Calculate the uncertainties dr = V(r2) and dp = Vp?) for a particle confined in the region -a < x < a. The wave function of the particle is: 1 = (x) 2a -a < r < a, COS (x) = 0, I > a, r < -a.
Calculate the uncertainties dr = V(r2) and dp = Vp?) for a particle confined in the region -a < x < a. The wave function of the particle is: 1 = (x) 2a -a < r < a, COS (x) = 0, I > a, r < -a.
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Calculate the uncertainties dr = V(r2) and dp = Vp?) for
a particle confined in the region -a < x < a. The wave function of the
particle is:
1
= (x)
2a
-a < r < a,
COS
(x) = 0,
I > a, r < -a.
Expert Solution
Step 1
As we can see the given wave function is normalised and in outside region it's zero. Therefore
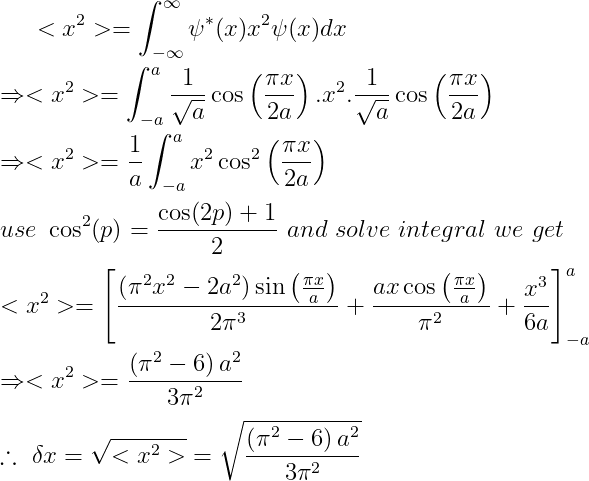
This is the position uncertainty.
Step by step
Solved in 2 steps with 3 images
