
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780321795465
Author: Michael Sullivan, Michael III Sullivan
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter A.2, Problem 43AYU
To determine
To find: The missing length and the missing angles if the triangles in each pair are similar.
Expert Solution & Answer
Answer to Problem 43AYU
units, .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
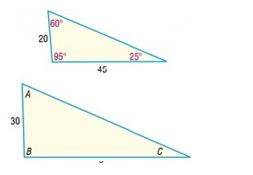
Calculation:
Because the triangles are similar, corresponding angles are equal. So . Also, the corresponding sides are proportional. That is, . Solve this equation for .
Multiply both sides by .
units.
Chapter A.2 Solutions
Precalculus Enhanced with Graphing Utilities
Ch. A.2 - Prob. 1AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 2AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 3AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 4AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 5AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 6AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 7AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 8AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 9AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 10AYU
Ch. A.2 - Prob. 11AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 12AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 13AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 14AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 15AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 16AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 17AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 18AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 19AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 20AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 21AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 22AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 23AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 24AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 25AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 26AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 27AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 28AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 29AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 30AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 31AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 32AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 33AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 34AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 35AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 36AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 37AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 38AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 39AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 40AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 41AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 42AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 43AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 44AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 45AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 46AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 47AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 48AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 49AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 50AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 51AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 52AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 53AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 54AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 55AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 56AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 57AYUCh. A.2 - Prob. 58AYU
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In Exercises 1–10, find the Taylor polynomials of orders 0, 1, 2, and 3 generated by f at a.
1.
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Stating the Null and Alternative Hypotheses In Exercises 25–30, write the claim as a mathematical statement. St...
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
For a population containing N=902 individual, what code number would you assign for a. the first person on the ...
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
In Exercises 11–14, use the population of {34, 36, 41, 51} of the amounts of caffeine (mg / 12 oz ) in Coca-Col...
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
The table by using the given graph of h.
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Fill in each blank so that the resulting statement is true.
1. A combination of numbers, variables, and opera...
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- DO these math problems without ai, show the solutions as well. and how you solved it. and could you do it with in the time spandarrow_forwardThe Cartesian coordinates of a point are given. (a) (-8, 8) (i) Find polar coordinates (r, 0) of the point, where r > 0 and 0 ≤ 0 0 and 0 ≤ 0 < 2π. (1, 0) = (r. = ([ (ii) Find polar coordinates (r, 8) of the point, where r < 0 and 0 ≤ 0 < 2π. (5, 6) = =([arrow_forwardThe Cartesian coordinates of a point are given. (a) (4,-4) (i) Find polar coordinates (r, e) of the point, where r > 0 and 0 0 and 0 < 0 < 2π. (r, 6) = X 7 (ii) Find polar coordinates (r, 8) of the point, where r < 0 and 0 0 < 2π. (r, 0) = Xarrow_forward
- r>0 (r, 0) = T 0 and one with r 0 2 (c) (9,-17) 3 (r, 8) (r, 8) r> 0 r<0 (r, 0) = (r, 8) = X X X x x Warrow_forward74. Geometry of implicit differentiation Suppose x and y are related 0. Interpret the solution of this equa- by the equation F(x, y) = tion as the set of points (x, y) that lie on the intersection of the F(x, y) with the xy-plane (z = 0). surface Z = a. Make a sketch of a surface and its intersection with the xy-plane. Give a geometric interpretation of the result that dy dx = Fx F χ y b. Explain geometrically what happens at points where F = 0. yarrow_forwardExample 3.2. Solve the following boundary value problem by ADM (Adomian decomposition) method with the boundary conditions მი მი z- = 2x²+3 дг Əz w(x, 0) = x² - 3x, θω (x, 0) = i(2x+3). ayarrow_forward
- 6. A particle moves according to a law of motion s(t) = t3-12t2 + 36t, where t is measured in seconds and s is in feet. (a) What is the velocity at time t? (b) What is the velocity after 3 s? (c) When is the particle at rest? (d) When is the particle moving in the positive direction? (e) What is the acceleration at time t? (f) What is the acceleration after 3 s?arrow_forwardConstruct a table and find the indicated limit. √√x+2 If h(x) = then find lim h(x). X-8 X-8 Complete the table below. X 7.9 h(x) 7.99 7.999 8.001 8.01 8.1 (Type integers or decimals rounded to four decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the graph to find the following limits. (a) lim f(x) (b) lim f(x) X-1 x→1 (a) Find lim f(x) or state that it does not exist. Select the correct choice X-1 below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. OA. lim f(x) = X-1 (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) OB. The limit does not exist. Qarrow_forward
- Officials in a certain region tend to raise the sales tax in years in which the state faces a budget deficit and then cut the tax when the state has a surplus. The graph shows the region's sales tax in recent years. Let T(x) represent the sales tax per dollar spent in year x. Find the desired limits and values, if they exist. Note that '01 represents 2001. Complete parts (a) through (e). Tax (in cents) T(X)4 8.5 8- OA. lim T(x)= cent(s) X-2007 (Type an integer or a decimal.) OB. The limit does not exist and is neither ∞ nor - ∞. Garrow_forwardDecide from the graph whether each limit exists. If a limit exists, estimate its value. (a) lim F(x) X➡-7 (b) lim F(x) X-2 (a) What is the value of the limit? Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box within your choice. OA. lim F(x) = X-7 (Round to the nearest integer as needed.) OB. The limit does not exist. 17 Garrow_forwardFin lir X- a= (Us -10 OT Af(x) -10- 10arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning