
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 1, Problem 1.26P
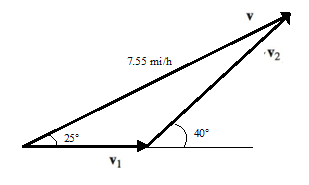
The velocity
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
(Read Image)
M16x2 grade 8.8 bolts No. 25 C1-
Q.2. The figure is a cross section of a grade 25 cast-iron pressure vessel. A
total of N, M16x2.0 grade 8.8 bolts are to be used to resist a separating
force of 160 kN. (a) Determine ks, km, and C. (b) Find the number of bolts
required for a load factor of 2 where the bolts may be reused when the joint 19 mm
is taken apart. (c) with the number of bolts obtained in (b), determine the
realized load factor for overload, the yielding factor of safety, and the
separation factor of safety.
19 mm
Problem4.
The thin uniform disk of mass m = 1-kg and radius R = 0.1m spins about the bent shaft OG with
the angular speed w2 = 20 rad/s. At the same time, the shaft rotates about the z-axis with the angular
speed 001 = 10 rad/s. The angle between the bent portion of the shaft and the z-axis is ẞ = 35°. The
mass of the shaft is negligible compared to the mass of the disk.
a. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point G, based on the axis
orientation as shown. Include an MVD in your solution.
b. Find the angular momentum of the disk with respect to point O, based on the axis
orientation as shown. (Note: O is NOT the center of fixed-point rotation.)
c. Find the kinetic energy of the assembly.
z
R
R
002
2R
x
Answer: H = -0.046ĵ-0.040 kg-m²/sec
Ho=-0.146-0.015 kg-m²/sec
T 0.518 N-m
=
Chapter 1 Solutions
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
Ch. 1 - A person weighs 30 lb on the moon, where...Ch. 1 - The radius and length of a steel cylinder are 40...Ch. 1 - Convert the following: (a) 400lbft to knm; (b)...Ch. 1 - A compact car travels 30 mi on one gallon of gas....Ch. 1 - The kinetic energy of a car of mass m moving with...Ch. 1 - In a certain application, the coordinate a and the...Ch. 1 - When a force F acts on a linear spring, the...Ch. 1 - In some applications dealing with very high...Ch. 1 - A geometry textbook gives the equation of a...Ch. 1 - A differential equation is d2ydt2=Ay2+Byt where y...
Ch. 1 - The position coordinate x of a particle is...Ch. 1 - A differential equation encountered in the...Ch. 1 - Determine the dimensions of constants A and B far...Ch. 1 - The typical power output of a compact car engine...Ch. 1 - Two 12-kg spheres are placed 400 mm apart. Express...Ch. 1 - Two identical spheres of radius 8 in. and weighing...Ch. 1 - A man weighs 170 lb on the surface of the earth....Ch. 1 - Use Eq. (1.4) to show that the weight of an object...Ch. 1 - Plot the earths gravitational acceleration g(m/s2)...Ch. 1 - Find the elevation h (km) where the weight of an...Ch. 1 - Calculate the gravitational force between the...Ch. 1 - The magnitudes of the two velocity vectors are...Ch. 1 - Determine the magnitudes of vectors v1 and v2 so...Ch. 1 - The pole AB is held up by the rope attached to B....Ch. 1 - Resolve the 20-kN force into components along the...Ch. 1 - The velocity vector of the boat has two...Ch. 1 - Two members of a truss apply the forces shown to...Ch. 1 - Two members of a truss apply the forces shown to...Ch. 1 - Determine the resultant of the position vectors A...Ch. 1 - Resolve the position vector A of the car (measured...Ch. 1 - Resolve the 360-lb force into components along the...Ch. 1 - The supporting cables AB and AC are oriented so...Ch. 1 - The two forces shown act on the structural member...Ch. 1 - The resultant of the two forces has a magnitude of...Ch. 1 - The forces acting on the bob of the pendulum are...Ch. 1 - A surveyor sights a target at C from points A and...Ch. 1 - Knowing that the resultant of the two forces is...Ch. 1 - To move the oil drum, the resultant of the three...Ch. 1 - The resultant of the 50-Ib and 30-lb forces is R....Ch. 1 - Obtain the rectangular representation of the force...Ch. 1 - The length of the position vector r is 240 mm....Ch. 1 - Determine the rectangular components of the 560-lb...Ch. 1 - The coordinates of points A and B are (-3, 0, 2)...Ch. 1 - The slider travels along the guide rod AB with the...Ch. 1 - Find the rectangular representation of the force...Ch. 1 - The magnitude of the force F is 160 lb. Find its...Ch. 1 - A rifle at A is fired at a target at B. If the...Ch. 1 - The pole OB is subjected to the 6004b force at B....Ch. 1 - The cables AB and AC are attached to the frame...Ch. 1 - The two forces are applied to the end of the boom...Ch. 1 - The magnitudes of the three forces are...Ch. 1 - Given that P=120lb and Q=130lb, find the...Ch. 1 - Knowing that P=90lb and that the resultant of P...Ch. 1 - If R is the resultant of the forces P and Q, find...Ch. 1 - The force R is the resultant of P and 0. Determine...Ch. 1 - The vertical post is secured by three cables. The...Ch. 1 - Compute the dot product A - B for each of the...Ch. 1 - Compute the cross product C=AB for each of the...Ch. 1 - Given r=4i6j+2km (position