
(a)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:
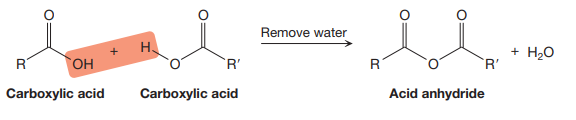
If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic anhydride in which the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(b)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule that corresponds to the given IUPAC name is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are the same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydrides are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
(c)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
(d)
Interpretation:
The structure of the molecule is to be drawn that corresponds to the given IUPAC name.
Concept introduction:
The rules for naming acid anhydrides are derived from the fact that an acid anhydride can be produced from two carboxylic acids in the dehydration reaction as shown below:

If the two R and R’ groups attached to the acid anhydride are same, then the anhydride is symmetrical, but if they are different, the acid anhydride is unsymmetrical.
Symmetrical anhydride are named according to general form alkanoic anhydride where the alkanoic portion corresponds to the specific carboxylic acid that could undergo dehydration to produce the anhydride.
Unsymmetrical anhydrides are named according to the general form alkanoic alkanoic anhydride, where each alkanoic portion corresponds to different carboxylic acids that would be required to produce the anhydride. The two carboxylic acids follow the alphabetical order.
Substituents attached to the carbon chain of any carboxylic acid portion are written as prefix in the IUPAC name.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter F Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solution and correct answerarrow_forwardH R Part: 1/2 :CI: is a/an electrophile Part 2 of 2 Draw the skeletal structure of the product(s) for the Lewis acid-base reaction. Include lone pairs and formal charges (if applicable) on the structures. 4-7: H ö- H Skip Part Check X :C1: $ % L Fi Click and drag to start drawing a structure. MacBook Pro & ㅁ x G 0: P Add or increase positive formal cha Save For Later Submit ©2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centearrow_forwardDraw the friedel-crafts acylation mechanism of m-Xylenearrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward1. Base on this experimental results, how do you know that the product which you are turning in is methyl 3-nitrobenzoate(meta substituted product ) rather than either of the other two products? 2. What observation suggests that at least a small amount of one or both of the other two isomers are in the mother liquor?arrow_forwardExplain Huckel's rule.arrow_forward
- here is my question can u help me please!arrow_forwardSo I need help with understanding how to solve these types of problems. I'm very confused on how to do them and what it is exactly, bonds and so forth that I'm drawing. Can you please help me with this and thank you very much!arrow_forwardSo I need help with this problem, can you help me please and thank you!arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

