
Extended Case Study for maintaining the record order while insertion:
Program plan:
- Include the required header files in your program.
- Define a class “Personal” with the following functions.
- Define the default constructor “Personal()” that initializes the member variables.
- Define the constructor “Personal()” with arguments that initializes the member variables.
- Define the function “writeToFile()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “readFromFile()” to read a record from the input stream.
- Define the function “readKey()” to read SSN from console.
- Define the function “size()” to get the size of a record.
- Define the function “operator==()” to check the equality of the two records.
- Define the function “operator<()” to check the current record is less than passed record.
- Define the function “writeLegibly()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “operator<<()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “readFromConsole()” to read a record from the input stream.
- Define the function “operator>>()” to read a record from the output stream.
- Define a class “Student” with the following functions.
- Define the default constructor “Student()” that initializes the member variables.
- Define the constructor “Student()” with arguments that initializes the member variables.
- Define the function “writeToFile()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “readFromFile()” to read a record from the input stream.
- Define the function “size()” to get the size of a record.
- Define the function “writeLegibly()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “operator<<()” to write a record to the output stream.
- Define the function “readFromConsole()” to read a record from the input stream.
- Define the function “operator>>()” to read a record from the output stream.
- Define a class “
Database ” with the following functions.- Define the default constructor “Database()” that initializes the member variables.
- Define the function “run()” that processes the user wishes.
- Define the function “add()” to add a record to the database.
- Define the function “find()” to find a record in the database.
- Define the function “modify()” to modify the existing record.
- Define the function “operator<<()” to write the database to the output stream.
- Define the function “print()” to display the database.
- Define the function “main()”.
- Create a database for “Personal” and call the function “run()”.
This program Extends the case study for inserting records in sorted order.
Explanation of Solution
Program:
//personal.h.
#ifndef PERSONAL
#define PERSONAL
// Include the required header files
#include<iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
//Personal class declaration.
class Personal
{
//Access Specifier.
public:
//constructor.
Personal();
//Argumented constructor.
Personal(char*,char*,char*,int,long);
//Function to write Person data to file.
void writeToFile(fstream&) const;
//Function to read Person data from file.
void readFromFile(fstream&);
//Function read SSN
void readKey();
//Function that returns the size of a record.
int size() const
{
//Sum all the fields length and return it.
return 9 + nameLen + cityLen + sizeof(year) + sizeof(salary);
}
/*Function to check the passed the record is equal to the current record.*/
bool operator==(const Personal& pr) const
{
//Compare the SSN's of current record and pr.
/*If they equal the function return true. otherwise it return false.*/
return strncmp(pr.SSN,SSN,9) == 0;
}
/*Function to check the passed record's SSN is less than the current record.*/
bool operator<(const Personal& pr) const
{
//Compare the SSN's of current record and pr.
/*If SSN's of current record less than pr.SSN then the function return true, otherwise return false*/
return strncmp(SSN,pr.SSN,9)<0;
}
//Access specifier.
protected:
//Declare variables.
const int nameLen, cityLen;
char SSN[10], *name, *city;
int year;
long salary;
//Function to write the record to the output stream.
ostream& writeLegibly(ostream&);
/*Overload the operator << to write to the output stream.*/
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Personal& pr)
{
//Call the member function to write.
return pr.writeLegibly(out);
}
//Function to read a record from the input stream.
istream& readFromConsole(istream&);
/*Overload the operator >> to read fromo the input stream.*/
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Personal& pr)
{
//Call the member function to read.
return pr.readFromConsole(in);
}
};
#endif
//personal.cpp
//Include the header files.
#include "personal.h"
//Constructor that fixes the length for name and city.
Personal::Personal() : nameLen(10), cityLen(10)
{
/*Create the character array for name and city with specified size.*/
name = new char[nameLen+1];
city = new char[cityLen+1];
}
//Constructor with input arguments.
Personal::Personal(char *ssn, char *n, char *c, int y, long s) :
nameLen(10), cityLen(10)
{
/*Create the character array for name and city with specified size.*/
name = new char[nameLen+1];
city = new char[cityLen+1];
//Copy the passed SSN
strcpy(SSN,ssn);
//Copy the name.
strcpy(name,n);
//Copy the city.
strcpy(city,c);
//store the year.
year = y;
//Store the salary.
salary = s;
}
//Function to write the record into the output stream.
void Personal::writeToFile(fstream& out) const
{
//Write the SSN.
out.write(SSN,9);
//Write the name.
out.write(name,nameLen);
//Write the city.
out.write(city,cityLen);
/*Convert the year into char* and write it on the output.*/
out.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&year),sizeof(int));
/*Convert the salary into char* and write it on the output.*/
out.write(reinterpret_cast<const char*>(&salary),sizeof(int));
}
//Function to read a record from the input stream.
void Personal::readFromFile(fstream& in)
{
//Read the SSN
in.read(SSN,9);
//Read the name.
in.read(name,nameLen);
//Read the city.
in.read(city,cityLen);
//Convert the char* to int and store it in year.
in.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&year),sizeof(int));
//Convert the char* to int and store it in salary.
in.read(reinterpret_cast<char*>(&salary),sizeof(int));
}
//Function to read the SSN from the user.
void Personal::readKey()
{
//Declare the variables.
char s[80];
//Prompt the user.
cout << "Enter SSN: ";
//Read the SSN
cin.getline(s,80);
//copy the SSN.
strncpy(SSN,s,9);
}
//Function to write the record to the console.
ostream& Personal::writeLegibly(ostream& out)
{
//Terminate the strings.
SSN[9] = name[nameLen] = city[cityLen] = '\0';
//Write SSN, name, year, city, salary to the console.
out << "SSN = " << SSN << ", name = " << name<< ", city = " << city << ", year = " << year<< ", salary = " << salary;
//Return the output stream.
return out;
}
//Function to read a record from the console.
istream& Personal::readFromConsole(istream& in)
{
//Terminate the strings.
SSN[9] = name[nameLen] = city[cityLen] = '\0';
char s[80];
//Read SSN in variable 's'.
cout << "SSN: ";
in.getline(s,80);
//Copy the SSN from 's'.
strncpy(SSN,s,9);
//Read name in variable 's'.
cout << "Name: ";
in.getline(s,80);
//Copy the name from 's'.
strncpy(name,s,nameLen);
//Read the city in 's'.
cout << "City: ";
in.getline(s,80);
//Copy the city from 's'.
strncpy(city,s,cityLen);
//Read the year.
cout << "Birthyear: ";
in >> year;
//Read the salary.
cout << "Salary: ";
in >> salary;
in.ignore();
//Return the input stream.
return in;
}
//student.h
//Defining the header file.
#ifndef STUDENT
#define STUDENT
//Include the header file
#include "personal.h"
//Derive the class Student from Personal
class Student : public Personal
{
//Access specifier.
public:
//Constructor
Student();
//Constructor with arguments*/
Student(char*,char*,char*,int,long,char*);
//Function to write record to the output stream.
void writeToFile(fstream&) const;
//Function to read a Student record from input stream.
void readFromFile(fstream&);
//Function to get the size of the Student record.
int size() const
{
/*Call the base call method to find the record size.*/
return Personal::size() + majorLen;
}
//Access specifier.
protected:
//Declare variables.
char *major;
const int majorLen;
//Function to write the record to the output stream.
ostream& writeLegibly(ostream&);
/*Overaloaded operator << to write to the output stream.*/
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Student& sr)
{
//Call member function to write the record.
return sr.writeLegibly(out);
}
//Function to read a record from the input stream.
istream& readFromConsole(istream&);
//Overload the operator >> to read fromo the input stream.
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Student& sr)
{
//Call the member function to read.
return sr.readFromConsole(in);
}
};
#endif
//student.cpp
//Include the header files.
#include "student.h"
//Constructor to initialize the variables.
Student::Student() : majorLen(10)
{
//Call base call constructor for initialization.
Personal();
//Create the character array for the major.
major = new char[majorLen+1];
}
//Constructor to initialize all the variables. This constructor takes arguments*/
Student::Student(char *ssn, char *n, char *c, int y, long s, char *m) :
majorLen(11)
{
//Call baseclass constructor.
Personal(ssn,n,c,y,s);
//Create the character array for the major.
major = new char[majorLen+1];
//Copy the major.
strcpy(major,m);
}
//Function to write the record to the output stream.
void Student::writeToFile(fstream& out) const
{
/*Call base class method to write the name, city, SSN, year, salary.*/
Personal::writeToFile(out);
//Write the major.
out.write(major,majorLen);
}
//Function to read a record from the input stream.
void Student::readFromFile(fstream& in)
{
/*Call baseclass method to read the name,city, SSN, year,salary.*/
Personal::readFromFile(in);
//Read the major.
in.read(major,majorLen);
}
/*Function to write the student record to the output stream.*/
ostream& Student::writeLegibly(ostream& out)
{
/*Call baseclass method to write the name,city, SSN, year,salary.*/
Personal::writeLegibly(out);
major[majorLen] = '\0';
//Write the major.
out << ", major = " << major;
//Return the output stream.
return out;
}
//Function to read a record from the input stream console.
istream& Student::readFromConsole(istream& in)
{
/*Call base class method to read name, city, year, SSN, salary from console.*/
Personal::readFromConsole(in);
char s[80];
//Prompt the user to enter the major.
cout << "Major: ";
//read the major in variable 's'.
in.getline(s,80);
//Copy the major from 's'.
strncpy(major,s,9);
//Return the input stream.
return in;
}
//database.h
//Define the header file.
#ifndef DATABASE
#define DATABASE
//Create the template class.
template<class T>
//Create the class Database
class Database
{
//Access Specifier.
public:
//Construtor.
Database();
/*Function that displays the menu and proceeds as per user wish.*/
void run();
//Access Specifier.
private:
/* Declare variables*/
fstream database;
char fName[20];
//Function to display the database
ostream& print(ostream&);
//Function to add a record into the database.
void add(T&);
/*Function to find a particular record in the database.*/
bool find(const T&);
//Function to modify the record in the database.
void modify(const T&);
/*Overloaded operator << to print the given database to the output stream.*/
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, Database& db)
{
//Call the method to print the database.
return db.print(out);
}
};
#endif
//database.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <
#include "student.h"
#include "personal.h"
#include "database.h"
//No argumented constructor.
template<class T>
Database<T>::Database()
{
}
//Function to add a record into the database.
template<class T>
void Database<T>::add(T& d)
{
//Declare the variables.
T tmp;
int rCnt=0;
/*Create a vector to store the records after 'd' record.*/
vector<Personal> per;
//Declare the flag to indicate the record inserted.
int flag=0;
//Open the database.
database.open(fName,ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary);
/*Inifinite loop that runs until record is inserted in the database.*/
while (true)
{
//Read a record from the file.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
//Increment the record count.
rCnt++;
/*Check database is null. If so exit from the loop.*/
if (database.eof())
break;
//Check tmp exists the 'd'
if ((d<tmp))
{
//Go back to the start of the tmp.
database.seekp(-d.size(),ios::cur);
/*Infinite loop to read the record from tmp to database end.*/
while(true)
{
//Read a record.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
/*Check database is null. If so, return. */
if (database.eof())
break;
//Push the tmp into per.
per.push_back(tmp);
}
//Clear the pointers.
database.clear();
//Move to the file beginning.
database.seekg(0);
//Goto the violating record position.
database.seekp((rCnt-1)*d.size(),ios::beg);
//Write d in that position.
d.writeToFile(database);
/*Loop to write back the vector of records into database. */
for(int kk=0;kk<per.size();kk++)
{
//Write kkth record into database.
per.at(kk).writeToFile(database);
}
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Return statement.
return;
}
}
//If record is not inserted.
if(flag==0)
{
//Open the database.
database.open(fName,ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary);
//Clear the file pointers.
database.clear();
//Goto the file end.
database.seekp(0,ios::end);
//Write 'd' to the database.
d.writeToFile(database);
}
//Close the database.
database.close();
}
//Function to modify the existing record in the database.
template<class T>
void Database<T>::modify(const T& d)
{
//Declare the variable.
T tmp;
//Open the database.
database.open(fName,ios::in|ios::out|ios::binary);
//Read a record from the file.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
//Check database is null. If so exit from the loop.
if (database.eof())
{
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Return statement.
return;
}
//Read until tmp less than d.
while (tmp<d)
{
//Read the record from the database.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
}
//Check tmp matches d.
if (tmp == d)
{
//Read the record
cin >> tmp;
//Seek to the record's position.
database.seekp(-d.size(),ios::cur);
//Write the record to the file.
tmp.writeToFile(database);
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Exit from the function.
return;
}
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Print the message indicating record not found.
cout << "The record to be modified is not in the database\n";
}
//Function to find the given record in the database.
template<class T>
bool Database<T>::find(const T& d)
{
//Declare the variable.
T tmp;
//Open the database.
database.open(fName,ios::in|ios::binary);
//Read a record from the file.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
//Check database is null. If so exit from the loop.
if (database.eof())
{
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Record not found, so return false.
return false;
}
//Read until tmp less than d.
while (tmp<d)
{
//Read the record from the database.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
}
//Check tmp matches d.
if (tmp == d)
{
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Record found, so return true.
return true;
}
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Record not found, so return false.
return false;
}
template<class T>
ostream& Database<T>::print(ostream& out)
{
//Declare the variable.
T tmp;
//Open the database.
database.open(fName,ios::in|ios::binary);
//Infinite loop.
while (true)
{
//Read a record from the file.
tmp.readFromFile(database);
/*Check database is null. If so exit from the loop.*/
if (database.eof())
//Exit from the loop.
break;
//Write the record tmp to the output stream.
out << tmp << endl;
}
//Close the database.
database.close();
//Return the output stream.
return out;
}
//Function to process the user wish.
template<class T>
void Database<T>::run()
{
//Get the database filename.
cout << "File name: ";
cin >> fName;
//Declare variables.
char option[5];
T rec;
//Display menu.
cout << "1. Add 2. Find 3. Modify a record; 4. Exit\n";
//Get option.
cout << "Enter an option: ";
cin.getline(option,4);
//Infinite loop ends until user wishes to exit.
while (cin.getline(option,4))
{
//If user wants to add a record.
if (*option == '1')
{
//Get the record.
cin >> rec;
//Write the record into the database.
add(rec);
}
//If user wants to find a record,
else if (*option == '2')
{
//Read the SSN
rec.readKey();
//Display record is found or not.
cout << "The record is ";
//Check finding record returns false.
if (find(rec) == false)
cout << "not ";
cout << "in the database\n";
}
/*If user wants to modify a record in the database,*/
else if (*option == '3')
{
//Read the SSN of the record to be modified.
rec.readKey();
//Call the method modify()
modify(rec);
}
//If user enters wrong option.
else if (*option != '4')
//Print wrong input.
cout << "Wrong option\n";
//Otherwise exit from the loop.
else
//Return to the main function.
return;
//Display the database.
cout << *this;
//Ask the user for an option.
cout << "Enter an option: ";
}
}
//main() method.
int main()
{
/*Creating the database with Personal objects and call the function run().*/
Database<Personal>().run();
//To pause the console window.
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Output:
File name: student.txt
1. Add 2. Find 3. Modify a record; 4. Exit
Enter an option: 1
SSN: 456
Name: Mullen
City: Bangalore
Birthyear: 2015
Salary: 1000
SSN = 456, name = Mullen, city = Bangalore, year = 2015, salary = 1000
Enter an option: 1
SSN: 123
Name: Arlen
City: Delhi
Birthyear: 2000
Salary: 40000
SSN = 123, name = Arlen, city = Delhi, year = 2000, salary = 40000
SSN = 456, name = Mullen, city = Bangalore, year = 2015, salary = 1000
Enter an option: 2
Enter SSN: 456
The record is in the database
SSN = 123, name = Arlen, city = Delhi, year = 2000, salary = 40000
SSN = 456, name = Mullen, city = Bangalore, year = 2015, salary = 1000
Enter an option: 3
Enter SSN: 456
SSN: 456
Name: Mullen
City: Bangalore
Birthyear: 2005
Salary: 10000
SSN = 123, name = Arlen, city = Delhi, year = 2000, salary = 40000
SSN = 456, name = Mullen, city = Bangalore, year = 2005, salary = 10000
Enter an option: 4
Press any key to continue . . .
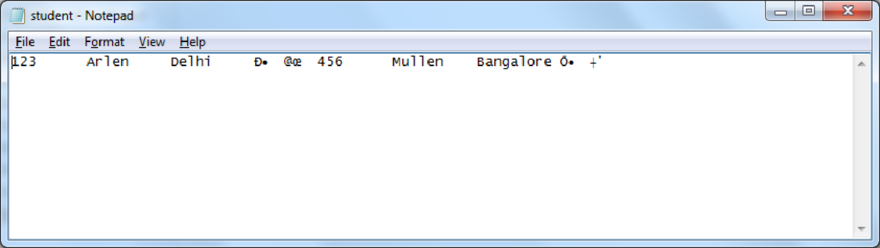
After running of the program, the file has been changed as follows,
student.txt:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C
 C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage LearningProgramming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Microsoft Visual C#Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102100Author:Joyce, Farrell.Publisher:Cengage Learning, New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning





