
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Constitutional isomers that has molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
Halogenation reaction is the one where atom or atoms of halogens get substituted in a carbon chain. Halogenation is a type of substitution reaction.
In
IUPAC rules for naming alkanes:
There are about five rules that has to be followed for naming an alkane and they are,
- The longest continuous carbon chain in the compound has to be identified. This is known as parent compound. From this the parent name is obtained. Suffix “–ane” (for alkane) is added at the end of the prefix which gives information about the number of carbon atoms.
- Numbering has to be done so that the lowest number is given to the first group that is encountered in the parent chain.
- Naming and numbering has to be given for each atom or group that is attached to the parent chain. Numbering has to be done in a way that substituents get the least numbering.
- If the same substitution is present in the parent chain more than once, a separate prefix is added which tells about the number of times the substituent occurs. Prefixes used are di-, tri-, tetra-, penta- etc.
- Name of the substituents has to be placed in an alphabetical order before the parent compound name.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecular formula of constitutional isomer is
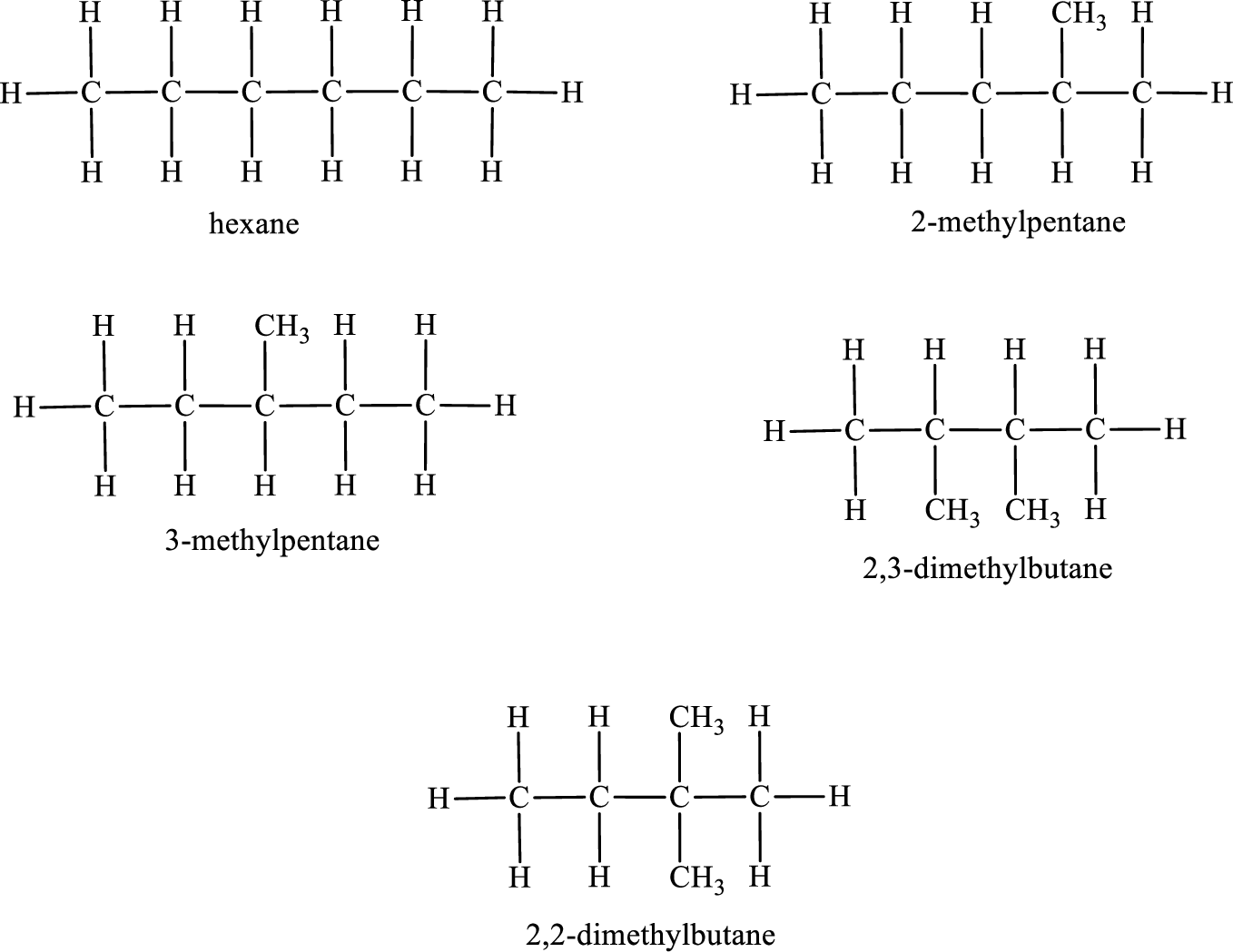
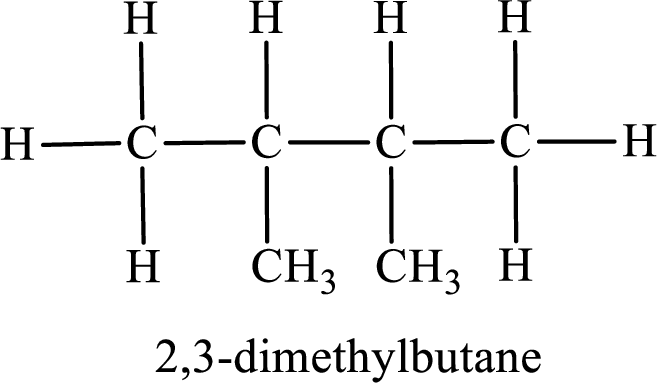
Among the constitutional isomers, the one that gives only two monobromo derivatives can be identified by looking into the structure that contain carbon atoms that has only two different environment. The structure is found to be 2,3-dimethylbutane.
