(a) p(Br2) = 1.84 atm, p(Cl2) = 7.24 atm, p(BrCl) = 16.8 atm; this reaction: does which one of the folllowing?? ___must shift toward product to achieve equilibrium ___is already reasonably close to equilibrium ___must shift toward reactants to achieve equilibrium (b) p(Br2) = 6.18 atm, p(Cl2) = 3.75 atm, p(BrCl) = 22.1 atm; this reaction: does which one of the folllowing?? ___must shift toward product to achieve equilibrium ___is already reasonably close to equilibrium ___must shift toward reactants to achieve equilibrium
The calculated value of KP for the equilibrium:
1 Br2(g) + 1 Cl2(g) 2 BrCl(g)
is 0.846 at 1961 oC. For each of the mixtures listed here select the option from the pulldown menu which indicates whether the mixture is reasonably close to being at equilibrium at 1961 oC. "Reasonably close" means that Q is within a factor of 2 of KP. If the mixture is not close to equilibrium choose the option which indicates which direction the reaction needs to shift (toward product or toward reactants) to achieve equilibrium.
(a) p(Br2) = 1.84 atm, p(Cl2) = 7.24 atm, p(BrCl) = 16.8 atm;
this reaction: does which one of the folllowing??
___must shift toward product to achieve equilibrium
___is already reasonably close to equilibrium
___must shift toward reactants to achieve equilibrium
(b) p(Br2) = 6.18 atm, p(Cl2) = 3.75 atm, p(BrCl) = 22.1 atm;
this reaction: does which one of the folllowing??
___must shift toward product to achieve equilibrium
___is already reasonably close to equilibrium
___must shift toward reactants to achieve equilibrium
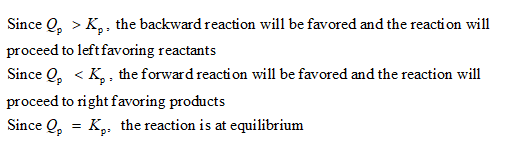
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images









