
(a)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(b)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(c)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
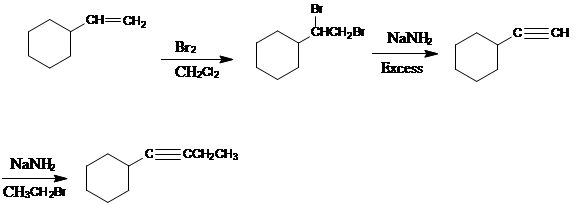 Adding
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
(d)
Interpretation:
A multi-step synthesis has to be designed for the given conversion.
Concept Introduction:
Target molecule is nothing but the desired product.
Adding
The elimination reaction should be carried out under SN2 condition i.e. with strong nucleophile. So there will be no compensating substitution reaction.
The bulky base is used in the elimination reaction to maximize the amount of elimination product.
To prepare cyclic ether, the alkyl halide and alcohol must be a part of the same molecule.
Addition of water to the given starting material creates bifunctional compound.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-W/S.G+SOLN.MANUAL
- Pt + H₂ Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the Tools (for bonds), Atoms, and Advanced Templ 9 2 0 © 120arrow_forwardComplete boxes in the flow chart. Draw the structure of the organic compound foundin each layer after adding 3M NaOH and extraction. Make sure to include any charges. Provide explanation on answers.arrow_forward== Vid4Q2 Unanswered ☑ Provide IUPAC name of product in the reaction below A 3,4-dimethylcyclohexene B 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane C 1,2-dimethylcyclohexene D 3,4-dimethylcyclohexane H₂ Pdarrow_forward
- 5. Use the MS data to answer the questions on the next page. 14.0 1.4 15.0 8.1 100- MS-IW-5644 26.0 2.8 27.0 6.7 28.0 1.8 29.0 80 4.4 38.0 1.0 39.0 1.5 41.0 1.2 42.0 11.2 43.0 100.0 44.0 4.3 79.0 1.9 80.0 2.6 Relative Intensity 40 81.0 1.9 82.0 2.5 93.0 8.7 20- 95.0 8.2 121.0 2.0 123.0 2.0 136.0 11.8 0 138.0 11.5 20 40 8. 60 a. Br - 0 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 m/z Identify the m/z of the base peak and molecular ion. 2 b. Draw structures for each of the following fragments (include electrons and charges): 43.0, 93.0, 95.0, 136.0, and 138.0 m/z. C. Draw a reasonable a-fragmentation mechanism for the fragmentation of the molecular ion to fragment 43.0 m/z. Be sure to include all electrons and formal charges. 6. Using the values provided in Appendix E of your lab manual, calculate the monoisotopic mass for the pyridinium ion (CsH6N) and show your work.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardStereochemistry: Three possible answers- diastereomers, enantiomers OH CH₂OH I -c=0 21108 1101 41745 HOR CH₂OH IL Но CH₂OH TIL a. Compounds I and III have this relationship with each other: enantiomers b. Compounds II and IV have this relationship with each other: c. Compounds I and II have this relationship with each other: d. *Draw one structure that is a stereoisomer of II, but neither a diastereomer nor an enantiomer. (more than one correct answer)arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
