
Concept explainers
Write Lewis structures for these ions. Show all valence electrons and all formal charges.
- (a) Amide ion, NH2−
- (b) Bicarbonate ion, HCO3−
- (c) Carbonate ion, CO32−
- (d) Nitrate ion, NO3−
- (e) Formate ion, HCOO−
- (f) Acetate ion, CH3COO−
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is amide ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron for the hydrogen atom is one, the valence electron for the nitrogen is five, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
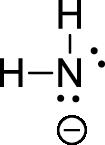
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
(b)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is bicarbonate ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron for the hydrogen atom is one, the valence electron for the carbon is four and valence electron of oxygen is six, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
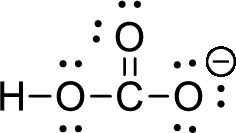
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
(c)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is carbonate ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron the carbon is four and valence electron of oxygen is six, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
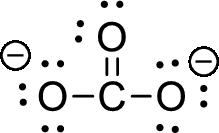
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
(d)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is nitrate ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron for the nitrogen atom is five, the valence electron for the carbon is four and valence electron of oxygen is six, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
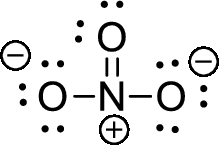
Formal charge for nitrogen atom can be calculated by using following formula,
Formal charge for oxygen can be calculated by using following formula,
(e)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is formate ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron for the hydrogen atom is one, the valence electron for the carbon is four and valence electron of oxygen is six, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
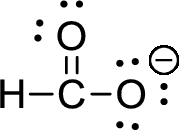
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
(f)
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of the ions, valence electron and formal charge has to be identified.
Concept introduction:
Lewis structure: The Lewis structure is based on the concept of the octet rule so that the electrons shared in each atom should have 8 electrons in its outer shell. Sometimes the chemical bonding of a molecule cannot be represented using a single Lewis structure. In these cases, the chemical bonding are described by delocalization of electrons and is known as resonance. All the possible resonance structures are imaginary whereas the resonance hybrid is real. These structures will differ only in the arrangement of the electrons not in the relative position of the atomic nuclei.
Valence shell:
The outer most shell of the element is called as valence shell.
Valence electron:
The electrons present in the outer shell are called valence electron.
For example:
Nitrogen element has seven electrons and it has two shells, the second shell is the valence shell and it has five electrons in the valence shell. The five electrons are called as valence electrons.
Formal charge:
The charge on an atom in a molecule is called its formal charge.
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Explanation of Solution
The given ion is acetate ion,
First the skeletal structure for the given molecule is drawn then the total number of valence electrons for all atoms present in the molecule is determined. The next step is to subtract the electrons present in the total number of bonds present in the skeletal structure of the molecule with the total valence electrons such that considering each bond contains two electrons with it. Finally, the electrons which got after subtractions have to be equally distributed such that each atom contains eight electrons in its valence shell.
The valence electron for the hydrogen atom is one, the valence electron for the carbon is four and valence electron of oxygen is six, therefore, and the Lewis structure of the ion is given below,
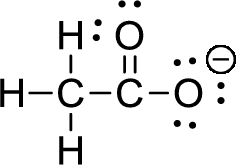
Formal charge can be calculated by using following formula,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- 9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Vanctions +H₂504 4.50+ T C. +212 Fellz 237 b. Praw the potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Rauctions and account For any differences that appear in the two potential Puergy Diagrams which of here two reactions 19 Found to be Reversable, Rationalice your answer based upon the venation mechanisms and the potential energy diagrams.arrow_forward9. Write Me product as well as the reaction Mechanism For each of the Following Veritious +H2504 4.50+ + 1/₂ Felly ◎+ 7 b. Praw he potential energy Diagrams For each OF Mese Ronctions and account for any differences that appeak in the two potential Puergy Diagramsarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Incorrect, 3 attempts remaining 1. excess Br2, NaOH 2. neutralizing workup Qarrow_forward
- Given the electrode Pt | Ag | Ag+ (aq), describe it.arrow_forwardAt 25°C, the reaction Zn2+ + 2e ⇄ Zn has a normal equilibrium potential versus the saturated calomel electrode of -1.0048 V. Determine the normal equilibrium potential of Zn versus the hydrogen electrode.Data: The calomel electrode potential is E° = 0.2420 V versus the normal hydrogen electrode.arrow_forwardElectrochemistry. State the difference between E and E0.arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery notation. Is that correct?arrow_forwardIn an electrolytic cell, the positive pole is always assumed to be on the right side of the battery. Is that correct?arrow_forwardCalculate the free energy of formation of 1 mol of Cu in cells where the electrolyte is 1 mol dm-3 Cu2+ in sulfate solution, pH 0. E° for the Cu2+/Cu pair in this medium is +142 mV versus ENH.Assume the anodic reaction is oxygen evolution.Data: EH2 = -0.059 pH (V) and EO2 = 1.230 - 0.059 pH (V); 2.3RT/F = 0.059 Varrow_forward
- If the normal potential for the Fe(III)/Fe(II) pair in acid at zero pH is 524 mV Hg/Hg2Cl2 . The potential of the saturated calomel reference electrode is +246 mV versus the NHE. Calculate E0 vs NHE.arrow_forwardGiven the galvanic cell whose scheme is: (-) Zn/Zn2+ ⋮⋮ Ag+/Ag (+). If we know the normal potentials E°(Zn2+/Zn) = -0.76V and E°(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799 V. Indicate the electrodes that are the anode and the cathode and calculate the E0battery.arrow_forwardIndicate the functions that salt bridges have in batteries.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





