
Cost Data for Managerial Purposes—Finding Unknowns
Quince Products is a small company in southern California that makes jams and preserves. Recently, a sales rep from one of the company’s suppliers suggested that Quince could increase its profitability by 50 percent if it introduced a second line of products, packaged fruit. She offered to do the analysis and show the company her assumptions.
When Quince’s management opened the spreadsheet sent by the sales rep, they noticed that there were several blank cells. In the meantime, the sales rep had taken a job with a competitor and told the managers at Quince that she could no longer advise them. Although they were not sure they should rely on the analysis, they asked you to see if you could reconstruct the sales rep’s analysis. They had been considering this new business already and wanted to see if their analysis was close to that of an outside observer. The incomplete spreadsheet follows.
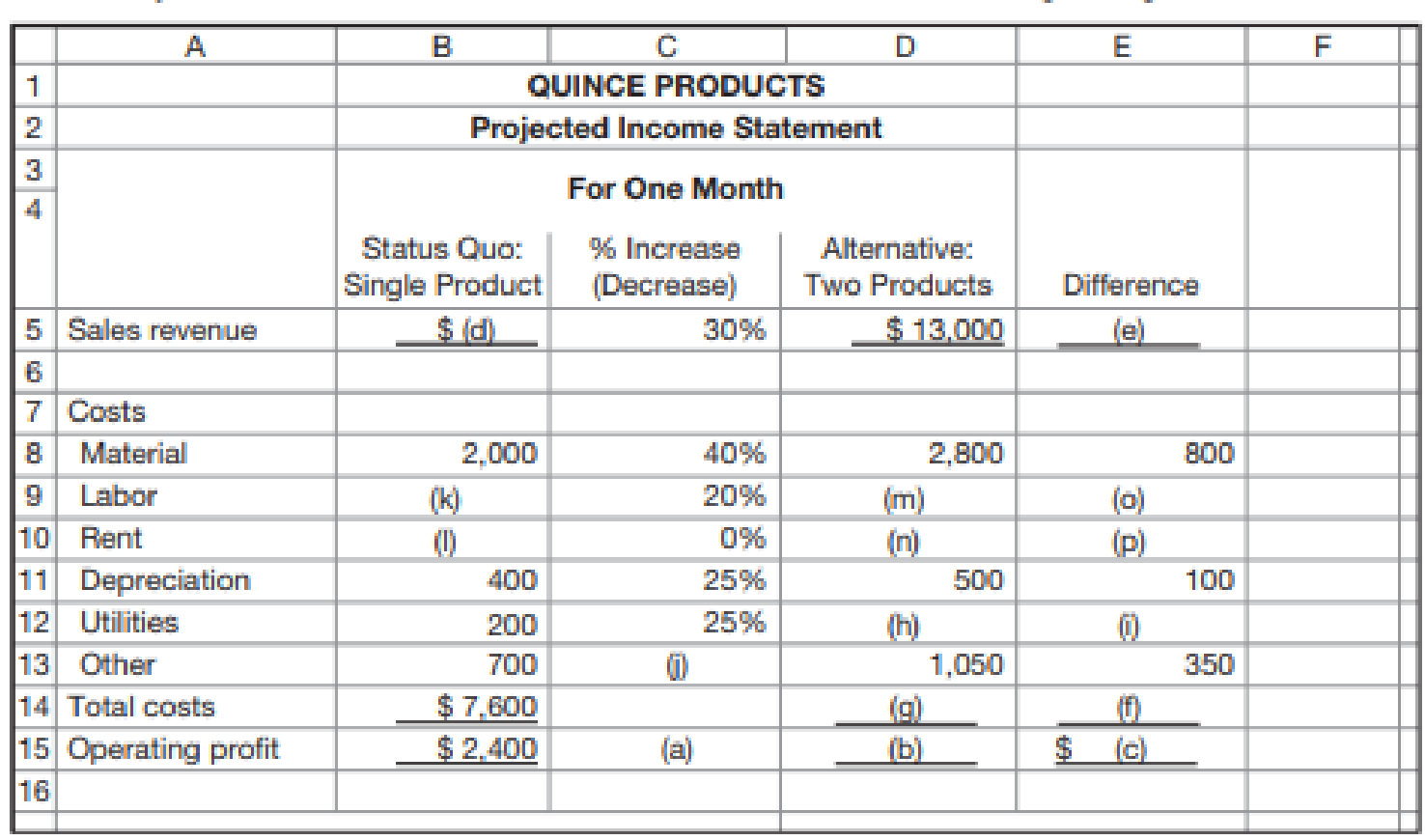
Required
Fill in the blank cells.
Fill in the blank cells of the projected income statement.
Explanation of Solution
Projected income statement: The projected income statement represents the future financial position of the entity. The projected income statement is prepared with an objective of showing the financial results for a future period of time.
