interpretation:
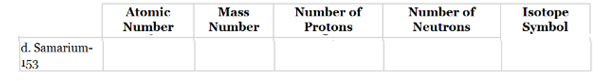
The following table of isotopes should be completed:
Concept Introduction:
Isotopes are the compounds having the same atomic number but different atomic mass.
To write an isotope symbol atomic number(Z) is written on the lower left side and atomic mass(A) is written on the upper left side of an element.
Answer to Problem 10.28P
The complete table for isotopes symbol is represented as follows:
| Atomic number(Z) | Mass number(A) | Number of protons | Number of neutrons | Isotope symbol | |
| d.Samarium-153 | 62 | 153 | 62 | 91 |
Explanation of Solution
The mass number of element is 153.
The atomic number of samarium is 62.
Since atomic number = number of protons
Thus, the number of protons for this element is 62 and the number of neutrons in samarium can be calculated by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number as follows:
Therefore, the isotope symbol for Samarium is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ACCESS CARD F/GEN. ORG.CHEM
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure HO-C-CH2-CH3 O -OH CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-C-OH CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-C-OH Explanation Check S namearrow_forwardtheres 2 productsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this solvolysis reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. + CH3CH2OH Drawing Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OCH2CH3 || OEt Charges OH 00-> | Undo Reset | Br Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts. CH3CO2Na CH3CO2H Drawing + Br Q Atoms, Bonds and Rings OAC Charges OH ОАс Na ဂ Br Undo Reset Remove Done Drag To Pan +arrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups entifying positions labeled with Greek letters in acids and derivatives 1/5 ssible, replace an H atom on the a carbon of the molecule in the drawing area with a ce an H atom on the ẞ carbon with a hydroxyl group substituent. ne of the substituents can't be added for any reason, just don't add it. If neither substi er the drawing area. O H OH Oneither substituent can be added. Check D 1 Accessibility ado na witharrow_forwardDifferentiate between electrophilic and nucleophilic groups. Give examples.arrow_forward
- An aldehyde/ketone plus an alcohol gives a hemiacetal, and an excess of alcohol gives an acetal. The reaction is an equilibrium; in aldehydes, it's shifted to the right and in ketones, to the left. Explain.arrow_forwardDraw a Haworth projection or a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H- -OH H- OH H- -OH CH₂OHarrow_forwardAnswer the question in the first photoarrow_forward
- Ggggffg2258555426855 please don't use AI Calculate the positions at which the probability of a particle in a one-dimensional box is maximum if the particle is in the fifth energy level and in the eighth energy level.arrow_forwardExplain the concepts of hemiacetal and acetal.arrow_forwardBriefly describe a nucleophilic addition.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





