
Mary Williams, owner of Williams Products, is evaluating whether to introduce a new product line. After thinking through the production process and the costs of raw materials and new equipment, Williams estimates the variable costs of each unit produced and sold at $6 and the fixed costs per year at $60,000.
- If the selling price is set at $18 each, how many unit must be produced and sold for Williams to break even? Use both graphic and algebraic approaches to get your answer.
- Williams
forecasts sales of 10,000 units for the first year if the selling price is set at $14 each. What would be the total contribution to profits from this new product during the first year? - If the selling price is set at $12.50, Williams forecasts that first-year sales would increase to 15,000 units. Which pricing strategy ($14.00 or $12.50) would result in the greater total contribution to profits?
- What oilier considerations would be crucial to the final decision about making and marketing the new product?
a.
To calculate: The break even quantity using both graphic and algebraic approaches.
Concept Introduction: Break-even point is explained as a point where a company is earning no profits and incurring no losses reflecting that total cost is equivalent to total income.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Variable costs: $6 per unit
Fixed costs: $60,000
Selling price: $18 per unit
Break-even quantity: ?
Calculation of break even quantity:
Hence, the break even quantity is 5,000 units.
Graphic approach for calculating break even quantity:
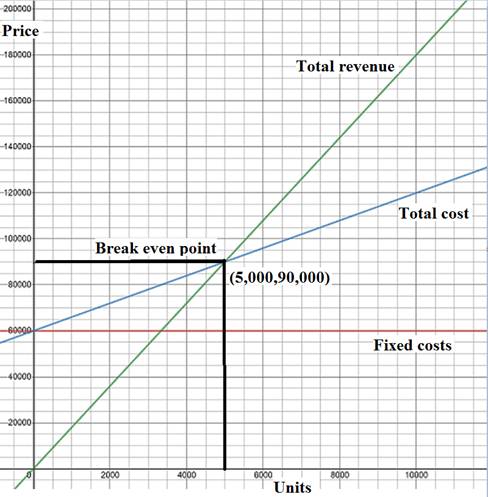
Fig (1)
b.
To calculate: The total contribution to profits from this new product.
Concept Introduction: Profit is explained as surplus of total income over total costs.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Forecasted sales: 10,000 units
Selling price: $14 per unit
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
Therefore, the total contribution from the new product is $20,000.
c.
To calculate: The total contribution to profits from this new product if selling price is $12.50.
Concept Introduction: Profit is explained as surplus of total income over total costs.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Forecasted sales: 15,000 units
Selling price: $12.50 per unit
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
Therefore, the total contribution from the new product is $37,500.
If selling price is $14 and forecasted sales are 15,000 units, then,
Calculation of total contribution to the profits:
It can be concluded that when selling price is $14 then it can get a greater total contribution to Company W.
d.
To identify: The other considerations that would be crucial for final decision making for the new product.
Concept Introduction: Decision making is a process in which members of an organization select a particular course of action in response to both problem and opportunity. The objective of decision making is to gain a maximum and profitable result.
Explanation of Solution
Other considerations that would be crucial for final decision making of new product are:
- Company W can identify and evidently state the problems.
- Various other alternatives should be evaluated and for the same information should be collected.
Decisions are taken by organizations on the basis these procedures that are generally performed: break even analysis, decision tree, preference matrix and preference decision tree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter A Solutions
MyLab Operations Management with Pearson eText -- Access Card -- for Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Microeconomics
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
Intermediate Accounting (2nd Edition)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
- I need answer typing clear urjent no chatgpt used pls i will give 5 Upvotes.arrow_forwardassume that you are police commander which leads and supervises the department’s internal affairs division. Your goal is to reduce civilian complainants against personnel in the department. Using what you have learned and at least three scholarly sources, document two changes you see the department can implement, whether it be training, planning, mitigating, and resolving, to improve police/community relations.arrow_forwardNess Engineering is a private limited company mainly engaged in the continuous production and assembly of domestic products. The annual turnover is $900,000,000. The largest area of expenditure is raw materials and components where the annual spend is approximately $450,000,000. The Managing Director, Bill, considers that profit margins are too small and has asked you to suggest how profitability might be increased. Bill suggests that this might be done by appointing additional sales staff and by an advertising campaign, which would, hopefully, increase turnover and thereby reduce overhead cost per item. You find that purchasing is little more than a post-office function. Specifications are received from the design or user departments and sent either to supplies designated by the directors or to the supplier providing the cheapest quotation. The company does, in fact, deal with many suppliers and issues many orders for low-cost items. All purchasing is done by manual means. None of the…arrow_forward
- The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. 1. What is the probability that he wandered into Abu Ilan? 2. What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forward2-22 The lost Israeli soldier mentioned in Problem 2-21 decides to rest for a few minutes before entering the desert oasis he has just found. Closing his eyes, he dozes off for 15 minutes, wakes, and walks toward the center of the oasis. The first person he spots this time he again recognizes as a Bedouin. What is the posterior probability that he is in El Kamin?*Note* 2-21 The oasis outpost of Abu Ilan, in the heart of the Negev desert, has a population of 20 Bedouin tribesmen and 20 Farima tribesmen. El Kamin, a nearby oasis, has a population of 32 Bedouins and 8 Farima. A lost Israeli soldier, accidentally separated from his army unit, is wandering through the desert and arrives at the edge of one of the oases. The soldier has no idea which oasis he has found, but the first person he spots at a distance is a Bedouin. What is the probability that he has wandered into Abu Ilan? What is the probability that he is in El Kamin?arrow_forwardHello, please make an excel of this. Show all the cells thanks. some replied with a paper answer thank you I just cant understand the way the did it. Can someone show me all screenshots o fthis problem solved and in excel? i need to solver too for the constraints. I seen multiple times across other platforms that one of the chairs optimal solutions is 0 but they both have to be higher than 1 The Heinrich Company manufactures two types of plastic hangerracks (Foldaways and Straightaways) especially suited for mountingnear clothes dryers. Because permanent press clothing must be hungon hangers immediately after removal from the dryer, these items havebeen especially popular. However, there is some concern that thePreppie movement (popularized by its own handbook) will extinguishpolyester clothing; Heinrich is terribly interested in doing the best withthe resources it has while its products are still in demand. The firsttype of hanger rack, the Foldaway, requires 10 ounces of…arrow_forward
- Review the Profit Ratio by Product chart again. What information is uncovered when the data is less aggregated than the data in Profit Ratio by Category chart?arrow_forwardWhat is the correlation between Measure A and Measure B in this example?arrow_forward1) View the video ON Unveils ‘Lightspray’ Technology (4.55 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), and The Secret of Lightspray (8.27 mins, Ctrl+Click in the link), answer the following questions: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wjmeaC-wlZs a) What is new about the design of ON’s shoes? b) How will ON’s new manufacturing technique affect location planning for footwear firms? c) How does ON focus on it sustainability strategy? Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs for each of the questions. 2) Unimed Hospital currently processes patient admissions through three admitting clerks who are set up to work in series, with respective reliabilities of 0.96, 0.95, and 0.90 (see figure below). a) Find the reliability of the current admission process. Due to rising patient complaints, the hospital administrator, Chimeg Ganbaatar, has decided to improve the reliability of the admission process by providing backup clerks for two of the…arrow_forward
- + < Question 21 of 39 What is the correct common name for the compound shown here? 2-methoxyprop ane | 3-1-2- n-tert- iso sec- eth prop meth methoxy propoxy ethoxy yl acid ether ester ane Reset ☑ Submitarrow_forward(25 Marks) Discuss how you would "reset the store estate" to remain competitive and relevant in the market?arrow_forwardHello, please make an excel of this. Show all the cells thanks The Heinrich Company manufactures two types of plastic hangerracks (Foldaways and Straightaways) especially suited for mountingnear clothes dryers. Because permanent press clothing must be hungon hangers immediately after removal from the dryer, these items havebeen especially popular. However, there is some concern that thePreppie movement (popularized by its own handbook) will extinguishpolyester clothing; Heinrich is terribly interested in doing the best withthe resources it has while its products are still in demand. The firsttype of hanger rack, the Foldaway, requires 10 ounces of plasticmaterial and 0.3 hours of labor. Plastic costs Heinrich 10 cents anounce; labor costs Heinrich $20 per hour. The second type of hangerrack, the Straightaway, requires 15 ounces of plastic and 0.175 hoursof labor. The prices of these resources are the same as those for theFoldaway. Under current market conditions, Heinrich can sell…arrow_forward
- MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
 Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033777Author:Louis E. Boone, David L. KurtzPublisher:Cengage Learning