The reaction can be given as,
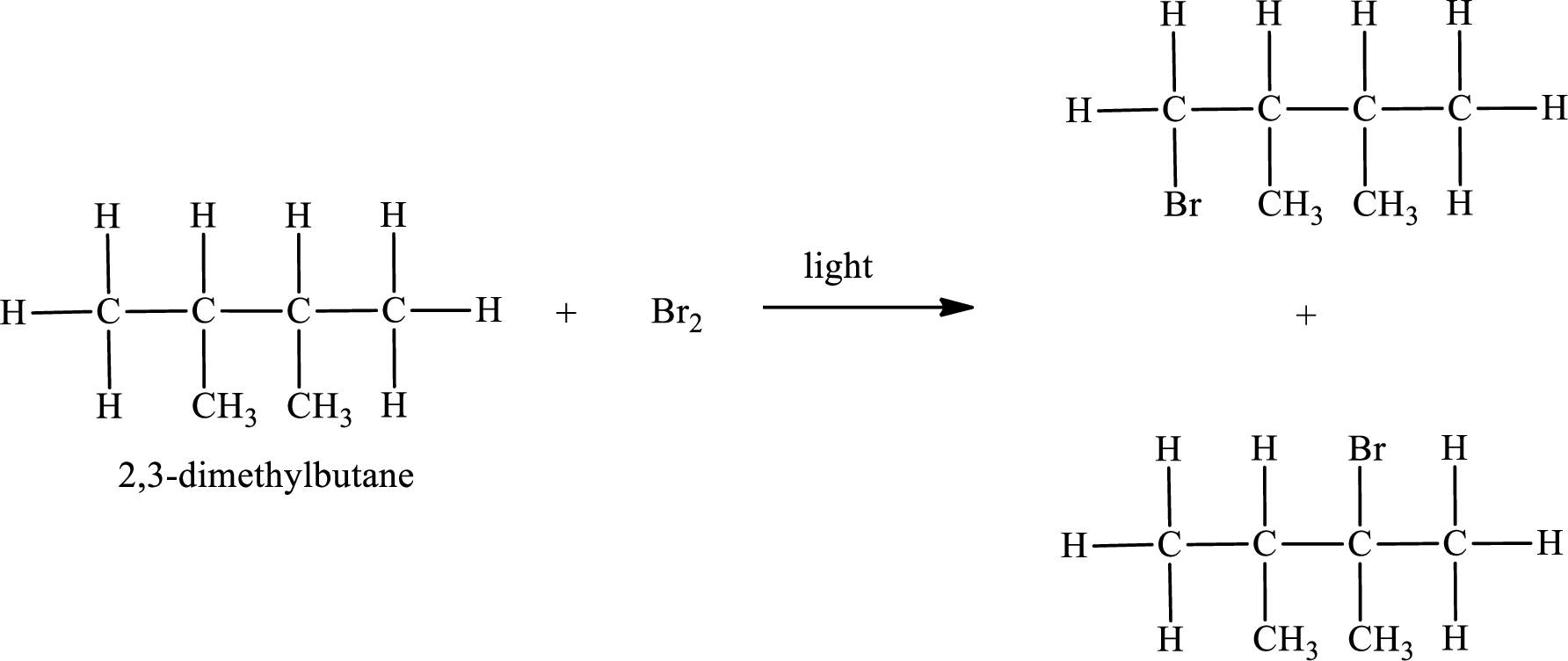
IUPAC names:
First monobromo derivative:
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain four carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is butane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
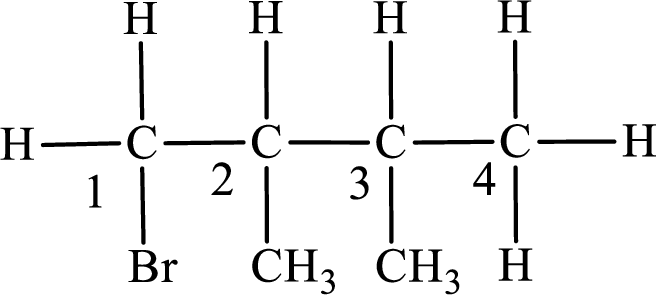
The substituent present in the given compound are a bromine atom and two methyl groups. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
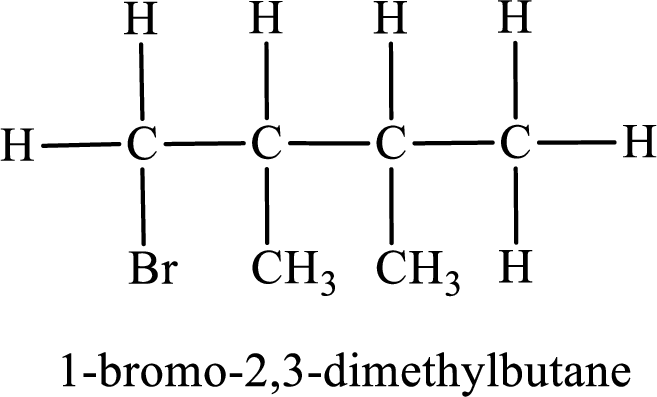
Parent chain is butane and the substituent present is 1-bromo-2,3-dimethyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 1-bromo-2,3-dimethylbutane.
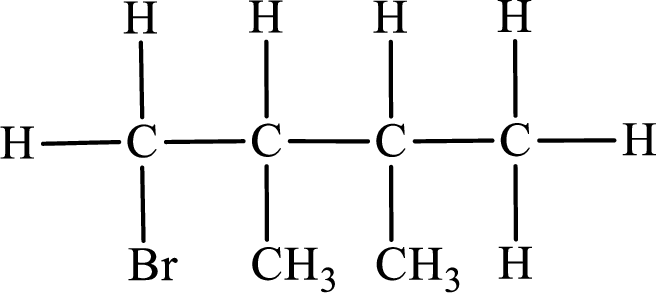
Second monobromo derivative:
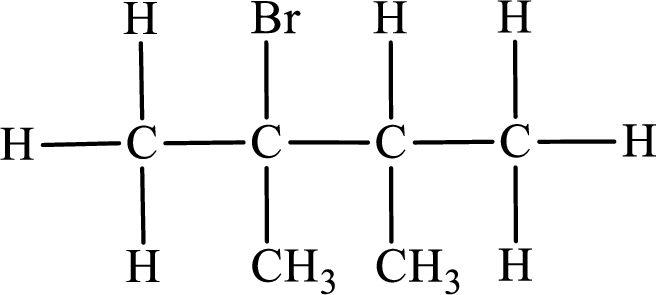
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain four carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is butane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
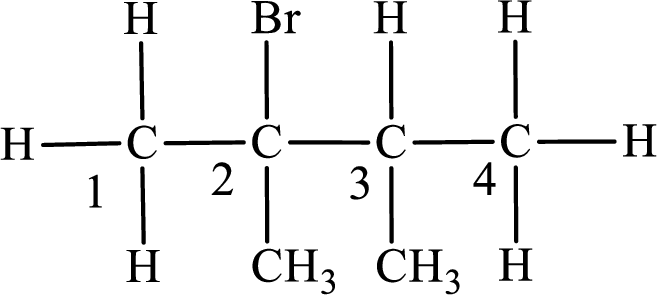
The substituent present in the given compound are a bromine atom and two methyl groups. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
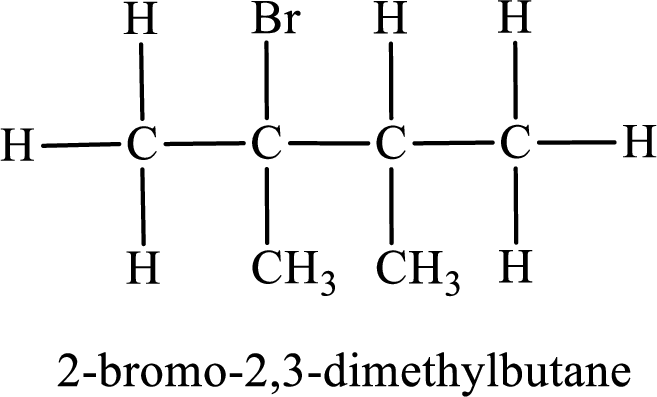
Parent chain is butane and the substituent present is 2-bromo-2,3-dimethyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 2-bromo-2,3-dimethylbutane.
