
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780077633707
Author: Janice Smith
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Higher Education (us)
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.32UKC
(a) Which representation(s) in Problem 1.31 illustrate a mixture of two elements? (b) Which representation(s) in Problem 1.31 illustrate a mixture of a compound and an element?
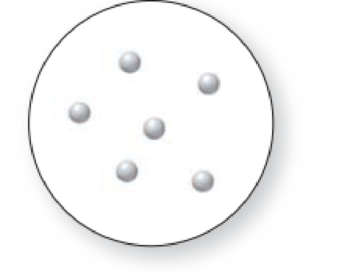


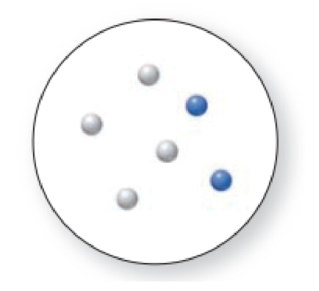
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Determine whether each molecular diagram represents a pure substance or a mixture. If it represents a pure substance, classify the substance as an element or a compound. If it represents a mixture, classify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous.
Classify each of the following as an element, a compound, or a mixture:(a) copper(b) water(c) nitrogen(d) sulfur(e) air(f) sucrose(g) a substance composed of molecules each of which contains two iodine atoms(h) gasoline
Classify each of the following as an element, a compound, or a mixture:(a) iron(b) oxygen(c) mercury oxide(d) pancake syrup(e) carbon dioxide(f) a substance composed of molecules each of which contains one hydrogen atom and one chlorine atom(g) baking soda(h) baking powder
Chapter 1 Solutions
Connect 1-Semester Online Access for Principles of General, Organic & Biochemistry
Ch. 1.1 - Imagine that your job as a healthcare professional...Ch. 1.2 - Characterize each process as a physical change or...Ch. 1.2 - Does the molecular art represent a chemical change...Ch. 1.3 - Classify each example of molecular art as a pure...Ch. 1.3 - Prob. 1.5PCh. 1.3 - Classify each item as an element or a compound:...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 1.7PCh. 1.4 - If a nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000...Ch. 1.4 - Prob. 1.9PCh. 1.4 - Prob. 1.10P
Ch. 1.5 - How many significant figures does each number...Ch. 1.5 - Indicate whether each zero in the following...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1.13PCh. 1.5 - Carry out each calculation and give the answer...Ch. 1.5 - Prob. 1.15PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 1.16PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 1.17PCh. 1.6 - Prob. 1.18PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 1.19PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 1.20PCh. 1.7 - Prob. 1.21PCh. 1.7 - Carry out each of the following conversions. a....Ch. 1.8 - Prob. 1.23PCh. 1.8 - A patient is prescribed 0.100 mg of a drug that is...Ch. 1.8 - Prob. 1.25PCh. 1.9 - Prob. 1.26PCh. 1.9 - Prob. 1.27PCh. 1.10 - How does the mass of liquid A in cylinder [1]...Ch. 1.10 - Prob. 1.29PCh. 1.10 - Prob. 1.30PCh. 1 - Classify each example of molecular art as a pure...Ch. 1 - (a) Which representation(s) in Problem 1.31...Ch. 1 - When a chunk of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) is...Ch. 1 - The inexpensive preparation of nitrogen-containing...Ch. 1 - a. What is the temperature on the given Fahrenheit...Ch. 1 - (a) What is the length of the given crayon in...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.37UKCCh. 1 - Prob. 1.38UKCCh. 1 - Prob. 1.39UKCCh. 1 - Red light has a wavelength of 683 nm. Convert this...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.41UKCCh. 1 - Prob. 1.42UKCCh. 1 - Prob. 1.43UKCCh. 1 - Prob. 1.44UKCCh. 1 - Label each component in the molecular art as an...Ch. 1 - Label each component in the molecular art as an...Ch. 1 - Describe solids, liquids, and gases in terms of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.48APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.49APCh. 1 - Classify each process as a chemical or physical...Ch. 1 - Which quantity in each pair is larger? a. 5 mL or...Ch. 1 - Which quantity in each pair is larger? a. 10 km or...Ch. 1 - Label each quantity as an exact or inexact number....Ch. 1 - Rank the quantities in each group from smallest to...Ch. 1 - How many significant figures does each number...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.56APCh. 1 - Round each number to three significant figures. a....Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.58APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.59APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.60APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.61APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.62APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.63APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.64APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.65APCh. 1 - Rank the numbers in each group from smallest to...Ch. 1 - Write the recommended daily intake of each...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.68APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.69APCh. 1 - Carry out each of the following conversions. a. 25...