
(a)
Interpretation:
Pouring temperature in the cooling curve needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
The cooling curve represents a changein temperature as a function of time.
Cooling curves are of two types of metal- for metal with no inoculation and for metal with inoculation.
Cooling curve represents different temperatures.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
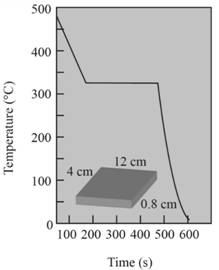
Pouring temperature is
Explanation of Solution
Pouring temperature is the temperature of the liquid at which it is added in the mold.
Hence from the graph shown, temperature is
(b)
Interpretation:
The solidification temperature of the metal in cooling curves needs to be determined
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from the molten metal during cooling.
The temperature at which molten metal starts forming crystal is solidification temperature.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Solidification temperature of metal is
Explanation of Solution
Solidification temperature at which the solidification starts.Hence from the graph, the solidification temperature is
Thus,
(c)
Interpretation:
The superheat temperature of the metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Difference between pouring temperature and freezing temperature is known as superheating.
Pouring temperature is the temperature at which metal is introduced in a casting.
Freezing temperature is the temperature at which metal solidifies.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Superheat temperature is
Explanation of Solution
Superheat is a temperature between pouring temperature and freezing temperature.
Pouring temperature,
Freezing temperature,
(d)
Interpretation:
The cooling rate at the starting of solidification needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Cooling curves are of two types of metal- for metal with no inoculation and for metal with inoculation.
Cooling curve represents different temperatures.
The cooling curve shows the different regions according to the change in temperature at a specific time.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Cooling rate of metal is
Explanation of Solution
The cooling rate is the rate of change in temperature with respect to time.
According to the graph,the slope of the curve from pouring temperature to freezing temperature shows the rate of cooling.
It is denoted by
Cooling rate
(e)
Interpretation:
The total solidification time needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from molten metal during cooling. The time required to form crystal structure from the molten metal is solidification time.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Total solidification time of metal is
Explanation of Solution
The time required to remove the specific heat and the latent heat of fusion during cooling of metal is total solidification time.It is the time between the pouring of metal to the completion of solidification.
From the graph,
(f)
Interpretation:
The local solidification time of metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Solidification is a process of forming crystal structure from molten metal during cooling. The time required to form crystal structure from molten metal is called solidification time.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Local solidification time of metal is 340 sec.
Explanation of Solution
The time required to remove the latent heat of fusion at a specific casting location is local solidification time.It is the time between the start of solidification and the end of solidification.
Hence from the graph,
(g)
Interpretation:
The undercooling in the cooling curve needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
There are mainly two types of the cooling curve, when metal is well inoculated and when metal is not well inoculated.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
There is no undercooling in the cooling curve.
Explanation of Solution
Liquids don't have nucleating assent.Homogeneous nucleation takes place in B-C region.For cooling curve when the metal is well inoculated, undercooling is not necessary.Solidification starts at melting temperature.
(h)
Interpretation:
The identity of metal needs to be stated.
Concept Introduction:
Cooling curves are of two types of metal- for metal with no inoculation and for metal with inoculation.
Cooling curve represents different temperatures.The cooling curve represents a change in temperature as a function of time.
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Probably the metal should be cadmium.
Explanation of Solution
Given the cooling curve is for metal having well inoculation.For this metal, solidification starts at melting temperature.Solidification of the temperature of this metal is
Hence the probable metal should be cadmium.
(i)
Interpretation:
Mold constant of metal needs to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
As per Chvorinov's rule, solidification time is directly proportional to the square of volume- area ratio of the cast metal.