(b)
Interpretation:
Constitutional isomers that has molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecular formula of constitutional isomer is
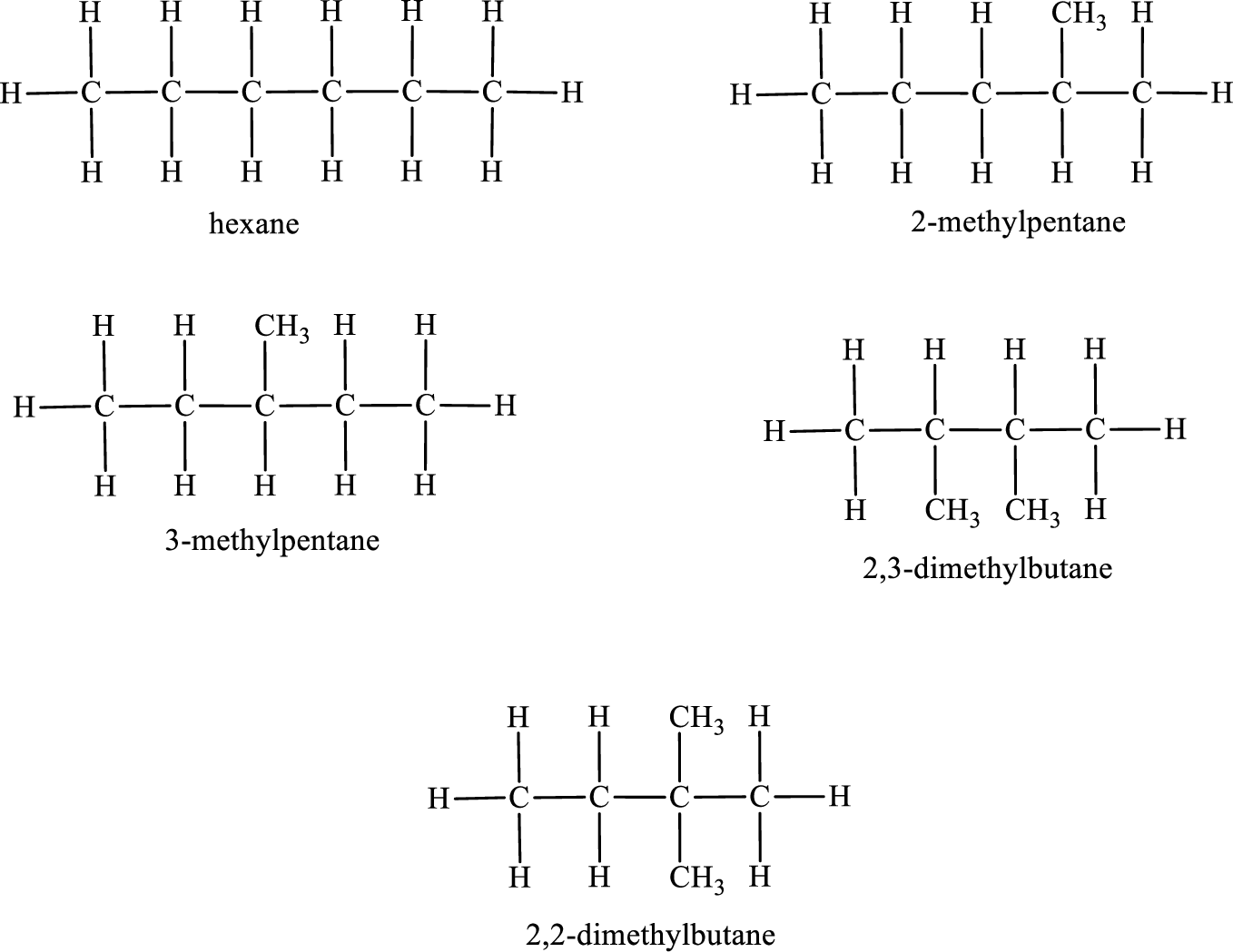
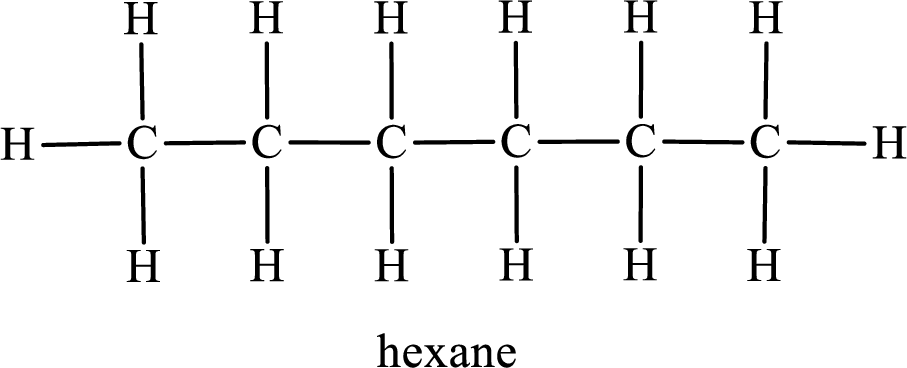
Among the constitutional isomers, the one that gives only three monobromo derivatives can be identified by looking into the structure that contain carbon atoms that has only three different environment. The structure is found to be hexane.
