D. 4.59 × 10* 8. In an experiment, 0.200 mole of CO(g) and 0.400 mole of O2(g) were placed in a 1.00 dm³ container and the following equilibrium is established: 2CO(g) + O2(g) = 2CO2(g) At equilibrium, the concentration of CO2(g) was found to be 0.160 mol dm³. What is the equilibrium constant, Ke, for the reaction? A. 16.7 dm³ mol¯ B. 50.0 dm³ mol C. 58.9 dm³ mol D. 66.7 dm³ mol¯!

Reactions occurring in closed container proceeds upto a certain extent and after that there is an equilibrium establishment among products and reactants. The value of [products] over [reactants] at this stage remains unchanged and is referred as "equilibrium constant".
Given:
The initial amount of CO is 0.200 mol.
The initial amount of O2 is 0.400 mol.
The equilibrium concentration of CO2 is 0.160 mol dm-3.
The volume of container is 1.00 dm3.
The given reaction is shown below.
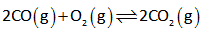
The equilibrium constant expression is as follows,
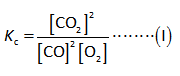
Here,
The equilibrium concentration of carbon dioxide is “[CO2]”.
The equilibrium concentration of carbon monoxide is “[CO]”.
The equilibrium concentration of oxygen is “[O2]”.
Initially, the reaction contains 0.200 moles and 0.400 moles of CO and O2 in 1 dm3 of container respectively.
Therefore, the concentration of CO is 0.2 mol dm3.
The concentration of O2 is 0.4 mol dm3.
The ICE table of reaction is shown below.
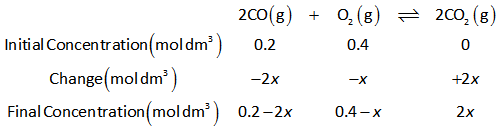
But the equilibrium concentration of CO2 is 0.160 mol dm-3.
Thus, value of x is calculated as follows,
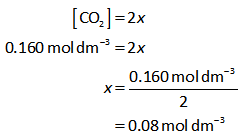
The equilibrium concentration of CO and O2 is calculated below.
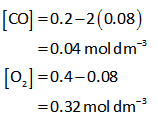
Substitute all required values in equation (I).
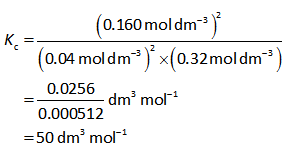

Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 8 images