vector) F=20i+40j30kN...Ch. 1 - Compute AB and CB for the position vectors shown.Ch. 1 - Use the dot product to find the angle between the...Ch. 1 - Use the dot product to find the angle between the...Ch. 1 - Let A and B be two nonparallel vectors that lie in...Ch. 1 - Determine (a) the angle between the position...Ch. 1 - Find a unit vector that is perpendicular to both...Ch. 1 - The three points A(0,2,2),B(1,4,1), and C(3,0,0)...Ch. 1 - For the position vectors P and Q shown, determine...Ch. 1 - Compute the orthogonal Component of F=6i+20j12klb...Ch. 1 - Compute the value of the scalar a for which the...Ch. 1 - Resolve A=3i+5j4k in. into two vector...Ch. 1 - The force F=5i+12j+4k lb is applied to the handle...Ch. 1 - Determine the value of the scalar a if the...Ch. 1 - Resolve the force F=20i+30j+50klb into two...Ch. 1 - It can be show that a plane area may he...Ch. 1 - The coordinates of the corners of a triangle ABC...Ch. 1 - Show that |abc| equals the volume of a...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 3. The assembly shown consists of a solid sphere of mass m and the uniform slender rod of the same mass, both of which are welded to the shaft. The assembly is rotating with angular velocity w at a particular moment. Find the angular momentum with respect to point O, in terms of the axes shown. Answer: Ñ。 = ½mc²wcosßsinßĵ + (}{mr²w + 2mb²w + ½ mc²wcos²ß) k 3 m r b 2 C لا marrow_forwardOnly question 2arrow_forwardOnly question 1arrow_forward
- Only question 3arrow_forwardI have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of N relative to Q, e = -0.7071*n3, e4 = 0.7071. I have Euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to N, e = -1/sqrt(3)*n1, e4 = sqrt(2/3). After using euler parameter rule of successive rotations, I get euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q, e = -0.4082*n1 - 0.4082*n2 - 0.5774*n3. I need euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis of q instead of n. How do I get that?arrow_forwardDescribe at least 4 processes in engineering where control charts are (or should be) appliedarrow_forward
- Describe at least two (2) processes where control charts are (or should be) applied.arrow_forwardProblem 3: A cube-shaped spacecraft is in a circular Earth orbit. Let N (n,) be inertial and the spacecraft is denoted S (ŝ₁). The spacecraft is described such that ¯½º = J ŝ₁ŝ₁ + J ŝ₂§₂ + J §¸Ŝ3 Location of the spacecraft in the orbit is determined by the orbit-fixed unit vectors ê, that are oriented by the angle (Qt), where is a constant angular rate. 52 €3 3> 2t 55 Λ Из At the instant when Qt = 90°, the spacecraft S is oriented relative to the orbit such that 8₁ = 0° Space-three 1-2-3 angles 0₂ = 60° and ES = $₂ rad/s 0₁ = 135° (a) At this instant, determine the direction cosine matrix that describes the orientation of the spacecraft with respect to the inertial frame N.arrow_forwardThis problem illustrates that the factor of safety for a machine element depends on the particular point selected for analysis. Here you are to compute factors of safety, based upon the distortion-energy theory, for stress elements at A and B of the member shown in the figure. This bar is made of AISI 1006 cold-drawn steel and is loaded by the forces F = 1.100 kN, P = 8.00 kN, and T = 50.00 N-m. Given: Sy = 280 MPa. B -100 mm- 15-mm D. a) Determine the value of the axial stress at point B. b) Determine the value of the shear stress at point B. c) Determine the value of the Von Mises stress at point B. P Farrow_forward
- A piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.08 m^3 of nitrogen gas at 130 kPa and 170°C. The nitrogen is expanded to a pressure of 80 kPa via isentropic expansion. Determine the final temperature and the boundary work done by the system during this process.arrow_forwardA Carnot (ideal) heat pump is to be used to heat a house and maintain it at 22°C in winter. On a day when the average outdoor temperature remains at about 0°C, the house is estimated to lose heat at a rate of 65,000 kJ/h. If the heat pump consumes 6 kW of power while operating, determine: (a) how long the heat pump ran on that day (b) the total heating costs, assuming an average price of 11¢/kWh for electricity (c) the heating cost for the same day if an 85% efficient electric furnace is used instead of a heat pump.arrow_forwardFrom the information in the image, I needed to find the orientation of U relative to Q in vector basis q_hat. I transformed the euler angle/axis representation to euler parameters. Then I got its conjugate in order to get the euler parameter in N frame relative to Q. The problem gave the euler angle/axis representation in Q frame relative to N, so I needed to find the conjugate. Then I used the euler parameter rule of successive rotation to find the final euler parameters that describe the orientation of U relative to Q. However that orientation is in n_hat which is the intermediate frame. How do I get the final result in q_hat?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY