
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
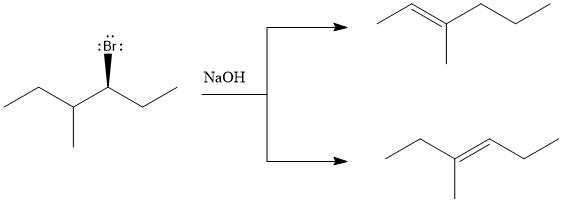
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
The first and second alkene product is highly substituted than the third alkene product. Therefore, the first and second alkene products are more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(b)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
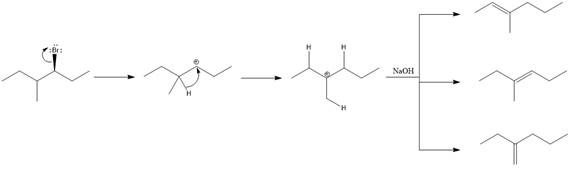
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(c)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
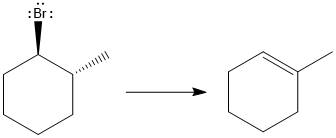
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable, i.e., highly alkyl substituted, alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
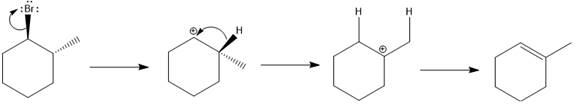
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(d)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
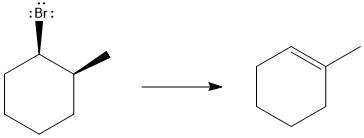
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
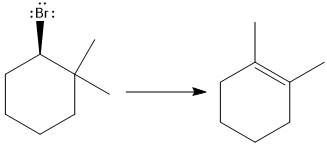
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
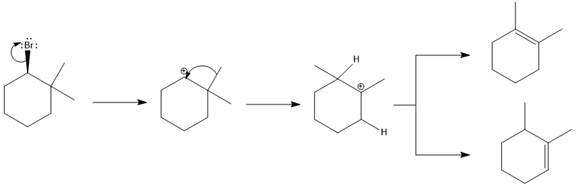
The first alkene product is highly substituted than the second alkene product. Therefore, the first alkene product is more stable. The base in this reaction is OH, which is not bulky, so the first and second products are the major products.

From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
(e)
Interpretation:
For the given substrate, when
Concept introduction:
As the number of alkyl groups on the carbon bonded to the leaving group increases, the rate of E1 reaction increases. Each additional alkyl group, which is electron donating, stabilizes the carbocation intermediate produced and thus helps the leaving group leave. The
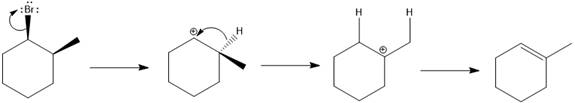
Answer to Problem 9.69P
The major E1 product for the given reaction is shown below:
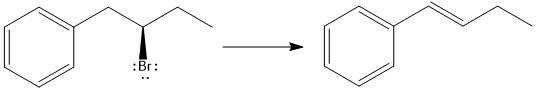
Explanation of Solution
Elimination usually takes place so as to produce the most stable that means highly alkyl substituted alkene.
The possible E1 products are obtained by eliminating the leaving group and a proton on the carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the leaving group. Here the
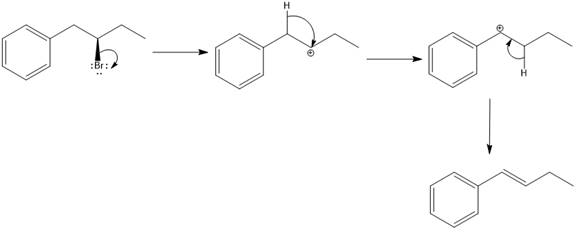
From the stability of the product formed, the major E1 product is drawn.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
ORG CHEM W/ EBOOK & SW5 + STUDY GUIDE
- 3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardPlease provide a synthesis for the Ester using proponoic acid, thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help with the curved arrow mechanism of this reaction, thank youarrow_forward
- Concentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 Question: Determine the regression equation (a and b coefficients) from first principlesarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forwardNeed help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forward
- Draw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forwardE Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