Fill in the blank cells of the projected income statement:
| Company Q | ||||
| Projected Income Statement | ||||
| For One Month | ||||
| Status Quo: | % Increase | Alternative | ||
| Single Product | Decrease | Two Products | Difference | |
| Sales revenue | $ 10,000 (d) | 30% | $ 13,000 | $ 3,000 (e) |
| Costs | ||||
| Material | $ 2,000 | 40% | $ 2,800 | $ 800 |
| Labor | $ 2,500 (k) | 20% | $ 3,000 (m) | $ 500 (o) |
| Rent | $ 1,800 (l) | 0% | $ 1,800 (n) |
|
| Depreciation | $ 400 | 25% | $ 500 | $ 100 |
| Utilities | $ 200 | 25% | $ 250 (h) | $ 50 (i) |
| Other | $ 700 | 50% (j) | $ 1,050 | $ 350 |
| Total costs | $ 7,600 | $ 9,400 (g) | $ 1,800 (f) | |
| Operating profit | $ 2,400 (a) | $ 3,600 (b) | $ 1,200 (c) | |
Working note 1:
Compute value of (a):
It is given that the profit has increased by 50%, (a) represent the % increase or decrease in profit.
Working note 2:
Compute value of (b):
Working note 3:
Compute value of (c):
Working note 4:
Compute value of (d):
Working note 5:
Compute value of (e):
Working note 5:
Compute value of (f):
Working note 6:
Compute value of (g):
Working note 6:
Compute value of (h):
Working note 7:
Compute value of (i):
Working note 8:
Compute value of (j):
Working note 8:
Compute value of (k):
Labor plus rent (single product):
Labor plus rent (two products):
Increase in labor:
Thus,
Working note 8:
Compute value of (l):
Working note 8:
Compute value of (m):
Working note 9:
Compute value of (n):
Working note 10:
Compute value of (o):
Working note 11:
Compute value of (p):
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Fundamentals of Cost Accounting
- Problem 19-13 (Algo) Shoney Video Concepts produces a line of video streaming servers that are linked to personal computers for storing movies. These devices have very fast access and large storage capacity. Shoney is trying to determine a production plan for the next 12 months. The main criterion for this plan is that the employment level is to be held constant over the period. Shoney is continuing in its R&D efforts to develop new applications and prefers not to cause any adverse feelings with the local workforce. For the same reason, all employees should put in full workweeks, even if that is not the lowest-cost alternative. The forecast for the next 12 months is MONTH FORECAST DEMAND January February March April 530 730 830 530 May June 330 230 July 130 August 130 September 230 October 630 730 800 November December Manufacturing cost is $210 per server, equally divided between materials and labor. Inventory storage cost is $4 per unit per month and is assigned based on the ending…arrow_forwardCompute 007s gross profit percentage and rate of inventory turnover for 2016arrow_forwardHeadland Company pays its office employee payroll weekly. Below is a partial list of employees and their payroll data for August. Because August is their vacation period, vacation pay is also listed. Earnings to Weekly Vacation Pay to Be Employee July 31 Pay Received in August Mark Hamill $5,180 $280 Karen Robbins 4,480 230 $460 Brent Kirk 3,680 190 380 Alec Guinness 8,380 330 Ken Sprouse 8,980 410 820 Assume that the federal income tax withheld is 10% of wages. Union dues withheld are 2% of wages. Vacations are taken the second and third weeks of August by Robbins, Kirk, and Sprouse. The state unemployment tax rate is 2.5% and the federal is 0.8%, both on a $7,000 maximum. The FICA rate is 7.65% on employee and employer on a maximum of $142,800 per employee. In addition, a 1.45% rate is charged both employer and employee for an employee's wages in excess of $142,800. Make the journal entries necessary for each of the four August payrolls. The entries for the payroll and for the…arrow_forward
- Subject. General accountingarrow_forwardCompute the assets turnover ratioarrow_forwardExercise 5-18 (Algo) Calculate receivables ratios (LO5-8) Below are amounts (in millions) from three companies' annual reports. WalCo TarMart Costbet Beginning Accounts Receivable $1,795 6,066 609 Ending Accounts Receivable $2,742 6,594 645 Net Sales $320,427 65,878 66,963 Required: 1. Calculate the receivables turnover ratio and the average collection period for WalCo, TarMart and CostGet 2. Which company appears most efficient in collecting cash from sales? Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required C Calculate the receivables turnover ratio and the average collection period for WalCo, TarMart and CostGet. (Enter your answers in millions rounded to 1 decimal place.) Receivables Turnover Ratio: WalCo S TarMart. S CostGet S Choose Numerator Choose Numerator "ValCo FarMart CostGet 320,427 $ 65.878 66,963 Choose Denominator Receivables turnover ratio 2,742.0 116.9 times 0 times 0 times Average Collection Period Choose Denominator Average…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning