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.71APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.72APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.73APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.74APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.75APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.76APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.77APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.78APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.79APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.80APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.81APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.82APCh. 1 - Which is the upper layer when each of the...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.84APCh. 1 - A lab test showed an individuals cholesterol level...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.86APCh. 1 - Liposuction is a cosmetic procedure used to remove...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.88APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.89APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.90APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.91APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.92APCh. 1 - Prob. 1.93CPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.94CPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.95CPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.96CPCh. 1 - A soccer player weighed 70.7 kg before a match,...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.98CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1-55 Does the chemical nature of a substance change when it melts from a solid to a liquid?arrow_forwardClassify the substances represented by the models in Problem 1-57 as to the number of atoms present per molecule, that is, as diatomic, triatomic, tetraatomic, etc.arrow_forwardWhich of the following particulate illustrations represent pure substances and which represent mixtures?arrow_forward
- 1-65 While you drive your car, your battery is being charged. How would you describe this process in terms of kinetic and potential energy?arrow_forwardWhich of the following are elements, and which are compounds? a NaOH; b BaCl2; c He; d Ag; e Fe2O3.arrow_forward1.82 Which of the following molecular-scale diagrams best represents a pure compound? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- The following are properties of substances. Decide whether each is a physical property or a chemical property. a Chlorine gas liquefies at 35C under normal pressure. b Hydrogen burns in chlorine gas. c Bromine melts at 7.2C. d Lithium is a soft, silvery-colored metal. e Iron rusts in an atmosphere of moist air.arrow_forward1-85 In Japan, high-speed “bullet trains” move with an average speed of 220. km./h. If Dallas and Los Angeles were connected by such a train, how long would it take to travel nonstop between these cities (a distance of 1490. miles)?arrow_forwardAll of the following processes involve a separation of either a mixture into substances or a compound into elements. For each, decide whether a physical process or a chemical reaction is required. a Sodium metal is obtained from the substance sodium chloride. b Iron filings are separated from sand by using a magnet. c Sugar crystals are separated from a sugar syrup by evaporation of water. d Fine crystals of silver chloride are separated from a suspension of the crystals in water. e Copper is produced when zinc metal is placed in a solution of copper(II) sulfate, a compound.arrow_forward
- Which of the following are compounds, and which are elements? aNa2S bBr2 cPotassium hydroxide dFluorine eCompound or element fCompound or elementarrow_forwardDecide whether each of the following is a physical property or a chemical property of the substance. a Salt substitute, potassium chloride, dissolves in water. b Seashells, calcium carbonate, fizz when immersed in vinegar. c The gas hydrogen sulfide smells like rotten eggs. d Fine steel wool (Fe) can be burned in air. e Pure water freezes at 0C.arrow_forwardThe following pairs of substances represent heterogeneous mixtures. For each pair, describe the steps you would follow to separate the components and collect them. Explain. (a) sugar and sand (b) iron filings and sand (c) sand soaked with oilarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079250
Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed Peters
Publisher:Cengage Learning

General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285853918
Author:H. Stephen Stoker
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Types of Matter: Elements, Compounds and Mixtures; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dggHWvFJ8Xs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY