The calculations for a factorial experiment involving four levels of factor A, three levels of factor B, and three replications resulted in the following data: SST = 286, SSA= 26, SSB SSAB 178. Set up the ANOVA table. (Round your values for mean squares and F to two decimal places, and your p-values to three decimal places.) Source of Variation Factor A Factor B Interaction Error Total Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square F Test for any significant main effects and any interaction effect. Use a = 0.05. Find the value of the test statistic for factor A. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value for factor A. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value= State your conclusion about factor A. O Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is not significant. Because the p-value sa = 0.05, factor A is significant. O Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is significant. O Because the p-value sa = 0.05, factor A is not significant. p-value
The calculations for a factorial experiment involving four levels of factor A, three levels of factor B, and three replications resulted in the following data: SST = 286, SSA= 26, SSB SSAB 178. Set up the ANOVA table. (Round your values for mean squares and F to two decimal places, and your p-values to three decimal places.) Source of Variation Factor A Factor B Interaction Error Total Sum of Squares Degrees of Freedom Mean Square F Test for any significant main effects and any interaction effect. Use a = 0.05. Find the value of the test statistic for factor A. (Round your answer to two decimal places.) Find the p-value for factor A. (Round your answer to three decimal places.) p-value= State your conclusion about factor A. O Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is not significant. Because the p-value sa = 0.05, factor A is significant. O Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is significant. O Because the p-value sa = 0.05, factor A is not significant. p-value
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:Amos Gilat
Chapter1: Starting With Matlab
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1P
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:The calculations for a factorial experiment involving four levels of factor A, three levels of factor B, and three replications resulted in the following data: SST = 286, SSA = 26, SSB = 24,
SSAB = 178. Set up the ANOVA table. (Round your values for mean squares and F to two decimal places, and your p-values to three decimal places.)
Source
Sum
of Variation of Squares
Factor A
Factor B
Interaction
Error
Total
ONL
Degrees
of Freedom
Mean
Square
F
p-value
Test for any significant main effects and any interaction effect. Use α = 0.05.
Find the value of the test statistic for factor A. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the p-value for factor A. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
p-value =
State your conclusion about factor A.
Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is not significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor A is significant.
Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor A is not significant.

Transcribed Image Text:State your conclusion about factor A.
Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor A is not significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor A is significant.
Because the p-value > α = 0.05, factor A is significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor A is not significant.
Find the value of the test statistic for factor B. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the p-value for factor B. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
p-value =
State your conclusion about factor B.
Because the p-value > a = 0.05, factor B is not significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor B is significant.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, factor B is not significant.
Because the p-value > α = 0.05, factor B is significant.
Find the value of the test statistic for the interaction between factors A and B. (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
Find the p-value for the interaction between factors A and B. (Round your answer to three decimal places.)
p-value
State your conclusion about the interaction between factors A and B.
Because the p-value ≤ α = 0.05, the interaction between factors A and B is not significant.
Because the p-value < α = 0.05, the interaction between factors A and B is significant.
Expert Solution
Step 1
Given that
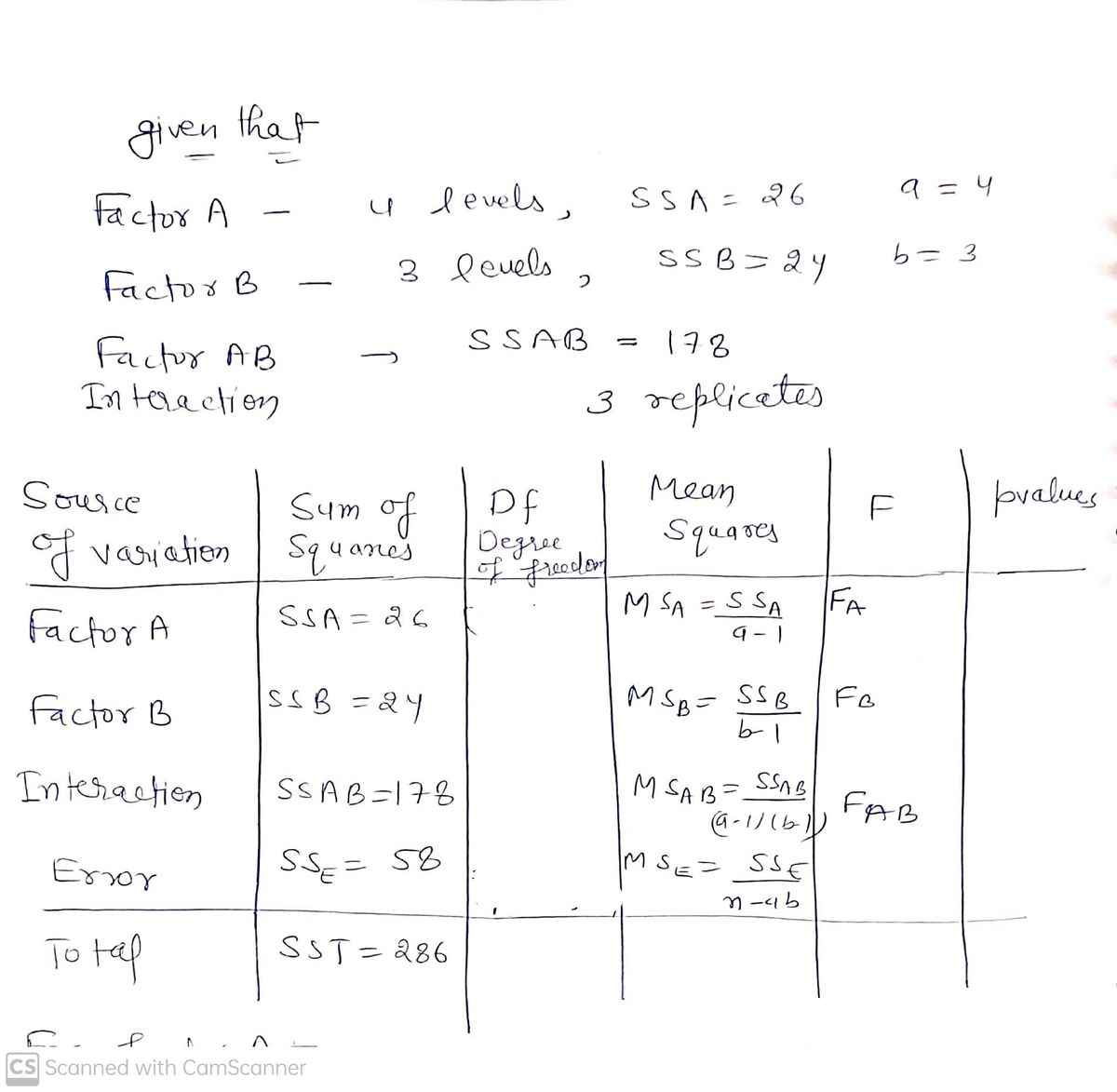
We have to Analyse the data using the Analysis of Variance technique:
Step by step
Solved in 7 steps with 7 images

Recommended textbooks for you

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:
9781119256830
Author:
Amos Gilat
Publisher:
John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305251809
Author:
Jay L. Devore
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C…
Statistics
ISBN:
9781305504912
Author:
Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E…
Statistics
ISBN:
9780134683416
Author:
Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:
PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319042578
Author:
David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:
9781319013387
Author:
David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:
W. H. Freeman