
Air pollution is a serious problem in many places. One form of air pollution that is suspected to cause respiratory illness is particulate matter (PM), which consists of tiny particles in the air. Particulate matter can come from many sources, most commonly ash from burning, but also from other sources such as tiny particles of rubber that wear off of automobile and truck tires.
The town of Libby. Montana, was recently the focus of a study on the effect of PM on the respiratory health of children. Many houses in Libby are heated by wood stoves, which produce a lot of particulate pollution. The level of PM is greatest in the winter when more stoves are being used, and declines as the weather becomes warmer. The study attempted to determine whether higher levels of PM affect the respiratory health of children. In one part of the study, schoolchildren were given a questionnaire to bring home to their parents. Among other things, the questionnaire asked whether the child had experienced symptoms of wheezing during the past 60 days. Most parents returned the questionnaire within a couple of weeks. Parents who did not respond promptly were sent another copy of the questionnaire through the mail. Many of these parents responded to this mailed version.
Table 1.2 presents, for each day, the number of questionnaires that were returned by parents of children who wheezed, the number returned by those who did not wheeze, the average concentration of particulate matter in the atmosphere during the past 60 days (in units of micrograms per cubic meter), and whether the questionnaires were delivered in school or through the mail.
We will consider a PM level of 17 or more to be high exposure, and a PM level of less than 17 to be low exposure.
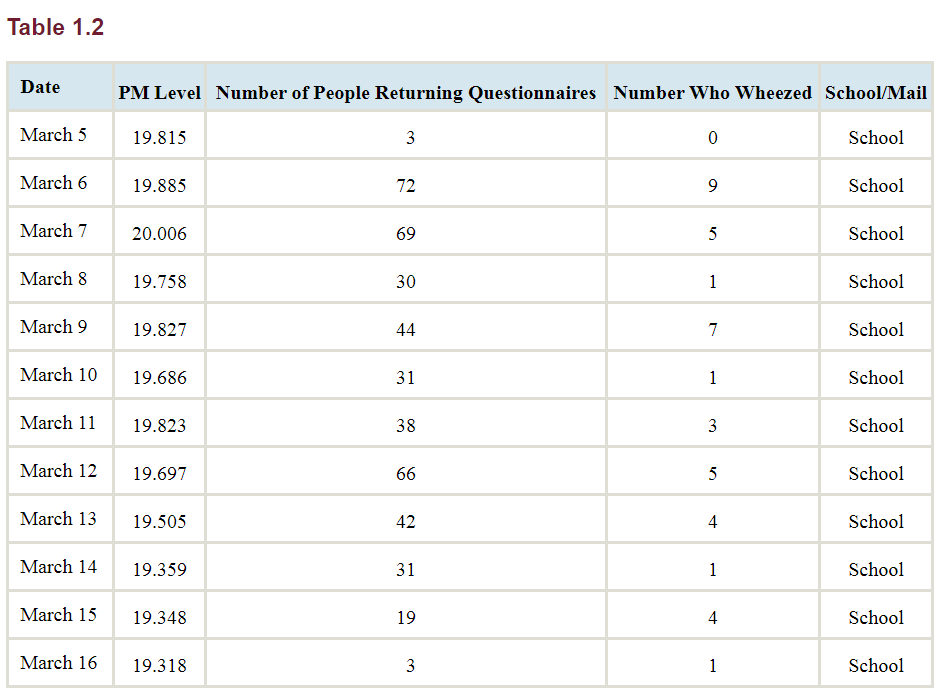
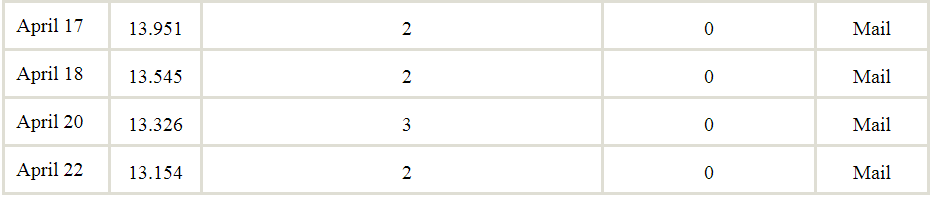
How many of the low-exposure people has wheeze symptoms?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Elementary Statistics (Text Only)
- Show all workarrow_forwardplease find the answers for the yellows boxes using the information and the picture belowarrow_forwardA marketing agency wants to determine whether different advertising platforms generate significantly different levels of customer engagement. The agency measures the average number of daily clicks on ads for three platforms: Social Media, Search Engines, and Email Campaigns. The agency collects data on daily clicks for each platform over a 10-day period and wants to test whether there is a statistically significant difference in the mean number of daily clicks among these platforms. Conduct ANOVA test. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: also please provide a step by on getting the answers in excel Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value.arrow_forward
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardBusiness Discussarrow_forwardThe following data represent total ventilation measured in liters of air per minute per square meter of body area for two independent (and randomly chosen) samples. Analyze these data using the appropriate non-parametric hypothesis testarrow_forward
 Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill



