
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
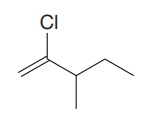
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the double bond has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentene. The root is numbered such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the lowest numbers. Thus, the chain should be numbered from the left-terminal carbon atom. The carbon carbon double bond is present between C1 and C2 carbon atoms, and thus, the lower locator number - 1 is added immediately before the suffix, ene. Thus, the complete root name for the molecule is:
The numbering system is shown below:
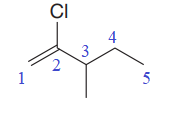
One chlorine atom and one methyl group is attached at C2 and C3 carbon atoms of the root. Out of chloro and methyl, chloro comes first alphabetically, hence it is written before the methyl.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
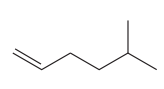
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the double bond has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is hexene. The root is numbered such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the lowest numbers. Thus, the chain should be numbered from the left-terminal carbon atom. The carbon-carbon double bond is present between C1 and C2 carbon atoms, and thus, the lower locator number -1 is added immediately before the suffix, ene. Thus, the complete root name for the molecule is:
The numbering system is shown below:
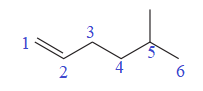
One methyl group is attached at the C5 carbon atom to the root.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
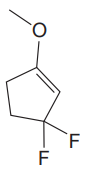
In this molecule, the largest carbon ring containing the double bond has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is cyclopentene. For a ring, the carbon atoms of the double bond are always assigned as C1 and C2. The ring is then numbered clockwise so as to give the remaining substituents the next lowest possible locator numbers. The numbering system is shown below:
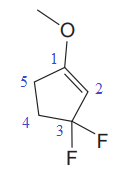
At C1, C3 and C3 carbon atoms of the ring, one methoxy group and two fluorine atoms are attached. The substituents will be named according to the alphabetical order.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
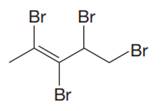
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the double bond has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentene. The root is numbered such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the lowest numbers. Thus, the chain should be numbered from the left-terminal carbon atom. The carbon-carbon double bond is present between C2 and C3 carbon atoms, and thus, the lower locator number - 2 is added immediately before the suffix, ene. Thus, the complete root name for the molecule is:
The numbering system is shown below:
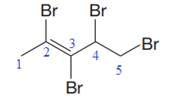
Four bromine atoms are attached at C2, C3, C4, and C5 carbon atoms to the root. Thus, prefix ‘tetra’ is used immediately before the name of the substituent.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
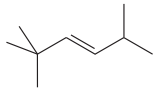
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the double bond has six carbon atoms. Hence, the root is hexene. The root is numbered such that the double bonded carbon atoms get the lowest numbers. If there is a tie, the chain is numbered such that the substituents get the lowest locator numbers. Thus, the chain should be numbered from the left-terminal carbon atom. The carbon-carbon double bond is present between C3 and C4 carbon atoms, and thus, the lower locator number - 3 is added immediately before the suffix, ene. Thus, the complete root name for the molecule is:
The numbering system is shown below:
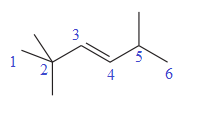
Three methyl groups are attached at C2, C2, and C5 carbon atoms to the root. Thus, prefix ‘tri’ is used immediately before the name of the substituent.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
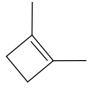
In this molecule, the largest carbon ring containing the double bond has four carbon atoms. Hence, the root is cyclobutene. For a ring, the carbon atoms of the double bond are always assigned as C1 and C2. The ring is then numbered clockwise so as to give the remaining substituents the next lowest possible locator numbers. The numbering system is shown below:
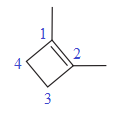
At C1 and C2 carbon atoms of the ring, two methyl groups are attached respectively. Thus, prefix ‘di’ should be added immediately before the name of the substituent.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(g)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given molecule is:
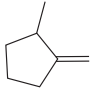
In this molecule, the double bond cannot be a part of the longest carbon chain or the largest carbon ring. Thus, in this case, the double bond will be a substituent to the parent ring, cyclopentane. The numbering system is shown below:
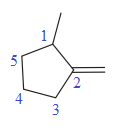
At C1 carbon atom, there is one methyl group attached to the root. At C2 carbon atom, the double bond is attached which is named as methylene.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
(h)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name for the given compound is to be determined.
Concept introduction:
In case of molecules containing a
If the root is a chain, numbering begins from that end of the chain which encounters the
The carbon atoms having a double or triple bond between them are always assigned C1 and C2, if the root is a ring. This must be done such that the locator numbers for the substituents are minimized. The lower of the two locator numbers for the
Answer to Problem B.27P
The IUPAC name for the given compound is:
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is:
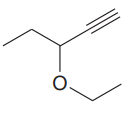
In this molecule, the longest carbon chain containing the triple bond has five carbon atoms. Hence, the root is pentyne. The root is numbered such that the triple-bonded carbon atoms get the lowest numbers. Thus, the chain should be numbered from the top right carbon atom. The carbon-carbon triple bond is present between C1 and C2 carbon atoms, and thus, the lower locator number - 1 is added immediately before the suffix, yne. Thus, the complete root name for the molecule is
The numbering system is shown below:
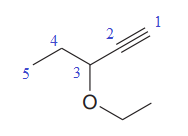
One methoxy group is attached at the C3 carbon atom to the root.
Thus, the IUPAC name of the compound is:
The IUPAC name of the compound is written according to the rules for nomenclature.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter B Solutions
Get Ready for Organic Chemistry
- Nonearrow_forwardIn the phase diagram of steel (two components Fe and C), region A is the gamma austenite solid and region B contains the gamma solid and liquid. Indicate the degrees of freedom that the fields A and B have,arrow_forwardFor a condensed binary system in equilibrium at constant pressure, indicate the maximum number of phases that can exist.arrow_forward
- Part V. Label ad match the carbons in compounds Jane and Diane w/ the corresponding peak no. in the Spectra (Note: use the given peak no. To label the carbons, other peak no are intentionally omitted) 7 4 2 -0.13 -0.12 -0.11 -0.10 -0.08 8 CI Jane 1 -0.09 5 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 -8 90 f1 (ppm) 11 8 172.4 172.0 f1 (ppr HO CI NH Diane 7 3 11 80 80 -80 -R 70 60 60 2 5 -8 50 40 8. 170 160 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 -0 80 70 20 f1 (ppm) 15 30 -20 20 -60 60 -0.07 -0.06 -0.05 -0.04 -0.03 -0.02 -0.01 -0.00 -0.01 10 -0.17 16 15 56 16 -0.16 -0.15 -0.14 -0.13 -0.12 -0.11 -0.10 -0.09 -0.08 -0.07 -0.06 -0.05 -0.04 17.8 17.6 17.4 17.2 17.0 f1 (ppm) -0.03 -0.02 550 106 40 30 20 20 -0.01 -0.00 F-0.01 10 0arrow_forwardConsider the reaction of 2-methylpropane with a halogen. With which halogen will the product be almost exclusively 2-halo-2-methylpropane? 1. F2 2. Cl2 3. Br2 4. I2arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardn Feb 3 A T + 4. (2 pts) Draw the structure of the major component of the Limonene isolated. Explain how you confirmed the structure. 5. (2 pts) Draw the fragment corresponding to the base peak in the Mass spectrum of Limonene. 6. (1 pts) Predict the 1H NMR spectral data of R-Limonene. Proton NMR: 5.3 pon multiplet (H Ringarrow_forwardPart VI. Ca H 10 O is the molecular formula of compound Tom and gives the in the table below. Give a possible structure for compound Tom. 13C Signals summarized C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 13C shift (ppm) 23.5 27.0 33.0 35.8 127 162 205 DEPT-90 + DEPT-135 + +arrow_forward
- 2. Using the following data to calculate the value of AvapH o of water at 298K. AvapH o of water at 373K is 40.7 kJ/mol; molar heat capacity of liquid water at constant pressure is 75.2J mol-1 K-1 and molar heat capacity of water vapor at constant pressure is 33.6 J mol-1 K-1.arrow_forwardPart VII. Below are the 'HNMR 13 3 C-NMR, COSY 2D- NMR, and HSQC 20-NMR (Similar with HETCOR but axes are reversed) spectra of an organic compound with molecular formula C6H13 O. Assign chemical shift values to the H and c atoms of the compound. Find the structure. Show complete solutions. Predicted 1H NMR Spectrum ли 4.7 4.6 4.5 4.4 4.3 4.2 4.1 4.0 3.9 3.8 3.7 3.6 3.5 3.4 3.3 3.2 3.1 3.0 2.9 2.8 2.7 2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6 1.5 1.4 1.3 1.2 1.1 1.0 0.9 0.8 f1 (ppm)arrow_forward3. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-pentene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: 4. Draw the expanded structural formula, the condensed structural formula, and the skeletal structural formula for 2-methyl-3-heptene. expanded structure: Condensed structure: Skeletal formula: following structurearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





