
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The eight alcohols have to be written with the molecular formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomer: A molecule having same molecular formula with different chemical formula is called isomer.
Alcohol:
The compound contains hydroxyl
Example is given below,
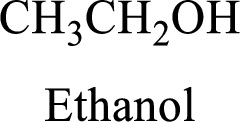
(b)
Interpretation:
Eight aldehydeswith the molecular formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomer: A molecule having same molecular formula with different chemical formula is called isomer.
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as
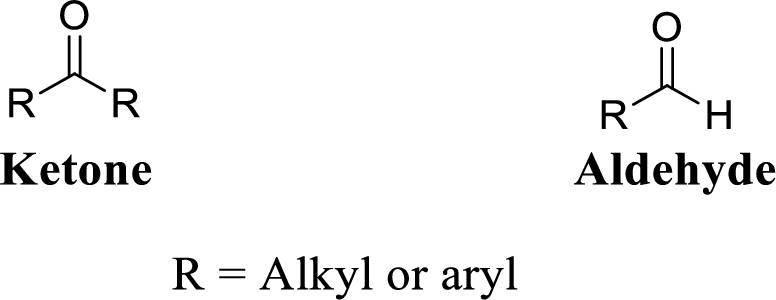
(c)
Interpretation:
Six ketones have to be written with the molecular formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomer: A molecule having same molecular formula with different chemical formula is called isomer.
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carbonyl group:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with two alkyl or aryl group is called as ketone, if the carbonyl carbon is attached with one hydrogen atom and one alkyl or aryl group is called as aldehyde.
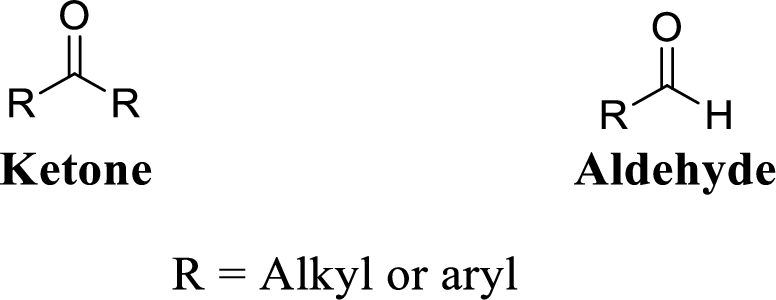
(d)
Interpretation:
Eight
Concept introduction:
Isomer: A molecule having same molecular formula with different chemical formula is called isomer.
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carboxylic acid:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
If the carbonyl carbon is attached with hydroxyl group is called as carboxylic acid.
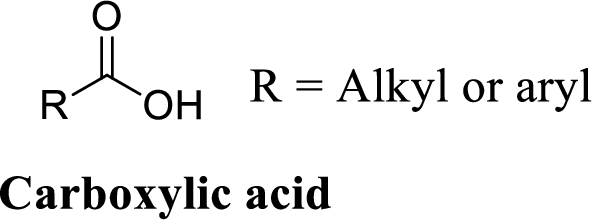
(e)
Interpretation:
Nine carboxylic estershave to be written with the molecular formula of
Concept introduction:
Isomer: A molecule having same molecular formula with different chemical formula is called isomer.
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Carboxylic ester:
A carbon atom is double-bonded to an oxygen atom
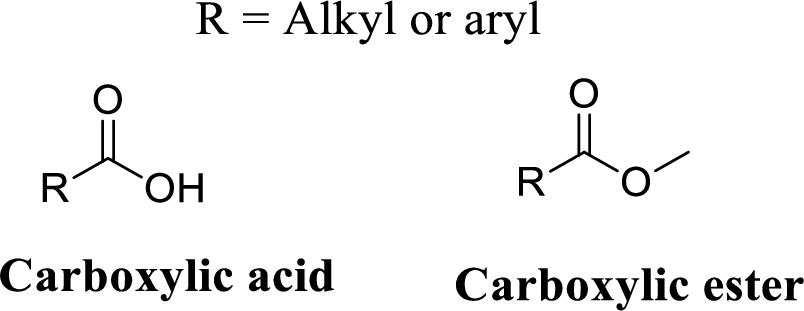
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Tarrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) of the following reactions. Indicate which of the following mechanisms is in operation: SN1, SN2, E1, or E2.arrow_forward(c) (4pts) Mechanism: heat (E1) CH3OH + 1.5pts each _E1 _ (1pt) Br CH3OH (d) (4pts) Mechanism: SN1 (1pt) (e) (3pts) 1111 I H 10 Ill!! H LDA THF (solvent) Mechanism: E2 (1pt) NC (f) Bri!!!!! CH3 NaCN (3pts) acetone Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) (SN1) -OCH3 OCH3 1.5pts each 2pts for either product 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H Br (g) “,、 (3pts) H CH3OH +21 Mechanism: SN2 (1pt) H CH3 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistry H 2pts 1pt if incorrect stereochemistryarrow_forward
- A mixture of butyl acrylate and 4'-chloropropiophenone has been taken for proton NMR analysis. Based on this proton NMR, determine the relative percentage of each compound in the mixturearrow_forwardQ5: Label each chiral carbon in the following molecules as R or S. Make sure the stereocenter to which each of your R/S assignments belong is perfectly clear to the grader. (8pts) R OCH 3 CI H S 2pts for each R/S HO R H !!! I OH CI HN CI R Harrow_forwardCalculate the proton and carbon chemical shifts for this structurearrow_forward
- A. B. b. Now consider the two bicyclic molecules A. and B. Note that A. is a dianion and B. is a neutral molecule. One of these molecules is a highly reactive compound first characterized in frozen noble gas matrices, that self-reacts rapidly at temperatures above liquid nitrogen temperature. The other compound was isolated at room temperature in the early 1960s, and is a stable ligand used in organometallic chemistry. Which molecule is the more stable molecule, and why?arrow_forwardWhere are the chiral centers in this molecule? Also is this compound meso yes or no?arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP! URGENT!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

