
EBK MATERIALS FOR CIVIL AND CONSTRUCTIO
4th Edition
ISBN: 8220102719569
Author: ZANIEWSKI
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.2QP
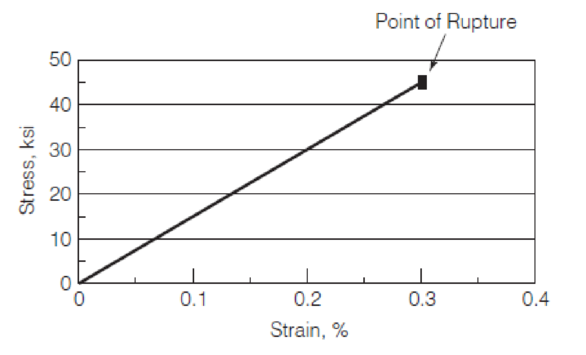
A material has the stress–strain behavior shown in Figure P1.2. What is the material strength at rupture? What is the toughness of this material?
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule03:29
Students have asked these similar questions
Fatigue strength for non-
ferrous materials in defined at
stress cycles
10^3
10^5
10^7
10^9
S Figure P1.16 shows the stress-strain relations of metals A and B during ten-
sion tests until fracture. Determine the following for the two metals (show all
calculations and units):
a. Proportional limit
b. Yield stress at an offset strain of 0.002 m/m.
c. Ultimate strength
d. Modulus of resilience
e. Toughness
f. Which metal is more ductile? Why?
900
Metal A
600
Metal B
300
0.00 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.14
Strain, m/m
FIGURE P1.16
Stress, MPa
A steel alloy specimen having a rectangular cross section of dimensions 19.1 mm x 3.1 mm (0.7520 in. × 0.1220 in.) has the
stress-strain behavior shown in the Animated Figure 6.22b. If this specimen is subjected to a tensile force of 98290 N
(22100 Ib;) then
(a) Determine the amount of elastic strain induced.
(b) Determine the amount of plastic strain induced.
(c) If its original length is 610 mm, what will be its final length after this force is applied and then released?
The elastic modulus for steel is 207 GPa.
(a) i
(b) i
(c) i
mm
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK MATERIALS FOR CIVIL AND CONSTRUCTIO
Ch. 1 - State three examples of a static load application...Ch. 1 - A material has the stressstrain behavior shown in...Ch. 1 - A tensile load of 50.000 lb is applied to a metal...Ch. 1 - A tensile load of 190 kN is applied to a round...Ch. 1 - A cylinder with a 6.0 in. diameter and 12.0 in....Ch. 1 - A metal rod with 0.5 inch diameter is subjected to...Ch. 1 - A rectangular block of aluminum 30 mm 60 mm 90...Ch. 1 - A plastic cube with a 4 in. 4 in. 4 in. is...Ch. 1 - A material has a stressstrain relationship that...Ch. 1 - On a graph, show the stressstrain relationship...
Ch. 1 - The rectangular block shown in Figure P1.11 is...Ch. 1 - The rectangular metal block shown in Figure P1.11...Ch. 1 - A cylindrical rod with a length of 380 mm and a...Ch. 1 - A cylindrical rod with a radius of 0.3 in. and a...Ch. 1 - A cylindrical rod with a diameter of 15.24 mm and...Ch. 1 - The stressstrain relationship shown in Figure...Ch. 1 - A tension test performed on a metal specimen to...Ch. 1 - An alloy has a yield strength of 41 ksi, a tensile...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.21QPCh. 1 - Figure P1.22 shows (i) elasticperfectly plastic...Ch. 1 - An elastoplastic material with strain hardening...Ch. 1 - A brace alloy rod having a cross sectional area of...Ch. 1 - A brass alloy rod having a cross sectional area of...Ch. 1 - A copper rod with a diameter of 19 mm, modulus of...Ch. 1 - A copper rod with a diameter of 0.5 in., modulus...Ch. 1 - Define the following material behavior and provide...Ch. 1 - An asphalt concrete cylindrical specimen with a...Ch. 1 - What are the differences between modulus of...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.33QPCh. 1 - A metal rod having a diameter of 10 mm is...Ch. 1 - What is the factor of safety? On what basis is its...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.36QPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.37QPCh. 1 - A steel rod, which is free to move, has a length...Ch. 1 - In Problem 1.38, if the rod is snugly fitted...Ch. 1 - A 4-m-long steel plate with a rectangular cross...Ch. 1 - Estimate the tensile strength required to prevent...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.42QPCh. 1 - Briefly discuss the variability of construction...Ch. 1 - In order to evaluate the properties of a material,...Ch. 1 - A contractor claims that the mean compressive...Ch. 1 - A contractor claims that the mean compressive...Ch. 1 - Prob. 1.47QPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.48QPCh. 1 - Prob. 1.49QPCh. 1 - Briefly discuss the concept behind each of the...Ch. 1 - Referring to the dial gauge shown in Figure P1.51,...Ch. 1 - Repeat Problem 1.51 using the dial gauge shown in...Ch. 1 - Measurements should be reported to the nearest...Ch. 1 - During calibration of an LVDT, the data shown in...Ch. 1 - During calibration of an LVDT, the data shown in...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The capacity for a certain foundation system is estimated to be 620 kN with a COV of 0.3. The demand on the fou...
Foundation Design: Principles and Practices (3rd Edition)
The moment at supports A and B and the bending moment diagram for the beam.
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
1.1 List 10 uses. for surveying in areas other than land
sunreying-
Elementary Surveying (14th Edition)
10.1 In adjusting measured traverse angles‘ why aren’t adjustments made in proportion to the
angle sizes?
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
How would you change the class MergeSort so that it can soft an array of values of type double instead of type ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (7th Edition)
The __________ property holds the item that is selected in a ListBox control. a. Index b. SelectedItem c. Selec...
Starting out with Visual C# (4th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Compare the engineering and true secant elastic moduli for the natural rubber in Example Problem 6.2 at an engineering strain of 6.0. Assume that the deformation is all elastic.arrow_forwardThe results of a tensile test are shown in Table 1.5.2. The test was performed on a metal specimen with a circular cross section. The diameter was 3 8 inch and the gage length (The length over which the elongation is measured) was 2 inches. a. Use the data in Table 1.5.2 to produce a table of stress and strain values. b. Plot the stress-strain data and draw a best-fit curve. c. Compute the, modulus of elasticity from the initial slope of the curve. d. Estimate the yield stress.arrow_forwardFigure P1.16 shows the stress–strain relations of metals A and B during tension tests until fracture. Determine the following for the two metals (show all calculations and units): Proportional limit Yield stress at an offset strain of 0.002 in./in. Ultimate strength Modulus of resilience Toughness Which metal is more ductile? Why?arrow_forward
- A material has the stress–strain behavior shown in Figure P1.2. What is the material strength at rupture? What is the toughness of this material?arrow_forwardPlease answer botharrow_forwardFigure shows the stress–strain relations of metals A and B during tension tests until fracture. Determine the following for the two metals (show all calculations and units): - Proportional limit- Yield stress at an offset strain of 0.002 in./in.- Ultimate strength- Modulus of resilience- Toughness- Which metal is more ductile? Why?arrow_forward
- 1.17 Figure P1.17 shows the stress-strain relations of metals A and B during tension tests until fracture. Determine the following for the two metals (show all calcu- lations and units): a. Proportional limit b. Yield stress at an offset strain of 0.002 in./in. 150 - - Metal A 100 • Metal B 50 0.00 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.14 Strain, in./in. FIGURE P1.17 c. Ultimate strength d. Modulus of resilience e. Toughness f. Which metal is more ductile? Why? Stress, ksiarrow_forwardA steel column has a sectional area of 0.126 m^2 and a length of 3 m. IF a 50000 KN load is applied to the column, determine the deformation in the column. A steel has a modulus of elasticity of 200 GpPaarrow_forwardPROBLEM 1 A steel rod with a cross sectional area of 150 mm? is stretched between two fixed points. The tensile load at 20°C is 5000 N. a.) What will be the stress at -20°C? b.) At what temperature will the stress be zero? Assume a = 11 .7 µm/m°C, and E = 200 Gpa *Show geometry of deformation ©sidewararrow_forward
- Q.3: A steel rod with a cross sectional area of 150 mm² is stretched between two fixed points. The tensile load at 20°C is 5000 N. a) What will be the stress at -20°C. b) At what temperature will the stress be zero? Assume a-11.7 μm/m . °C and E= 200 GPa?arrow_forward1 The principal stresses at a point in an elastic material are 1.50 (tensile), o (tensile) and 0.50 (compressive). The elastic limit in tension is 210 MPa and μ = 0.3. What would be the value of o at failure when computed by different theories of failure.arrow_forwardA round steel alloy bar with a diameter of 19 mm and a gauge length of 76 mm was subjected to tension, with the results shown in Table P3.26. Using a computer spreadsheet program, plot the stress-strain relationship. From the graph, determine the Young's modulus of the steel alloy and the deformation corresponding to a 37 kN load. TABLE P3.26 Deformation, Load, kN mm 9 0.0286 18 0.0572 27 0.0859 36 0.1145 45 0.1431 54 0.1718arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337094740Author:Segui, William T.Publisher:Cengage Learning

Materials Science And Engineering Properties
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781111988609
Author:Charles Gilmore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Steel Design (Activate Learning with these NEW ti...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337094740
Author:Segui, William T.
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Understanding Stresses in Beams; Author: The Efficient Engineer;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f08Y39UiC-o;License: Standard Youtube License