Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Chapter1: Chemical Foundations
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 1RQ: Define and explain the differences between the following terms. a. law and theory b. theory and...
Related questions
Question
2b) please see attached
![### Equilibrium Reaction and Constant
The following chemical reaction reaches equilibrium, and its equilibrium constant (Kc) is 1.81 x 10⁻⁵ at 25°C:
\[ \text{C}_2\text{H}_4\text{O}_2\text{(aq)} \ + \ \text{H}_2\text{O(l)} \ \rightleftharpoons \ \text{H}_3\text{O}^+\text{(aq)} \ + \ \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^-\text{(aq)} \]
#### Explanation of Terms:
- **C₂H₄O₂ (aq)**: Acetic acid in aqueous solution.
- **H₂O (l)**: Water, which remains in the liquid state.
- **H₃O⁺ (aq)**: Hydronium ion in aqueous solution.
- **C₂H₃O₂⁻ (aq)**: Acetate ion in aqueous solution.
#### Reaction Description:
In this reaction, acetic acid (C₂H₄O₂) reacts with water to form a hydronium ion (H₃O⁺) and an acetate ion (C₂H₃O₂⁻).
#### Equilibrium Constant (Kc):
- **Kc = 1.81 x 10⁻⁵ at 25°C**: This is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25 degrees Celsius, which indicates the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the reactants when the reaction is at equilibrium.
This reaction typically represents the ionization of a weak acid (acetic acid) in water.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F48deb947-3d41-43de-ac43-bef03e01cc59%2F19b590d2-087d-4c4d-90ee-f23f0e486fd0%2Fnd4a4tv.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Equilibrium Reaction and Constant
The following chemical reaction reaches equilibrium, and its equilibrium constant (Kc) is 1.81 x 10⁻⁵ at 25°C:
\[ \text{C}_2\text{H}_4\text{O}_2\text{(aq)} \ + \ \text{H}_2\text{O(l)} \ \rightleftharpoons \ \text{H}_3\text{O}^+\text{(aq)} \ + \ \text{C}_2\text{H}_3\text{O}_2^-\text{(aq)} \]
#### Explanation of Terms:
- **C₂H₄O₂ (aq)**: Acetic acid in aqueous solution.
- **H₂O (l)**: Water, which remains in the liquid state.
- **H₃O⁺ (aq)**: Hydronium ion in aqueous solution.
- **C₂H₃O₂⁻ (aq)**: Acetate ion in aqueous solution.
#### Reaction Description:
In this reaction, acetic acid (C₂H₄O₂) reacts with water to form a hydronium ion (H₃O⁺) and an acetate ion (C₂H₃O₂⁻).
#### Equilibrium Constant (Kc):
- **Kc = 1.81 x 10⁻⁵ at 25°C**: This is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25 degrees Celsius, which indicates the ratio of the concentrations of the products to the reactants when the reaction is at equilibrium.
This reaction typically represents the ionization of a weak acid (acetic acid) in water.
![### Equilibrium in Chemical Reactions
#### Example Problem:
**b)** A solution in which this reaction takes place is analyzed, and found to have \([C_2H_4O_2] = 0.073 \, M\) and \([C_2H_3O_2^-] = 0.251 \, M\), and \(pH = 2.131\). Is the system at equilibrium? (Calculate \(Q\) and comment).
---
#### Explanation:
1. **Given Data**:
- Concentration of \(C_2H_4O_2\) (Acetic Acid): \(0.073 \, M\)
- Concentration of \(C_2H_3O_2^-\) (Acetate Ion): \(0.251 \, M\)
- pH of the solution: \(2.131\)
2. **Required**:
- Determine if the system is at equilibrium by calculating the reaction quotient \(Q\) and compare it with the equilibrium constant \(K\).
3. **Steps to Determine Equilibrium**:
1. **Calculate the Hydronium Ion Concentration \([H^+]\)**:
\[
[H^+] = 10^{-pH} = 10^{-2.131}
\]
Find the numeric value using a calculator.
2. **Calculate the Reaction Quotient \(Q\)**:
\[
Q = \frac{[C_2H_3O_2^-][H^+]}{[C_2H_4O_2]}
\]
Insert the known values into the equation and compute \(Q\).
3. **Compare \(Q\) with the Equilibrium Constant \(K\)**:
- If \(Q = K\), the system is at equilibrium.
- If \(Q \ne K\), the system is not at equilibrium.
**Note**: The equilibrium constant \(K\) for this reaction is typically given or can be found in a reference, depending on the specific reaction and conditions.](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F48deb947-3d41-43de-ac43-bef03e01cc59%2F19b590d2-087d-4c4d-90ee-f23f0e486fd0%2Fdusm2vu.png&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Equilibrium in Chemical Reactions
#### Example Problem:
**b)** A solution in which this reaction takes place is analyzed, and found to have \([C_2H_4O_2] = 0.073 \, M\) and \([C_2H_3O_2^-] = 0.251 \, M\), and \(pH = 2.131\). Is the system at equilibrium? (Calculate \(Q\) and comment).
