
(a)
Interpretation:
The pouring temperature in the cooling curve needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The cooling curve represents a change in temperature as a function of time. Cooling curve is of two types: Curve for metals having no inoculation and curve for metals with inoculation.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Pouring temperature is
Explanation of Solution
The figure shows the cooling curve for casting.
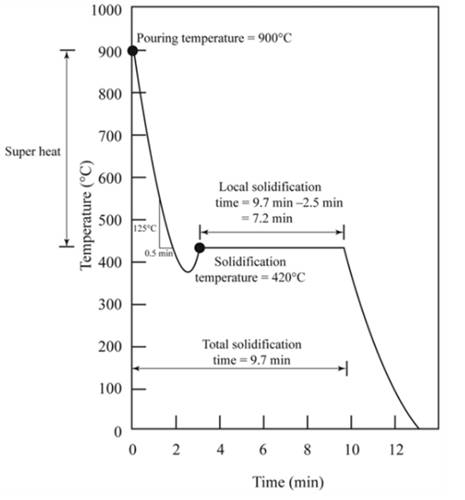
Pouring temperature is the temperature of the liquid at which liquid is added in the mold.Hence from the graph shown, temperature
(b)
Interpretation:
Solidification temperature of the metal in cooling curves needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from molten metal during cooling.The temperature at which molten metal starts forming crystal is solidification temperature.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Solidification temperature of metal is
Explanation of Solution
Solidification temperature at which solidification starts.Hence from the graph, solidification temperature is
Or,
(c)
Interpretation:
The superheat temperature of the metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Difference between pouring temperature and freezing temperature is known as superheating.
Pouring temperature is the temperature at which metal is introduced in a casting.
Freezing temperature is the temperature at which metal solidifies.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Superheat temperature is
Explanation of Solution
Superheat is a temperature between pouring temperature and freezing temperature.
Pouring temperature,
Freezing temperature,
Thus,
(d)
Interpretation:
At the starting of the solidification, thecooling rate needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Cooling curves are of two types of metal- for metal with no inoculation and for metal with inoculation.
Cooling curve represents different temperatures.
The cooling curve shows different regions according to change in temperature at a specific time.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Cooling rate of metal is
Explanation of Solution
The cooling rate is the rate of change in temperature with respect to time.
According to the graph,the slope of the curve from pouring temperature to freezing temperature shows the rate of cooling.
It is denoted by
Thus,
Cooling rate
(e)
Interpretation:
The total solidification time needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from molten metal during cooling. The time required to form crystal structure from molten metal is solidification time.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Total solidification time of metal is
Explanation of Solution
The time required to remove specific heat and latent heat of fusion during cooling of metal is total solidification time.It is the time between the pouring of metal to the completion of solidification.
From the graph,
(f)
Interpretation:
The local solidification time of metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from molten metal during cooling. The time required to form crystal structure from molten metal is solidification time.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Local solidification time of metal is 7.2 min.
Explanation of Solution
The time required to remove latent heat of fusion is at specific casting location is local solidification time.
It is the time between the start of solidification and the end of solidification.
Hence from the graph,
(g)
Interpretation:
The identity of metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Cooling curves are of two types of metal- for metal with no inoculation and for metal with inoculation.
Cooling curve represents different temperatures.The cooling curve represents charge in temperature as a function of time.
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Probable metal should be Zinc.
Explanation of Solution
Given the cooling curve is for metal having well inoculation.For this metal, solidification starts at melting temperature.Solidification of the temperature of this metal is
Hence, the probable metal should be zinc.
(h)
Interpretation:
The mold constant of metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
As per Chvorinov's rule, solidification time is directly proportional to the square of volume- area ratio of cast metal.
Here,
Answer to Problem 9.61P
Mold constant is
Explanation of Solution
As per Chvorinov's rule,
Volume of casting can be calculated as follow:
Area of castingcan be calculated as follow:
Putting the value.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- please explain in detail. I am most confused about 3.2 and 3.3. thank youarrow_forwardCivil engineering quantiarrow_forwardProblem 1 (30 Points) Consider the following 2 scenarios. In scenario 1, a mass m slides on a cylindrical surface of radius R. In scenario 2, a mass m hangs at the end of a thin massless rod of length R. In both scenarios, there is no friction either on the surface (scenario 1), or at the pivot point of the pendulum (scenario 2). Also in both scenarios, there is one generalized coordinate, . R Scenario 1 R m R g Scenario 2 m HINT: In both scenarios, it is much easier to choose your datum for potential energy as the center of the bowl (scenario 1), or the pivot point of the pendulum (scenario 2). Part I a) Determine the Lagrangian for each system. DO NOT FIND THE EQUATIONS OF MOTION (5 points) b) What can you say about the systems based on the Lagrangian? (2 points) c) Solve for the equations of motion for both systems. (8 points) Part II Now, for scenario 1, introduce an additional coordinate and treat it as a nonholonomic system to determine the normal force acting on the mass. a)…arrow_forward
- Consider 0.65 kg of N2 at 300 K, 1 bar contained in a rigid tank connected by a valve to another rigid tank holding 0.3 kg of CO2 at 300 K, 1 bar. The valve is opened and gases are allowed to mix, achieving an equilibrium state at 290 K. Determine: (a) the volume of each tank, in m³. (b) the final pressure, in bar. (c) the magnitude of the heat transfer to or from the gases during the process, in kJ. (d) the entropy change of each gas and of the overall system, in kJ/K.arrow_forwardWhat are the two errors in my pseudocode?Module getAverage(Integer value1, Integer value2, Integer value3) Declare Integer average average = value1 + value2 + value3 / 3 Display average End Modulearrow_forwardWhere did I make an error in my pseudocode module???Code:Module main() Call raiseToPower(2, 1.5) End main Module raiseToPower(Real value, Integer power) Declare Real result Set result = value ^ power Display result End raiseToPowerarrow_forward
- Why does my pseudocode not perform what I asked? Don't know whats wrong with it.// This program asks the user to enter a value // between 1 and 10 and validates the input. Declare Integer value // Get a value from the user. Display "Enter a value between 1 and 10." Input value // Make sure the value is between 1 and 10. While value < 1 AND value > 10 Display "ERROR: The value must be between 1 and 10." Display "Enter a value between 1 and 10." Input value End Whilearrow_forwardWhat's wrong with my pseudocode? // The calcDiscountPrice function accepts an item’s price and // the discount percentage as arguments. It uses those // values to calculate and return the discounted price. Function Real calcDiscountPrice(Real price, Real percentage) // Calculate the discount. Declare Real discount = price * percentage // Subtract the discount from the price. Declare Real discountPrice = price – discount // Return the discount price. Return discount End Functionarrow_forwardNeed help converting my pseudocode to python, AND have a flowchart showing everything!The code: Function getScore() // Prompt the user to enter a test score Display "Enter a test score as a percentage (0-100): " Input score // Return the score entered by the user Return scoreEnd Function Function getGPAPoint(Integer score) // Determine GPA point based on the score If score >= 90 Then Return 4.0 Else If score >= 80 Then Return 3.0 Else If score >= 70 Then Return 2.0 Else If score >= 60 Then Return 1.0 Else Return 0.0 End IfEnd Function Function getAverage() // Initialize variables to store the sum of scores and GPA points totalScore = 0 totalGPA = 0.0 // Loop to collect 5 test scores For i = 1 to 5 Do score = getScore() // Call getScore function to get a test score totalScore = totalScore + score // Add score to totalScore gpaPoint = getGPAPoint(score) // Convert…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





