
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The equation that shows the reaction of the given acid with water by considering the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base theory is to be written. All the electron pairs, formal chargers and curved arrows that represent the electron movement in the respective reaction are to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An acid is a chemical substance that readily donates protons and a base is a chemical substance that can easily accept a proton. During an acid-base reaction, the interaction between an acid and a base is taken place because of the transfer of a proton. The stronger the acid, the smaller its
Answer to Problem 63P
Solution:
a)
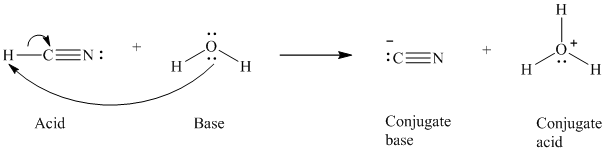
The formal charge on the the oxygen atom is
b)
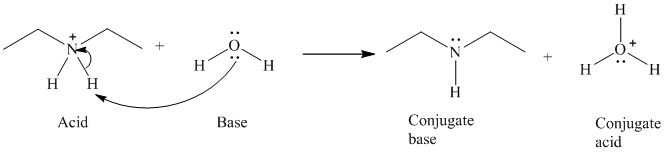
The formal charge on both the the oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom is
c)
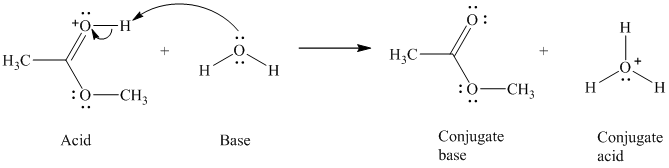 The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
The formal charge on the oxygen atom is
Explanation of Solution
a) The reaction of an acid with water.
In the respective reaction, the water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of oxygen atom present in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement is given below:
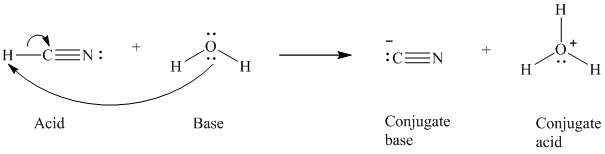
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the conjugate base is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
b) The reaction of an acid with water.
The given acid reacts with water. So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
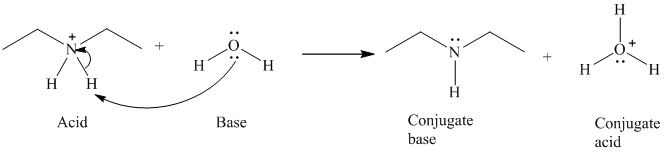
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the nitrogen atom is as follows:
Substitute
For calculating formal charge on the oxygen atom, recall the electron count formula:
Substitute
Recall the formula for formal charge:
Substitute
c) The given acid reacts with water.
So water acts as a base. The unshared electron pair of the oxygen atom in water is used to remove the proton from the acid. Water, after accepting the proton, is converted to its conjugate acid, that is, hydronium ion and the acid is converted to its conjugate base.
The curved arrows showing the electron movement are shown below:
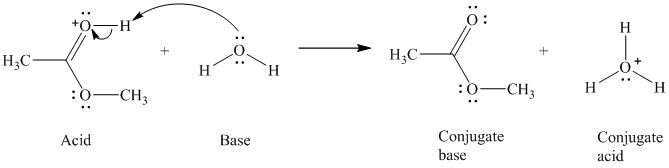
The formula that is used to calculate the electron count on the oxygen is as follows:
Substitute
The formula that is used to calculate the formal charge on the oxygen atom is as follows:
Substitute
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- Indicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting D-Galactose with hydroxylamine.arrow_forward
- helparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning