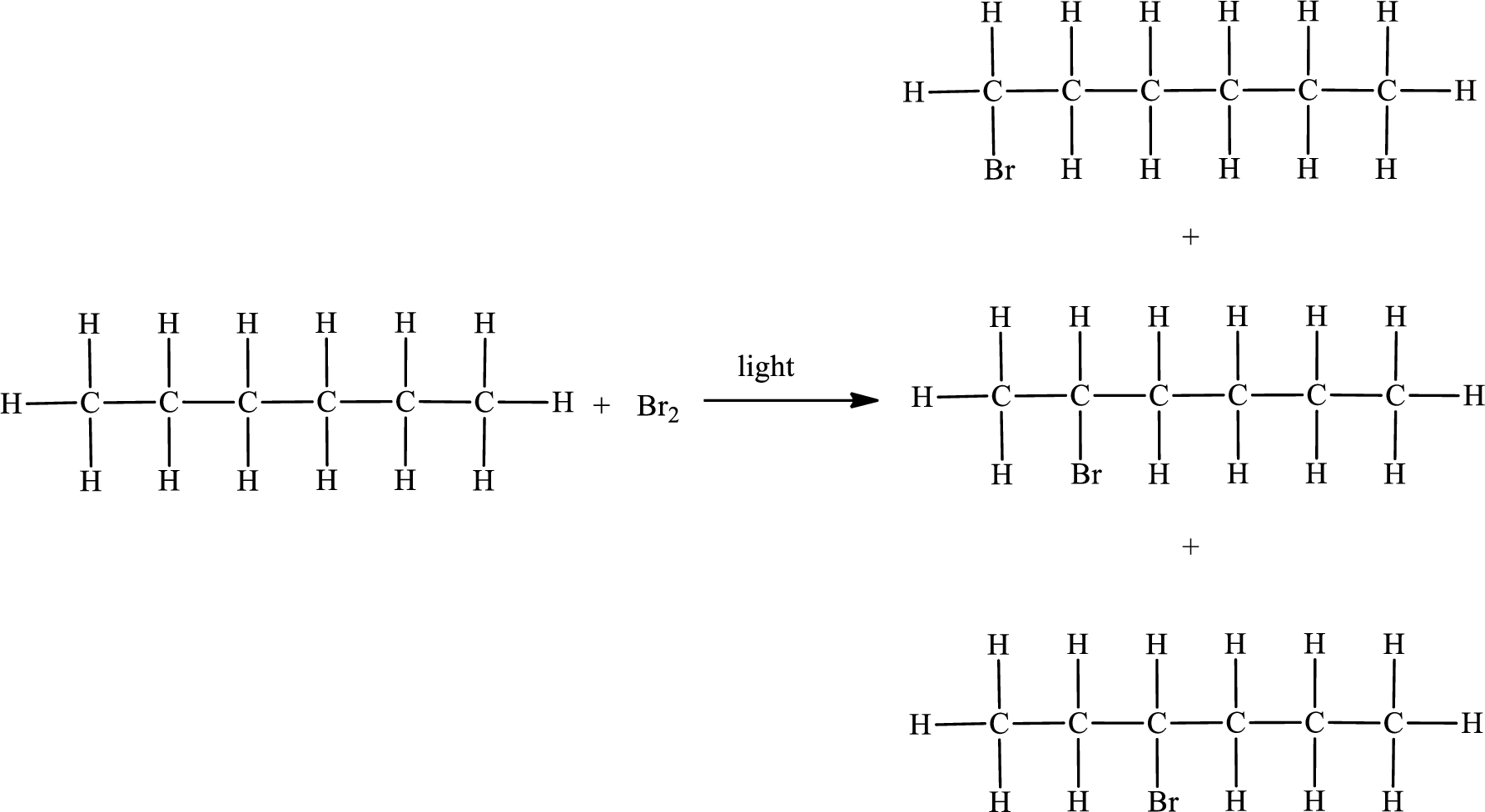
The reaction can be given as,
IUPAC names:
First monobromo derivative:
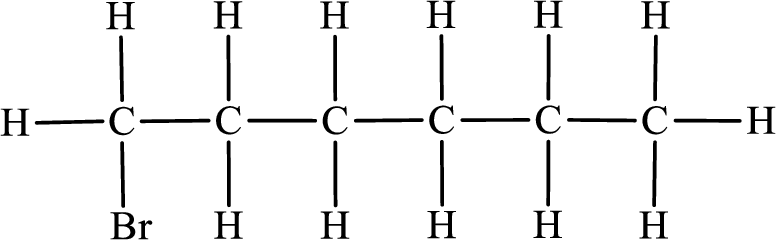
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is hexane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
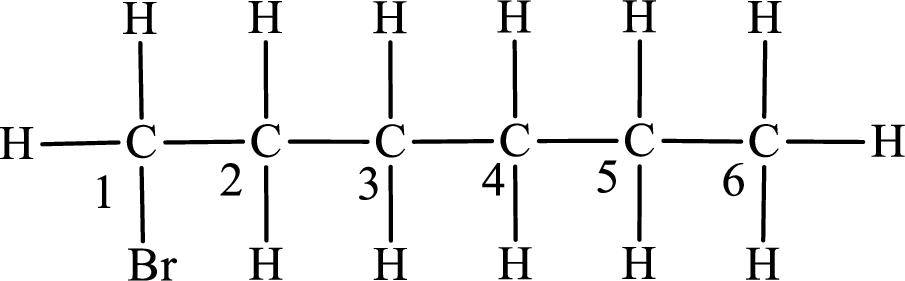
The substituent present in the given compound is a bromine atom. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
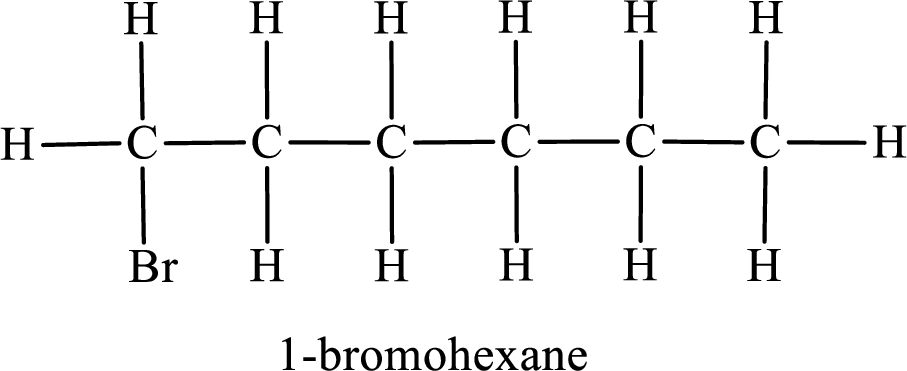
Parent chain is hexane and the substituent present is 1-bromo. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 1-bromohexane.
Second monobromo derivative:
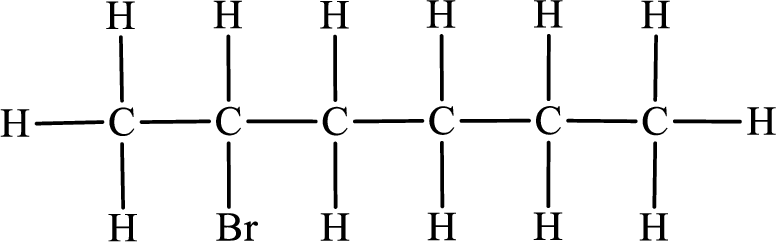
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is hexane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
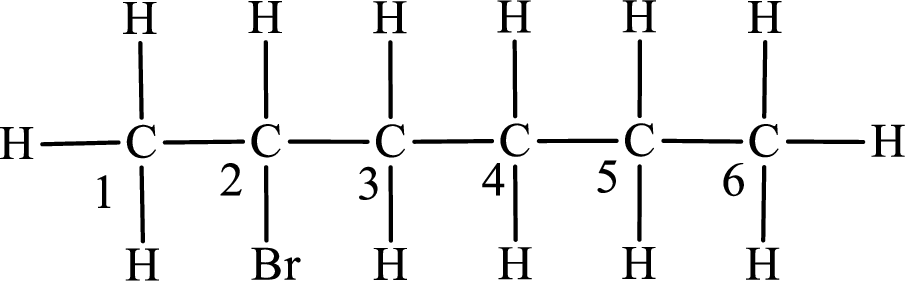
The substituent present in the given compound is a bromine atom. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
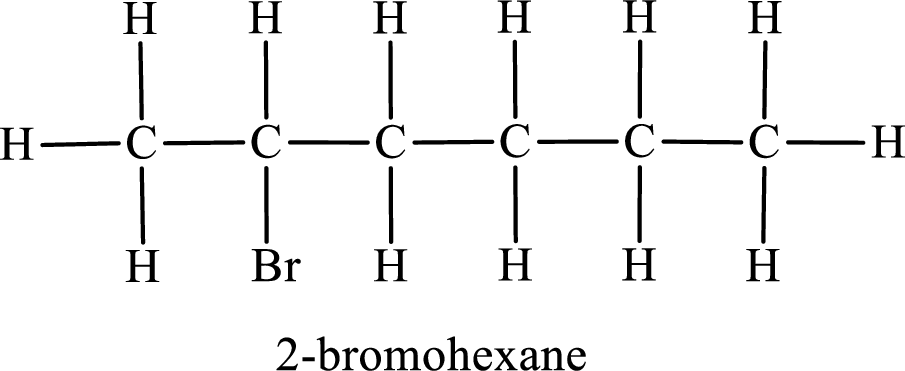
Parent chain is hexane and the substituent present is 2-bromo. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 2-bromohexane.
