ngineer is studying the following reaction: HCN (aq) + NH3(aq) → CN (aq) + NH(aq) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.1. The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen cyanide and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. A chem reaction vessel A B с compound HCN NH3 CN NH4 HCN NH3 CN NHA HCN NH3 CN ΝΗ, concentration 0.28 M 0.12 M 1.05 M 0.94 M 0.67 M 0.51 M 0.66 M 0.55 M 0.31 M 0.15 M 1.02 M 0.91 M expected change in concentration ↑ increase O decrease ↓ Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase Ot increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase O † increase ↑ O decrease ↓ O decrease ↓ Odecrease O decrease ↓ O decrease ↓ O decrease Odecrease Odecrease O decrease ↓ Odecrease O decrease O (no change) (no change) O(no change) (no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change) (no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change)
ngineer is studying the following reaction: HCN (aq) + NH3(aq) → CN (aq) + NH(aq) At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.1. The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen cyanide and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below. Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions. A chem reaction vessel A B с compound HCN NH3 CN NH4 HCN NH3 CN NHA HCN NH3 CN ΝΗ, concentration 0.28 M 0.12 M 1.05 M 0.94 M 0.67 M 0.51 M 0.66 M 0.55 M 0.31 M 0.15 M 1.02 M 0.91 M expected change in concentration ↑ increase O decrease ↓ Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase ↑ increase Ot increase Ot increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase ↑ increase O † increase ↑ O decrease ↓ O decrease ↓ Odecrease O decrease ↓ O decrease ↓ O decrease Odecrease Odecrease O decrease ↓ Odecrease O decrease O (no change) (no change) O(no change) (no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change) (no change) (no change) O(no change) O(no change) O(no change)
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A chem ngineer is studying the following reaction:
+
HCN(aq) + NH3(aq) → CN¯(aq)+NH (aq)
At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.1.
C
The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen cyanide and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the
mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below.
Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions.
reaction
vessel
A
B
C
compound
HCN
NH3
CN
NH4
HCN
NH3
CN
NH₁
HCN
NH₂
CN
NHA
4
concentration
0.28 M
0.12 M
1.05 M
0.94 M
0.67 M
0.51 M
0.66 M
0.55 M
0.31 M
0.15 M
1.02 M
0.91 M
expected change in concentration
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓ decrease
888888
↓decrease
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓decrease
decrease
↓ decrease
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution!
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 5 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:Try Again
Your answer is incorrect.
• reaction vessel B: Your answer is incorrect.
A chemical engineer is studying the following reaction:
HCN (aq) + NH3(aq) → CN¯(aq)+NH(aq)
At the temperature the engineer picks, the equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.1.
The engineer charges ("fills") four reaction vessels with hydrogen cyanide and ammonia, and lets the reaction begin. He then measures the composition of the
mixture inside each vessel from time to time. His first set of measurements are shown in the table below.
Predict the changes in the compositions the engineer should expect next time he measures the compositions.
reaction
vessel
A
compound
HCN
ΝΗ,
CN
NH₁
concentration
0.28 M
0.12 M
1.05 M
0.94 M
expected change in concentration
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓ decrease
↑ increase O decrease
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
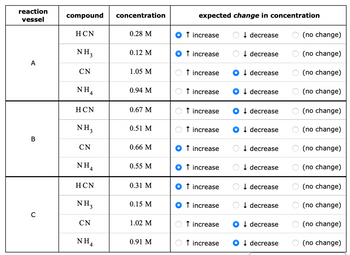
Transcribed Image Text:reaction
vessel
A
B
C
compound
HCN
NH₂
CN
NH₁
HCN
NH3
CN
NH4
HCN
NH3
CN
NH₁
4
concentration
0.28 M
0.12 M
1.05 M
0.94 M
0.67 M
0.51 M
0.66 M
0.55 M
0.31 M
0.15 M
1.02 M
0.91 M
expected change in concentration
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↑ increase
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
decrease
↓ decrease
↓ decrease
↓decrease
↓decrease
↓decrease
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
(no change)
Solution
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY