could you help me work out these problem step by step


Please find the following answers step by step as given in the problem.
Part 1
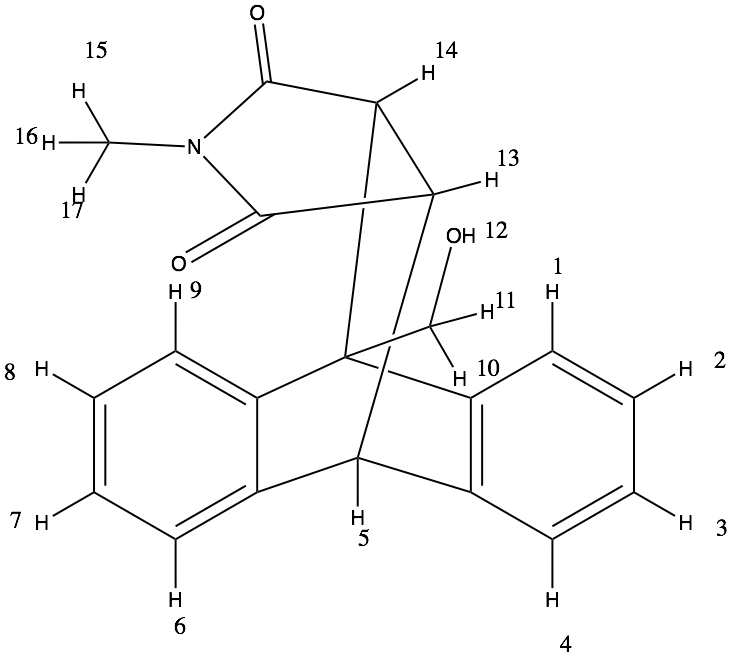
1. From the structural distribution of the molecule we can think of H2, H3, H7 and H8 should come in one place-1 type
H1, H4, H6 and H9 ideally should appear together- 1 type
H10 and H11 being diastereotopic protons, they should appear in two different ppm values-2 types
H5 would come seperately - 1 type
OH proton H12 would appear differently- 1 type
H13 and H14 being chemically different would appear at two differetn ppm values-2 type
Finally the methyl protons bein chemically same would appear at the same place- 1 type
Summing them together, ideally there should be 9 different signals one can expect in the NMR spectra.
2. Diastereotopic protons are those protons which are chemically non equivalent and each produce distinct chemical shifts. Usually, the CH2 protons are considered as Diastereotopic protons. In this structure H10 and H11 are two diastereotopic protons.
3. ppm shift of each chemically equivalent proton
H2, H3, H7 and H8 --> 7.2 ppm
H1, H4, H6 and H9 --> 7.3 ppm
H15, H16 and H17 --> 2.5 ppm
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 2 images









