Select the best answer or answers from the choices given: What is formed during aerobic respiration when electrons are passed down the electron transport chain? (a) oxygen, (b) water, (c) glucose, (d) NADH + H+.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain, also known as the electron transport system, is a group of proteins that transfer electrons through a membrane within mitochondria to create a gradient of protons that drives adenosine triphosphate (ATP)synthesis. The cell uses ATP as an energy source for metabolic processes and cellular functions. ETC involves series of reactions that convert redox energy from NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) + hydrogen (H)) and FADH2(flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)) oxidation into proton-motive force(PMF), which is then used to synthesize ATP through conformational changes in the ATP synthase complex, a process known as oxidative phosphorylation.
Metabolism
Picture a campfire. It keeps the body warm on a cold night and provides light. To ensure that the fire keeps burning, fuel needs to be added(pieces of wood in this case). When a small piece is added, the fire burns bright for a bit and then dies down unless more wood is added. But, if too many pieces are placed at a time, the fire escalates and burns for a longer time, without actually burning away all the pieces that have been added. Many of them, especially the larger chunks or damp pieces, remain unburnt.
Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is the cellular process involved in the generation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules from the organic nutritional source obtained from the diet. It is a universal process observed in all types of life forms. The glucose (chemical formula C6H12O6) molecules are the preferred raw material for cell respiration as it possesses a simple structure and is highly efficient in nature.
Select the best answer or answers from the choices given: What is formed during aerobic respiration when electrons are passed down the electron transport chain? (a) oxygen, (b) water, (c) glucose, (d) NADH + H+.
The respiration process in which the energy is released or formed in the form of ATP on the oxidation of glucose which is a most important monosaccharide carbohydrate. Aerobic respiration occurs in three steps, first is the glycolysis, breakdown of glucose to pyruvate, second is the Kreb's cycle or citric acid cycle in which acetyl CoA is used to form reducing powers, then third is the electron transport chain in which reducing powers are used to synthesize ATP for other body functions.
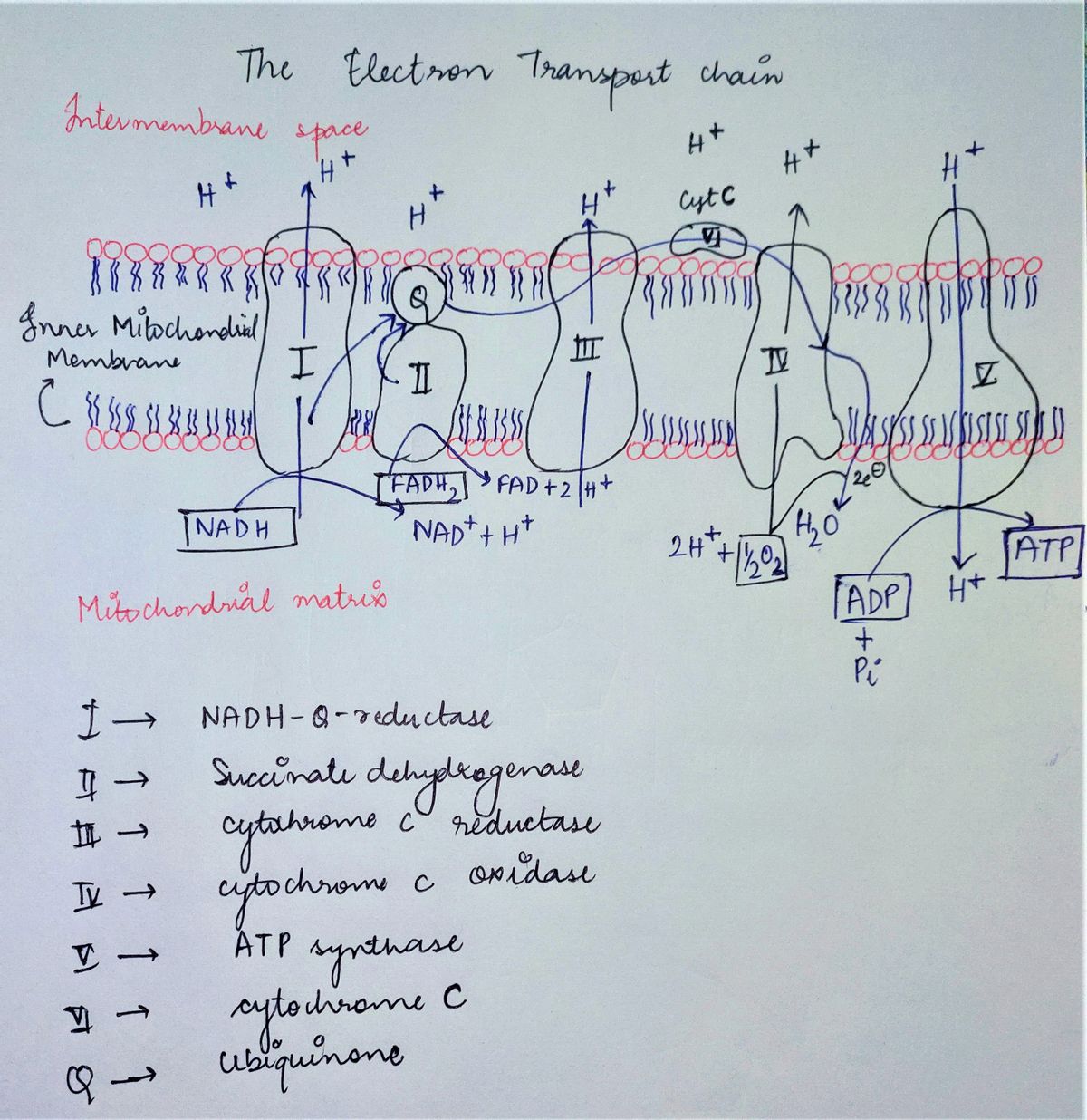
The electron transport chain or oxidative phosphorylation is the process that is the final stage of cellular respiration in which a series of protein molecules are found in the mitochondrial membrane that is used to transfer electrons from reducing powers from one molecule to another and energy is released which is used to pump hydrogen ions and forming an electrochemical gradient. The electrons are transferred to molecular oxygen which joins to the hydrogen ions, forming water molecules. The gradient is used to make ATP as they pass through the ATP synthase. The ETC is shown in the diagram given below:
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









