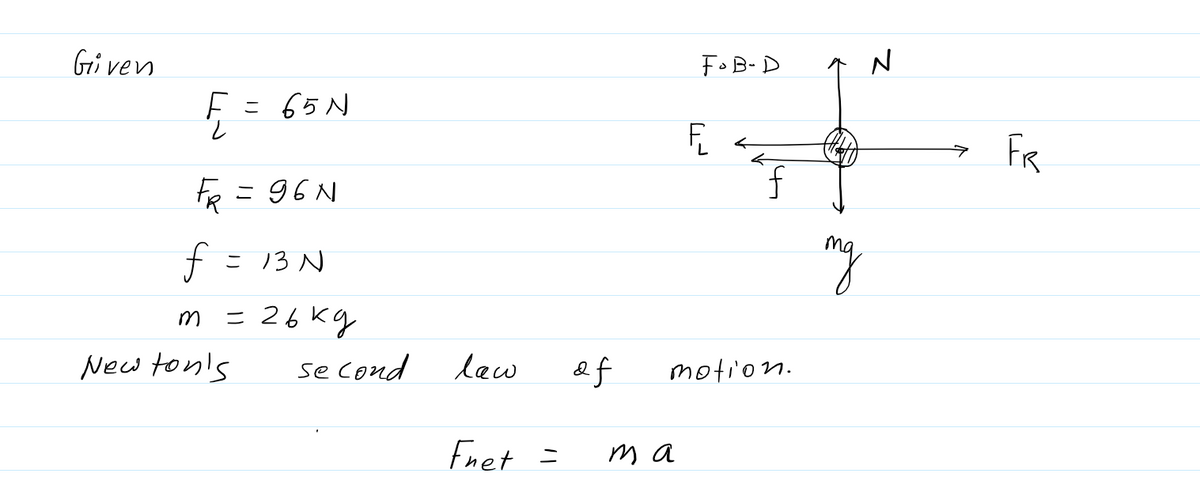
1. Your free body diagram for Part 2 should have looked like this: Construct the free-body diagram. 1. Place the tail of the vectors within the confines of the mass. 2. Orient the vectors by dragging the heads in the proper direction. Note: the angles may be within +15°, the magnitudes are not considered, and the vectors do not need to be centered on the mass. N:90° 1444 FL: 180; 179.87 mg; 270 FR: 0.04⁰ Suppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions, on a third child in a wagon. The first child exerts a force F₁ of 65.0 N, the second a force FR of 96.0 N, friction f is 13.0 N, and the mass of the third child plus wagon is 26.0 kg.
1. Your free body diagram for Part 2 should have looked like this: Construct the free-body diagram. 1. Place the tail of the vectors within the confines of the mass. 2. Orient the vectors by dragging the heads in the proper direction. Note: the angles may be within +15°, the magnitudes are not considered, and the vectors do not need to be centered on the mass. N:90° 1444 FL: 180; 179.87 mg; 270 FR: 0.04⁰ Suppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions, on a third child in a wagon. The first child exerts a force F₁ of 65.0 N, the second a force FR of 96.0 N, friction f is 13.0 N, and the mass of the third child plus wagon is 26.0 kg.
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology Update (No access codes included)
9th Edition
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Chapter3: Vectors
Section: Chapter Questions
Problem 3.4OQ: The culling tool on a lathe is given two displacements, one of magnitude 4 cm and one of magnitude 3...
Related questions
Question
![### Physics Problem on Acceleration
**(a) Calculate the acceleration.**
_Enter to 3 significant figures_
\[ a = \_\_\_\_ \, \text{m/s}^2 \]
**(b) What would the acceleration be if friction were 31 N?**
_Enter to 3 significant figures_
\[ a = \_\_\_\_ \, \text{m/s}^2 \]
### Notes:
- Ensure accuracy by maintaining three significant figures in your calculations.
- Apply Newton's second law and consider any forces acting on the object, such as friction when answering part (b).](/v2/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcontent.bartleby.com%2Fqna-images%2Fquestion%2F85a13651-0641-4e1f-9366-64e873b85445%2F03c7e8ad-d790-4d44-be9d-0ae0d557a054%2Fc24psj_processed.jpeg&w=3840&q=75)
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics Problem on Acceleration
**(a) Calculate the acceleration.**
_Enter to 3 significant figures_
\[ a = \_\_\_\_ \, \text{m/s}^2 \]
**(b) What would the acceleration be if friction were 31 N?**
_Enter to 3 significant figures_
\[ a = \_\_\_\_ \, \text{m/s}^2 \]
### Notes:
- Ensure accuracy by maintaining three significant figures in your calculations.
- Apply Newton's second law and consider any forces acting on the object, such as friction when answering part (b).

Transcribed Image Text:## Educational Content: Free Body Diagram and Forces
### Free Body Diagram Explanation
1. **Diagram Instructions:**
- Construct the free-body diagram.
1. Place the tail of the vectors within the confines of the mass.
2. Orient the vectors by dragging the heads in the proper direction.
- Note: The angles may be within ±15°, the magnitudes are not considered, and the vectors do not need to be centered on the mass.
2. **Diagram Details:**
- The diagram is a vector representation centered around a box, symbolizing the mass.
- Key Forces:
- **N** (Normal Force): Points upwards at 90°.
- **\(F_L\)** (Force to the Left): Arrows point left with an angle of 179.87° from the right.
- **\(F_R\)** (Force to the Right): Arrows point right at a slight angle of 0.04°.
- **\(mg\)** (Gravitational Force): Points directly downward at 270°.
- **f** (Friction): Not depicted separately but should be considered in force calculations.
### Problem Context and Analysis
Suppose two children push horizontally, but in exactly opposite directions, on a third child in a wagon. The first child exerts a force \(F_L\) of 65.0 N, the second a force \(F_R\) of 96.0 N. Friction \(f\) is 13.0 N, and the mass of the third child plus the wagon is 26.0 kg.
#### Think & Prepare
1. **Direction of Forces:**
- The forces applied by the two children are in opposition.
- Consider how friction acts in the context of the motion.
2. **Net Force Analysis:**
- Determine if friction acts to add to or subtract from the total net force.
- Analyze the resultant motion based on force interactions.
This explanation will help you understand the balance of forces and how vector components influence physical systems.
Expert Solution
Step 1: Determine the given variables
Step by step
Solved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology …
Physics
ISBN:
9781305116399
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations…
Physics
ISBN:
9781133939146
Author:
Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:
9781938168277
Author:
William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:
OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern …
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553292
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:
9781337553278
Author:
Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:
Cengage Learning