
a)
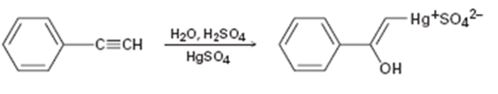
Interpretation:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of phenylacetylene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the first step attack of the π electrons of the triple bond on the electrophilic Hg2+ ion takes place to yield a mercury containing vinylic carbocation intermediate. In the second step nucleophilic attack of water takes place on the carbocation. A new C-O bond is formed leading to the formation of a protonated mercury containing enol. In the third step water abstracts a proton from the protonated enol to yield the organomercury intermediate.
To draw:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of ethynylbenzene.
b)
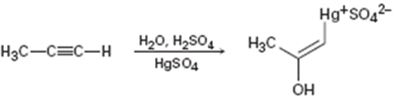
Interpretation:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of propyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the first step attack of the π electrons of the triple bond on the electrophilic Hg2+ ion takes place to yield a mercury containing vinylic carbocation intermediate. In the second step nucleophilic attack of water takes place on the carbocation. A new C-O bond is formed leading to the formation of a protonated mercury containing enol. In the third step water abstracts a proton from the protonated enol to yield the organomercury intermediate.
To draw:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of propyne.
c)
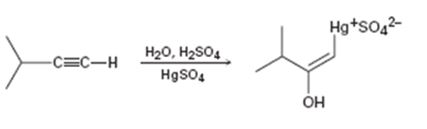
Interpretation:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of 3-methyl-1-butyne is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
In the first step attack of the π electrons of the triple bond on the electrophilic Hg2+ ion takes place to yield a mercury containing vinylic carbocation intermediate. In the second step nucleophilic attack of water takes place on the carbocation. A new C-O bond is formed leading to the formation of a protonated mercury containing enol. In the third step water abstracts a proton from the protonated enol to yield the organomercury intermediate.
To draw:
The electron pushing mechanism for the formation of the organo-mercury intermediate obtained during the mercury catalyzed hydration of 3-methyl-1-butyne.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