Here,
Answer to Problem 9.62P
Mold constant is
Explanation of Solution
As per Chvorinov's rule,
Volume of casting can be calculated as follows:
Area of casting can be calculated as follows:
Thus,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Essentials Of Materials Science And Engineering
- 1. Determine the bearings, azimuths, and lengths of lines AB, BC, CD, and DA for the closed loop traverse data shown below in Table 1. Show calculations. Table 1 Station Northing [ft] Easting [ft] A 1,000 1,000 B 750 1,750 C 1,345 2,255 D 1,567 1,345 2. Compute the bearings of sides BC and CD in Figure 1. Show all work for all angles. A B 70°10' S72°39'W C 94°35' Figure 1 Tt (+) B Darrow_forwardBài 1. Cho cơ hệ như hình 1. Hình biểu diễn lược đổ cơ hệ tại vị trí cân bằng tĩnh. Trục tọa độ Oy hướng theo phương chuyển động của vật 1, gốc O đặt tại vị trí cân bằng của vật 1(tức khi lò xo biến dạng tĩnh). Bỏ qua khối lượng của thanh số 3. Vật rắn 2 là pulley 2 tầng đồng chất có bán kính ngoài 21, bán kính trong I, bán kính quán tính đối với trục qua tâm P-1.5, khối lượng m:. Vật rắn 4 là thanh thắng đồng chất có khối lượng m, chiều dài 1. Cho các số liệu: m = 2kg, m= = 5kg, m = 4kg, k=40(N/cm), ! – 0.8(m),r=0.1(m). Điều kiện đầu y; =0.5 cm );j = 10 cm/s) . Giả sử hệ dao động bé, Vật rắn 2 chuyển động lăn không trượt trên mặt phẳng ngang. 1. Viết phương trình chuyển động của hệ. 2. Xác định tần số dao động tự do của hệ. 3. Xác định đáp ứng dao động tự do của hệ. dây dây 1 2r Hình 1 y 3 -2 I k www. -2arrow_forwardHints: Find the closed loop transfer function and then plot the step response for diFerentvalues of K in MATLAB. Show step response plot for different values of K. Auto Controls Show solutions and provide matlab code NO COPIED ANSWERS OR WILL REPORTarrow_forward
- Obtain the response of the system shown below for a parabolic or acceleration input r(t);where Auto Controls Show full solutionarrow_forward8. Name and Email AddressesWrite a program that keeps names and email addresses in a dictionary as key-value pairs. The program should display a menu that lets the user look up a person’s email address, add a new name and email address, change an existing email address, and delete an existing name and email address. The program should pickle the dictionary and save it to a file when the user exits the program. Each time the program starts, it should retrieve the dictionary from the file and unpickle it. How would the user be able to use the program?arrow_forwardProblem Statement A large plate of insulating material 8 cm thick has in it a 3 cm-diam hole, with axis normal to the surface. The temperature of the surroundings are 1800 K at one side of the plate and 400 K on the other side. Insulating plate D= 3 cm H= 8 cm Considering the sides of the hole to be black, (a) Draw a system of resistors that can be used to solve for the various heat transfer rates. For full credit you must label all "voltages", "currents," and resistances present. (b) Estimate the radiative heat transfer through the hole.arrow_forward
- hoph - AT 10x AT 10.076 ht 0.076 0 0-1846112 14884 xh T 1.632m h-4- (1-22) h = 1.022m 14. The 4-ft-diameter cylinder, 4 ft long, is acted upon by water on the left and oil of sp gr 0.800 on the right. Determine (a) the normal force at B if the cylinder weighs 4000 lb and (b) the horizontal force due to oil and water if the oil level drops 1 ft. Solution Water Oil Barrow_forward3. The following data was collected for the traverse shown in Figure 2. a. Determine the latitudes and departures for all sides. b. Determine the linear error of closure and the accuracy ratio. C. Correct and balance the latitudes and departures. A N80°27'E 467.81 ft 497.50 ft N56°46' W B S34°51'E 483.69 ft 325.06 ft D N81°48' Warrow_forwardQ2: Solve the equation using the simplex method Max. Z 13x1 +11x2 Subject to constraints 4x1 +5x21500 5x1 +3x21575 x1 +2x2 <420 x1, x2≥0arrow_forward
- Basically, you must build a desktop/android application that utilizes cryptographic techniques/protocols to secure communication (or data at rest). Try to achieve confidentiality, integrity, availability, authentication, non-repudiation (preferably all of them, otherwise few of them based on the requirement).You must demonstrate the use of these cryptographic techniques by showing some outputs/visualization results or captured traffic such as through Wireshark.1. Secure Chat ApplicationDescription: Build an encrypted chat application for desktop or Android that ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation.Features:-- End-to-end encryption using AES-256 or Signal Protocol.--Digital signatures for non-repudiation.--Message integrity verification using HMAC.Secure login using two-factor authentication (2FA).--Server-side availability mechanisms (e.g., load balancing, backup storage). Technologies: Python (PyQt + PyCryptodome), Java (Android), Firebase for…arrow_forwardQ1: Draw the equation of z with constraints according to the graphic method Max Z-3 P1+5 P2 s.t. P1 4 P2 6 3 P1+2 P2 <18 P1, P2 20arrow_forwardUsing MATLAB, plot the unit-step response curve for the following transfer function and Using MATLAB, obtain the rise time, peak time, maximum overshoot, and settling time. Auto Controls Provide codesarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsEngineeringISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage,
Essentials Of Materials Science And EngineeringEngineeringISBN:9781337385497Author:WRIGHT, Wendelin J.Publisher:Cengage, Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Industrial Motor ControlEngineeringISBN:9781133691808Author:Stephen HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
Basics Of Engineering EconomyEngineeringISBN:9780073376356Author:Leland Blank, Anthony TarquinPublisher:MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Steel Design (6th Edition)EngineeringISBN:9780134589657Author:Jack C. McCormac, Stephen F. CsernakPublisher:PEARSON Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Materials Science and Engineering...EngineeringISBN:9781119175483Author:William D. Callister Jr., David G. RethwischPublisher:WILEY





