
Estimate the coordinates of the points given in graph.
Given information:
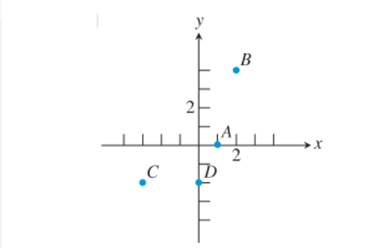
The given graph is:
Formula used:
- In a graph both the axes are marked with bars with equal length.
- The y coordinate of point on x -axis is 0.
- The x coordinate of point on y -axis is 0.
- The right side of x axis from the center is of positive points, and left is of negative.
- The above side of y axis from the center is of positive points, and downward side is of negative.
Calculation:
To estimate the coordinates of points, A, B, C and D note that both the axes( x and y ) in graph are divided equally with bars.
Since the second bar in x axis is marked 2, i.e. first should be 1 and second is 2, third is 3, and so on, similarly for y axis second is marked 2, i.e. first should be 1 and second is 2, third is 3, and so on.
Since, point A is on x -axis, i.e. the y coordinate of point A is 0 and it is on first bar to the right(i.e. positive), i.e. it’s x coordinate is 1. Thus, the coordinate of point A is (1, 0).
Similarly, for point B note that:
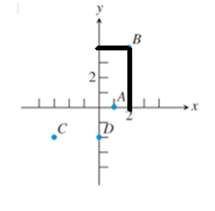
This point is along 2 bar to the right hand side from center on x- axis and 4 bars to the upper side from the center on y- axis, and since each bar is of 1 unit i.e. it’s coordinate is (2, 4).
Similarly, for point C note that
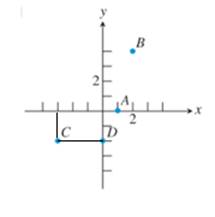
Note that it is corresponding to the 3 bars to the left side of the x -axis from the center and 2 bars down from the center on y- axis, i.e. it’s coordinates are in negative and are:
Now D is on y -axis thus it’s x coordinate of point on y -axis is 0, and it is 2 bars down from the center on y- axis, i.e. y-coordinate is negative.
Thus, coordinate of D is:
Thus, coordinates of given points are:
Chapter P Solutions
PRECALCULUS:...COMMON CORE ED.-W/ACCESS
- Find the Soultion to the following dy differential equation using Fourier in transforms: = , хуо, ухо according to the terms: lim u(x,y) = 0 x18 lim 4x (x,y) = 0 x14 2 u (x, 0) = =\u(o,y) = -y لوarrow_forwardCan you solve question 3,4,5 and 6 for this questionarrow_forwardwater at a rate of 2 m³/min. of the water height in this tank? 16) A box with a square base and an open top must have a volume of 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the box that will minimize the amount of material used (the surface area). 17) A farmer wishes toarrow_forward
- #14 Sand pours from a chute and forms a conical pile whose height is always equal to its base diameter. The height o the pile increases at a rate of 5 feet/hour. Find the rate of change of the volume of the sand in the conical pile when the height of the pile is 4 feet.arrow_forward(d)(65in(x)-5 cos(x) dx mins by 5x-2x² 3x+1 dx -dx 20 Evaluate each the following indefinite integralsarrow_forward19 Evaluate each the following definite integrals: a) લ b) (+3) 6) (2-2)(+33) dxarrow_forward
- #11 If a snowball melts so its surface area decreases at a rate of 1cm²/min, find the rate at which the diameter decreases when the diameter is 6 cm.arrow_forwardUse Deritivitve of the inverse to solve thisarrow_forwardEvaluate the following Limits: e6x-1 Lim +0Sin3x 7x-5x2 2x-1+ Cos 4x +6 c) Lim b) Lim + x³-x2 X-0 1-e' 4x d) Lim 6x²-3 X+0 6x+2x² Find the derivatives of the following functions using the Limit definition of derivativearrow_forward
- 15A cylindrical tank with radius 8 m is being filled with water at a rate of 2 m³/min. What is the rate of change of the water height in this tank? 6)A box with a square base and an open top must box that will minimiarrow_forward#12 The radius of a sphere increases at a rate of 3 in/sec. How fast is the volume increasing when the diameter is 24arrow_forward84 256 cubic inches. Find the dimensions of the of material used (the surface area). A farmer wishes to enclose a rectangular plot using 200 m of fencing material. One side of the land borders a river and does not need fencing. What is the largest area that can be enclosed? For the function y=x³-3x²-1, use derivatives to: 3 b) 2x - 6x2 (a) determine the intarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