---
#### Explanation:
1. **Given Data**:
- Concentration of \(C_2H_4O_2\) (Acetic Acid): \(0.073 \, M\)
- Concentration of \(C_2H_3O_2^-\) (Acetate Ion): \(0.251 \, M\)
- pH of the solution: \(2.131\)
2. **Required**:
- Determine if the system is at equilibrium by calculating the reaction quotient \(Q\) and compare it with the equilibrium constant \(K\).
3. **Steps to Determine Equilibrium**:
1. **Calculate the Hydronium Ion Concentration \([H^+]\)**:
\[
[H^+] = 10^{-pH} = 10^{-2.131}
\]
Find the numeric value using a calculator.
2. **Calculate the Reaction Quotient \(Q\)**:
\[
Q = \frac{[C_2H_3O_2^-][H^+]}{[C_2H_4O_2]}
\]
Insert the known values into the equation and compute \(Q\).
3. **Compare \(Q\) with the Equilibrium Constant \(K\)**:
- If \(Q = K\), the system is at equilibrium.
- If \(Q \ne K\), the system is not at equilibrium.
**Note**: The equilibrium constant \(K\) for this reaction is typically given or can be found in a reference, depending on the specific reaction and conditions.
Expert Solution
Step 1
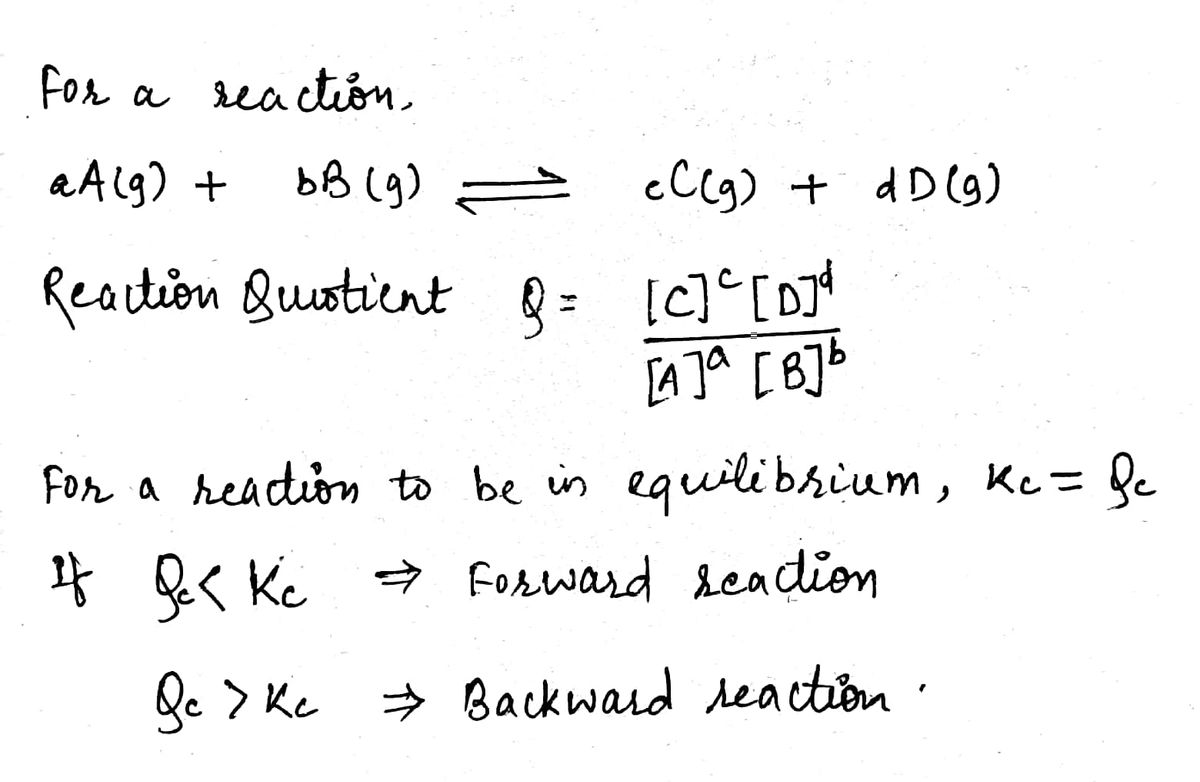
Step 2

Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305957404
Author:
Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781259911156
Author:
Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305577213
Author:
Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:
9780078021558
Author:
Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:
McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781305079373
Author:
William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind…
Chemistry
ISBN:
9781118431221
Author:
Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:
WILEY