Consider the following equilibrium: CH4 (e +H2 @ CH6 @ AH<0 Discuss how changes in temperature and volume could optimize the production of the product.
![**Optimization of Chemical Equilibrium: Ethene to Ethane**
**Equilibrium Reaction:**
\[ \text{C}_2\text{H}_4(\text{g}) + \text{H}_2(\text{g}) \rightleftharpoons \text{C}_2\text{H}_6(\text{g}) \ \Delta H < 0 \]
**Discussion Prompt:**
Discuss how changes in temperature and volume could optimize the production of the product.
### Explanation
In the given equilibrium reaction, ethene (C₂H₄) reacts with hydrogen (H₂) to form ethane (C₂H₆). The reaction is exothermic, indicated by the negative value of ΔH (enthalpy change).
#### **Temperature Effect:**
- **Exothermic Reaction**: The reaction releases heat (\(\Delta H < 0\)). According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, increasing the temperature would shift the equilibrium position to the left, favoring the reactants to absorb the excess heat.
- **Optimization Strategy**: To optimize the production of ethane (C₂H₆), the temperature should be decreased. Lower temperatures remove excess heat, thus shifting the equilibrium to the right, favoring the formation of more product.
#### **Volume Effect:**
- **Number of Moles of Gas**: There are 2 moles of gas (C₂H₄ and H₂) on the reactant side and 1 mole of gas (C₂H₆) on the product side.
- **Pressure and Volume Relationship**: Decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel increases the pressure. According to Le Chatelier’s Principle, the equilibrium shifts towards the side with fewer moles of gas to reduce the pressure.
- **Optimization Strategy**: To optimize production, the volume of the container should be decreased. This increases the pressure and shifts the equilibrium towards the product side, which has fewer moles of gas.
By carefully adjusting these parameters, the production of ethane can be maximized in an industrial setting.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2Ffbc1cd9d-8d4f-40e4-add2-a376f2364edb%2F37258c8b-06bb-46c0-841e-63db8582cb4e%2Fdr08f9g.png&w=3840&q=75)
According to LeChatleir's principle,
"when a system at equilibrium is subjected to a change in either pressure or concentration or temperature ,then the equilibrium will shift in such a direction that it nullifies the change."
For example:
A chemical reaction is in dynamic equilibrium.
When left side concentration of substrates is increased then, the equilibrium will shift towards right side to nullify the change.
In this case , forward reaction is favored.
The given chemical reaction is:
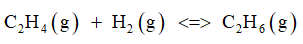
Effect of temperature on the given equilibrium reaction:
Given, 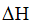 of the reaction is negative.
of the reaction is negative.
That means the forward reaction is exothermic.
According to LeChatleir's principle, decrease in temperature favors the forward reaction.
Increase in temperature favors the backward reaction.
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 2 images