Third monobromo derivative:
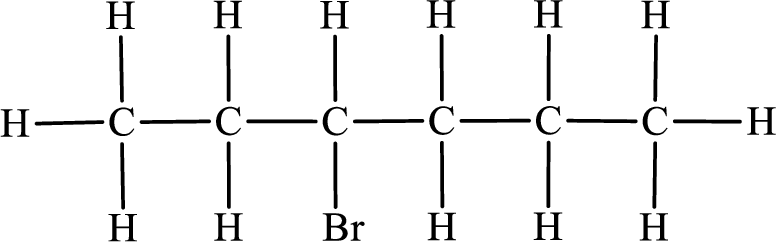
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain six carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is hexane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
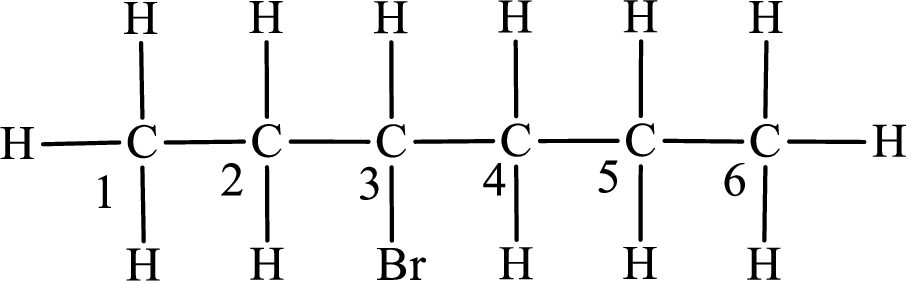
The substituent present in the given compound is a bromine atom. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
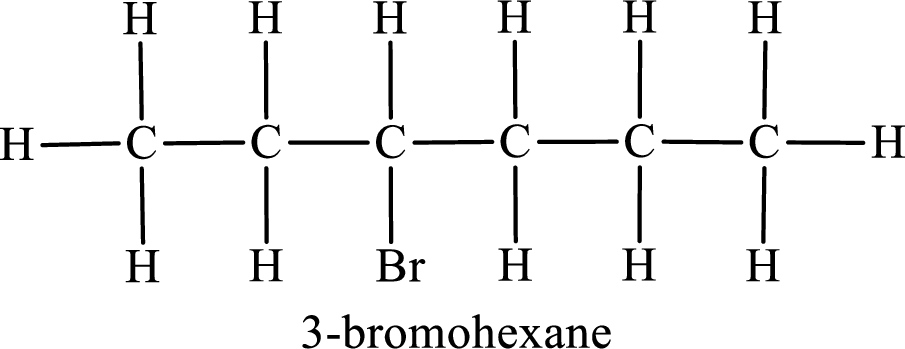
Parent chain is hexane and the substituent present is 3-bromo. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 3-bromohexane.
(c)
Interpretation:
Constitutional isomers that has molecular formula
Concept Introduction:
Refer part (a).
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given molecular formula of constitutional isomer is
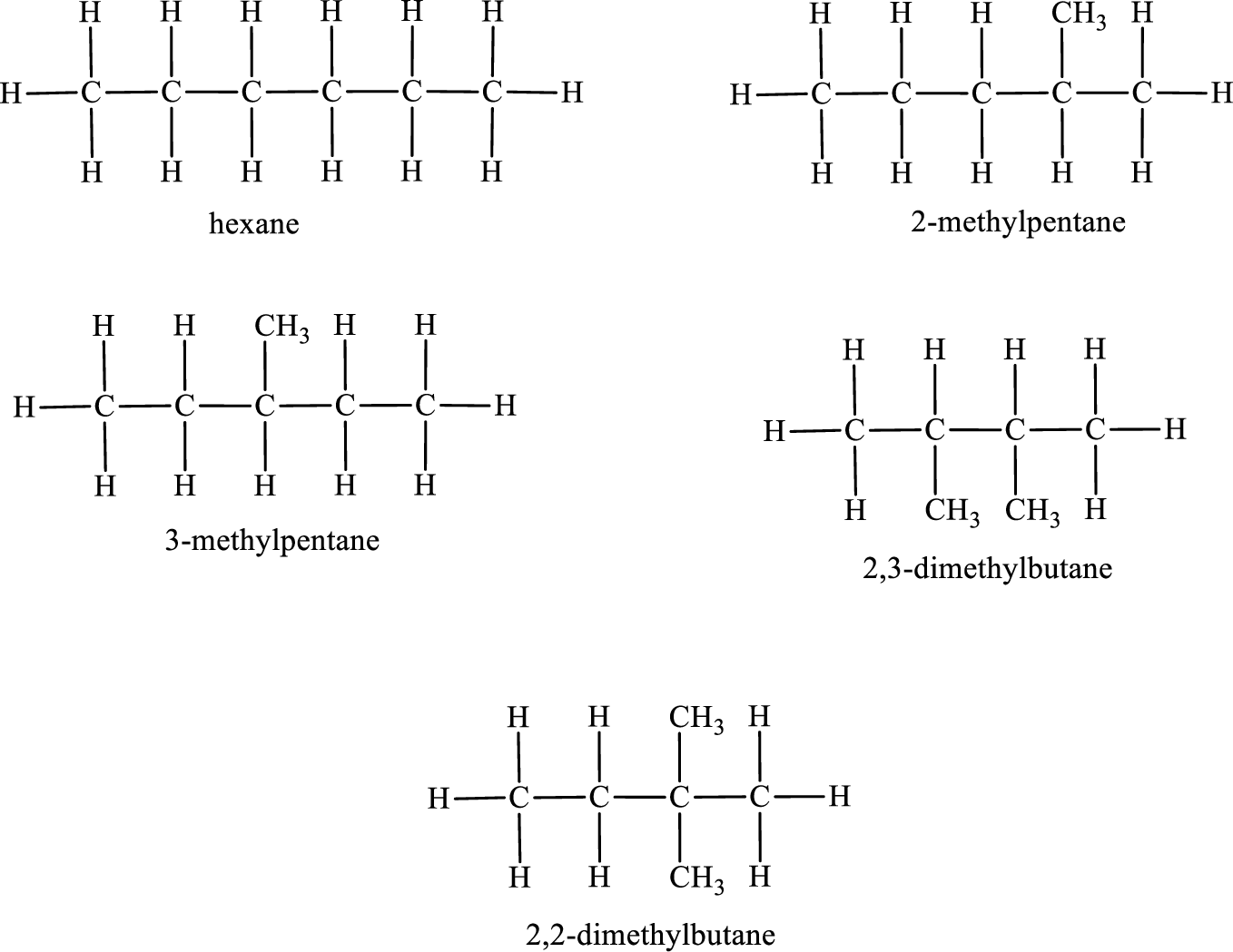
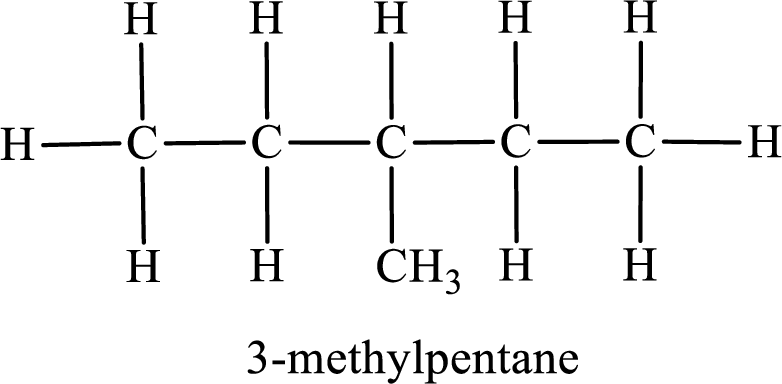
Among the constitutional isomers, the one that gives only four monobromo derivatives can be identified by looking into the structure that contain carbon atoms that has only four different environment. The structure is found to be 3-methylpentane.
