In a test run, a certain car accelerates uniformly from zero to 16.2 m/s in 2.30 s. (a) What is the magnitude of the car's acceleration? _____m/s2 (b) How long does it take the car to change its speed from 8.10 m/s to 16.2 m/s? _______s (c) Will doubling the time always double the change in speed? Yes No WHY?
Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration
In classical mechanics, kinematics deals with the motion of a particle. It deals only with the position, velocity, acceleration, and displacement of a particle. It has no concern about the source of motion.
Linear Displacement
The term "displacement" refers to when something shifts away from its original "location," and "linear" refers to a straight line. As a result, “Linear Displacement” can be described as the movement of an object in a straight line along a single axis, for example, from side to side or up and down. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Non-contact sensors such as LVDTs and other linear location sensors can calculate linear displacement. Linear displacement is usually measured in millimeters or inches and may be positive or negative.
In a test run, a certain car accelerates uniformly from zero to 16.2 m/s in 2.30 s.
_____m/s2
(b) How long does it take the car to change its speed from 8.10 m/s to 16.2 m/s?
_______s
(c) Will doubling the time always double the change in speed?
________m/s
(b) How far has the car gone?
________m
_______s
(b) How far has he traveled in that time?
_______m
_____m
(b) How long does it take to reach its highest point?
_____s
(c) How long does the ball take to hit the ground after it reaches its highest point?
_____s
(d) What is its velocity when it returns to the level from which it started?
_____m/s
Since you have asked multiple sub-parts only the 3 sub-parts will be solved for you. If you want any specific sub-part to be solved post the question again and highlight or mention the sub-part to be solved.
Write the given values using a suitable variable.
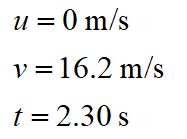
Here u signifies initial velocity, v signifies final velocity, and t signifies time.
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 5 images