The reaction can be given as,
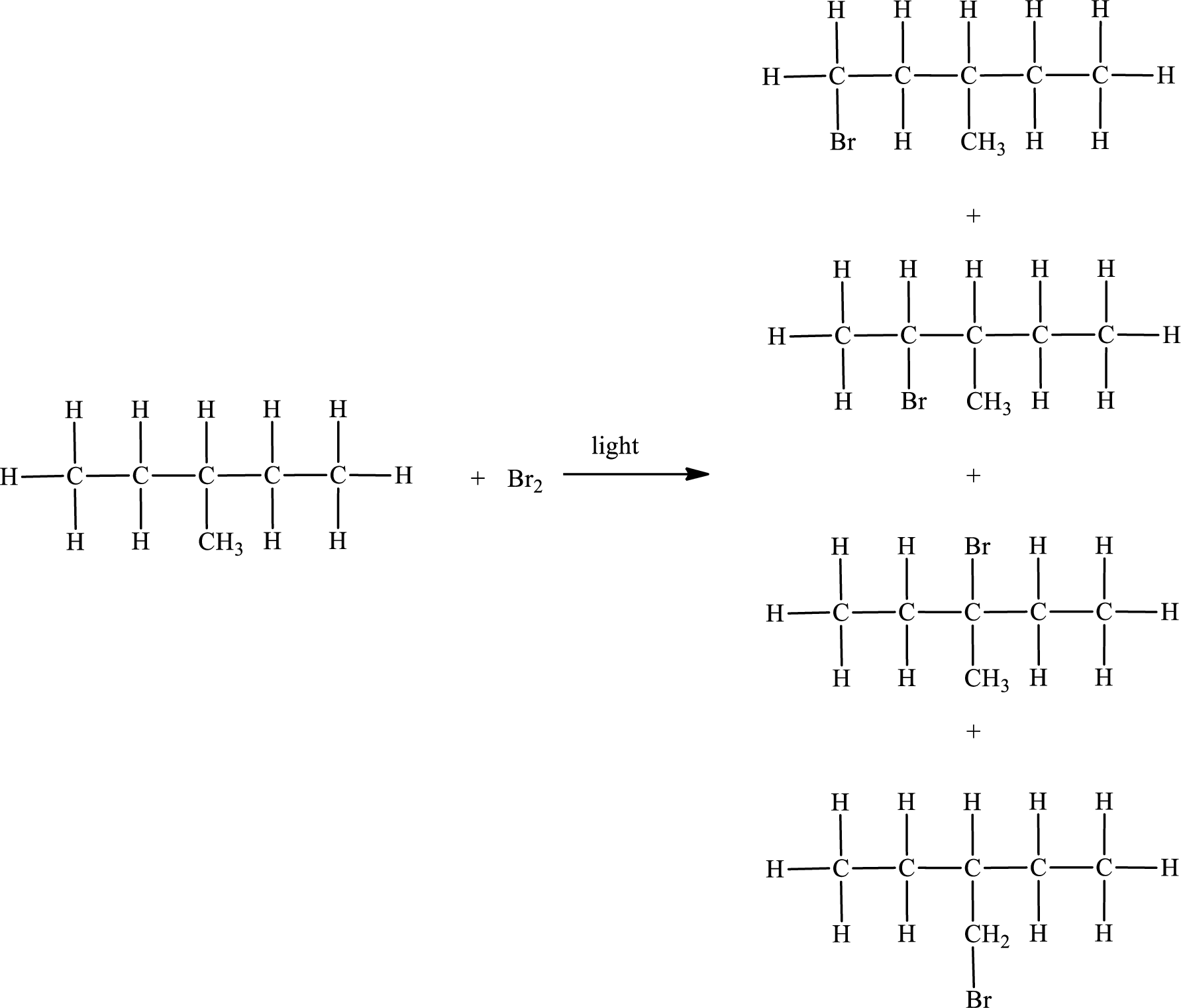
IUPAC names:
First monobromo derivative:
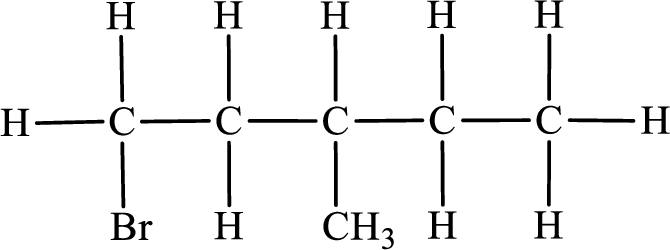
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is pentane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
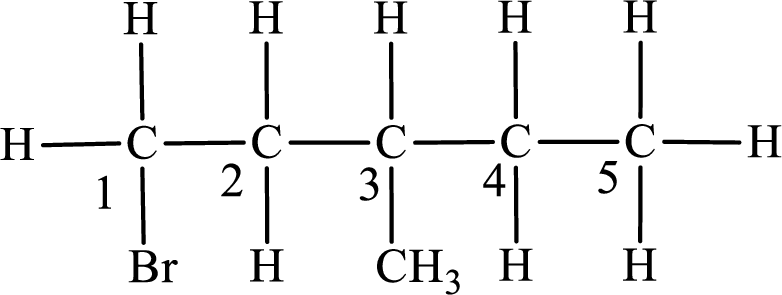
The substituent present in the given compound are a bromine atom and a methyl group. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
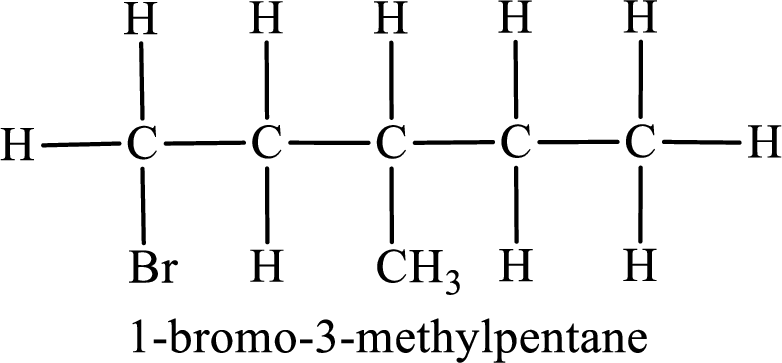
Parent chain is pentane and the substituent present is 1-bromo-3-methyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 1-bromo-3-methylpentane.
Second monobromo derivative:
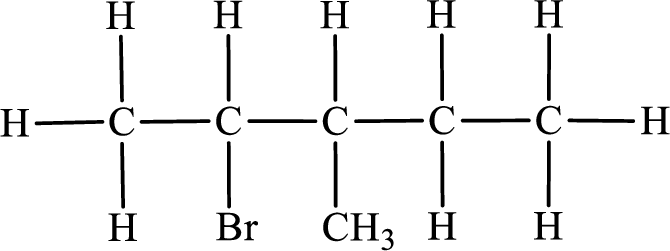
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is pentane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
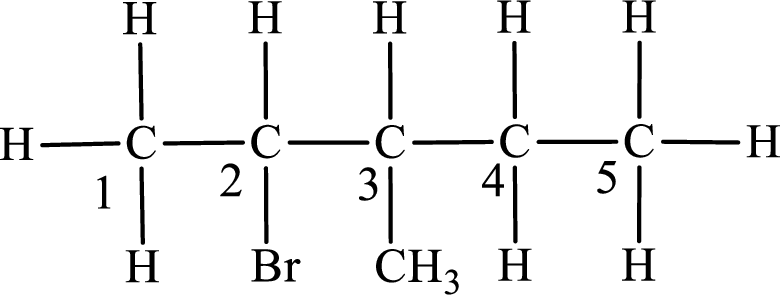
The substituent present in the given compound are a bromine atom and a methyl group. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
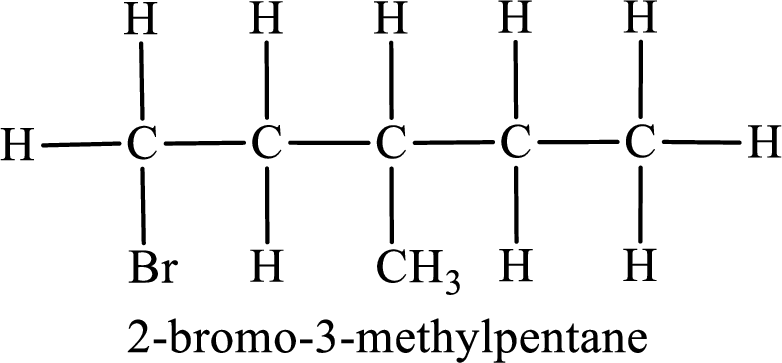
Parent chain is pentane and the substituent present is 2-bromo-3-methyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 2-bromo-3-methylpentane.
Third monobromo derivative:
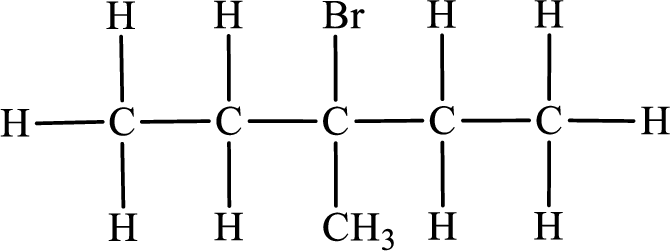
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is pentane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
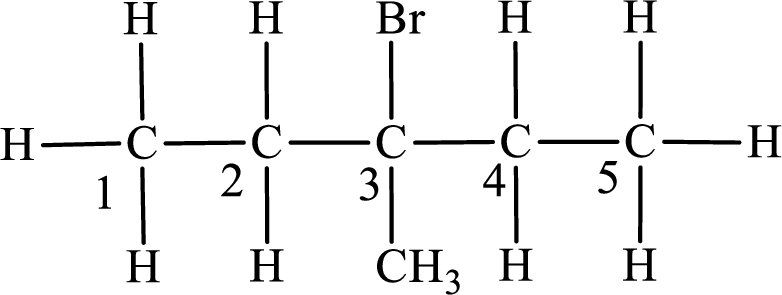
The substituent present in the given compound are a bromine atom and a methyl group. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
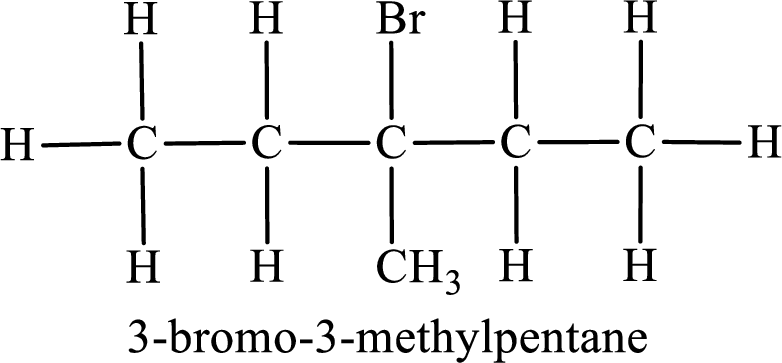
Parent chain is pentane and the substituent present is 3-bromo-3-methyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 3-bromo-3-methylpentane.
Fourth monobromo derivative:
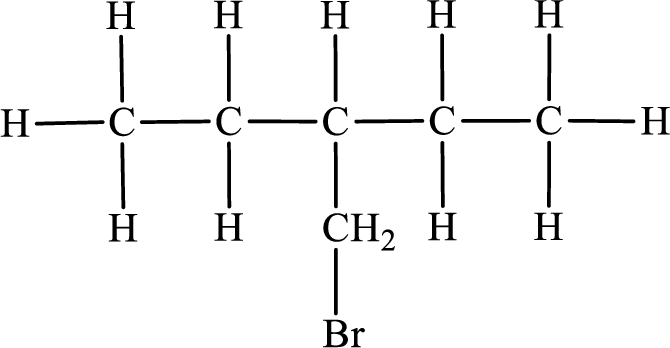
In the given compound, the longest carbon chain is found to contain five carbon atoms. Therefore, the parent alkane name is pentane.
Numbering of carbon atoms has to be done in a way that the substituents present in the longest carbon chain get the least numbering.
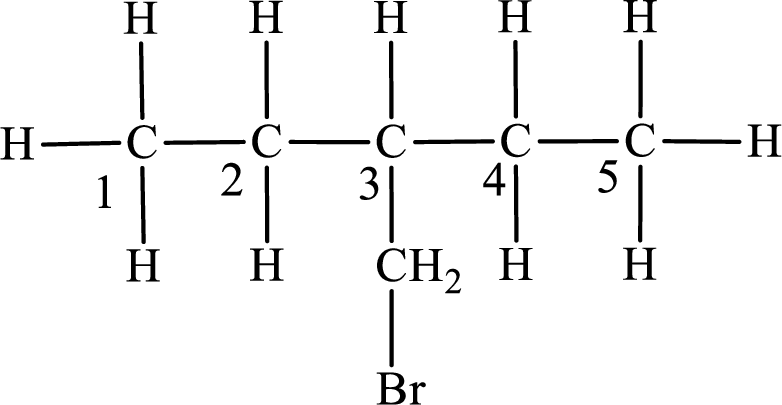
The substituent present in the given compound is a bromomethyl group. Number has to be added before the substituent indicating the carbon in which it is attached. Therefore, IUPAC name is obtained as,
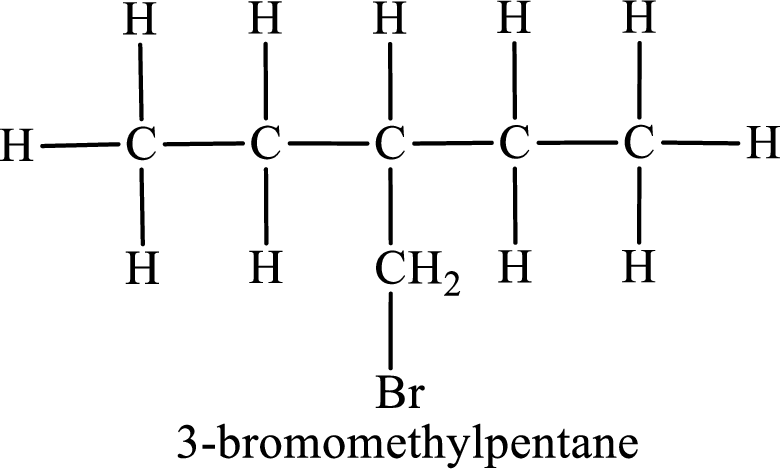
Parent chain is pentane and the substituent present is 3-bromomethyl. Hence, the IUPAC name is given as 3-bromomethylpentane.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Connect 2-Year Online Access for General, Organic, and Biochemistry
- Calculating the pH of a salt solution Calculate the pH at 25 °C of a 0.29M solution of potassium butanoate (KC3H,CO2). Note that butanoic acid (HC3H,CO2) is a weak acid with a pKa of 4.82. Round your answer to 1 decimal place. pH = -0 Х olo 18 Ararrow_forward: At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 1.58 × 10-12 N2(g) + O2(g) = 2 NO(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 38. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.93 mol of N2 and 0.93 mol of O2. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little N2 and O2. There will be very little NO. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 NO(g) N2(9)+02(9) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3 N2(9)+302(g) 6 NO(g) Neither of the above is true. K = ☐ K = ☐ ☐ X10 Х D ? 000 18 Ar Barrow_forwardwhen performing the reaction that involves 2 equivalents of 3-(diethylamino)-phenol and Phthalic anhydride with sulfuric acid and water react to form rhodamine b where the Phthalic anhydride cleaves in acid and how does Excessive Washing (w/ Base) & Subsequent Resonance Structure get affectedarrow_forward
- 3. The strongest acid of the following compounds is ___.A. p-nitrophenol; B. m-nitrophenol; C. o-chlorophenol;D. p-methoxyphenol; E. o-methylphenol Please explain your steps and thought process. Thank you!arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 1.3 × 10 4: Cl2(g) + CHCl3(g) HCl(g) + CC₁(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 16. L reaction vessel is filled with 1.6 mol of HCI and 1.6 mol of CCl4. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little Cl2 and CHCl3. ☐ x10 There will be very little HCI and CCl4. Neither of the above is true. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. HCl(g)+CC14(g) 12 Cl2(9)+CHCl3(9) K = 0 ☐ What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 2 Cl₂(9)+2CHCl3(9) 2 HCl(9)+2CC₁₁(9) K = ✓ 00. 18 Ararrow_forward10. The most important reason why Br- is a better nucleophile than Cl-is ___. A. polarizability; B. size; C. solvation; D. basicity; E. polarity. Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forward
- Predicting the qualitative acid-base properties of salts Consider the following data on some weak acids and weak bases: base acid Ка K₁₁ name formula name formula nitrous acid HNO2 4.5×10 4 pyridine CHEN 1.7 × 10 9 4 hydrofluoric acid HF 6.8 × 10 methylamine CH3NH2 | 4.4 × 10¯ Use this data to rank the following solutions in order of increasing pH. In other words, select a '1' next to the solution that will have the lowest pH, a '2' next to the solution that will have the next lowest pH, and so on. solution 0.1 M NaNO2 0.1 M KF pH choose one v choose one v 0.1 M C5H5NHBr 0.1 M CH3NH3CI choose one v ✓ choose one 1 (lowest) 2 ☑ 3 4 (highest) 000 18 Ararrow_forward4. The major product from treatment of 2-propanol with the Jonesreagent is ___.A. acetone; B. none of the other answers is correct C. propene; D.propanoic acid; E carbon dioxide. Please include all steps! Thank you!arrow_forward7. All of the following compounds that are at the same oxidation levelare ___.u. methyl epoxide, v. propyne, w. propanal, x. propene,y. 2,2-dihydroxypropane, z. isopropanol?A. u,v,w,y; B. u,v,w; C. v,w,y,z; D. v, z; E. x,y,z Please include all steps. Thank you!arrow_forward
- 9. Which one of the following substituents is the worst leaving group inan SN2 reaction? A. -NH2; B. -OH; C. –F; D. NH3; E. H2O Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 2.5 × 105: CO(g) + H2O(g) CO2(g) + H2(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 7.0 L reaction vessel is filled with 1.7 mol of CO and 1.7 mol of H2O. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. CO2(9)+H2(g) CO(g)+H₂O(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3 CO(g)+3H2O(g) = 3 CO2(g)+3H2(g) There will be very little CO and H2O. x10 There will be very little CO2 and H2. 000 Neither of the above is true. K = ☐ K = ☐ 18 Ararrow_forward8. When ethane thiol is treated with hydrogen peroxide the product is___.A. ethane disulfide; B. diethyl sulfide; C. ethane sulfoxide; D. ethanesulfate; E. ethyl mercaptan. Please include all steps. Thanks!arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





