
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
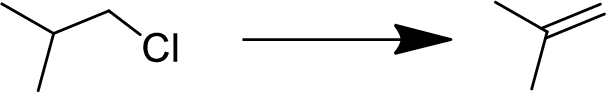
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
(b)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
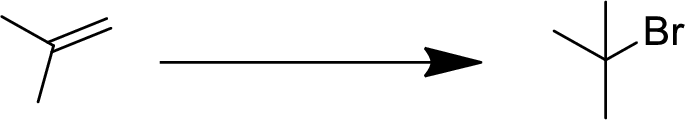
Concept Introduction:
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(c)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.

Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(d)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
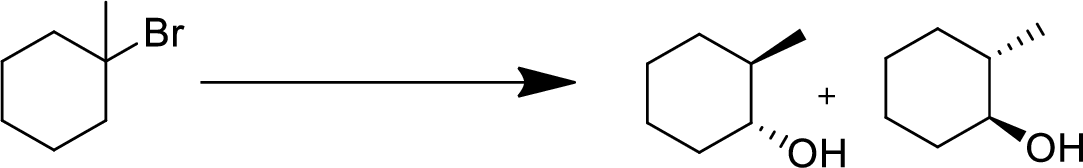
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(e)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
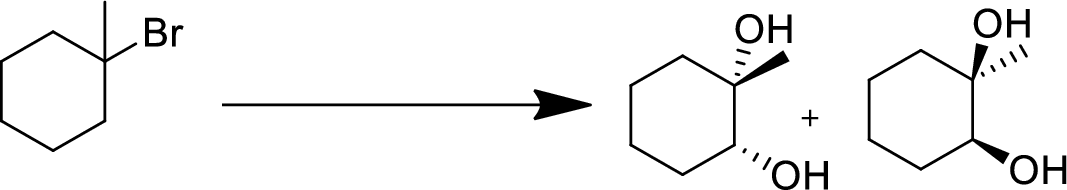
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(f)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
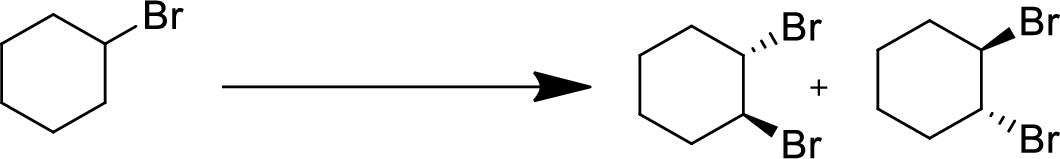
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Addition reaction:
Addition of atom or group in carbon–carbon double bond is known as addition reaction.
Markovnikov Rule:
The product of addition reaction is predicted by Markovnikov rule, it state that the negative part of HX is added in the less substituted carbon of alkene.
(g)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
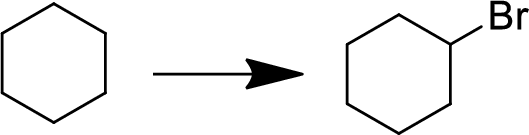
Concept Introduction:
(h)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
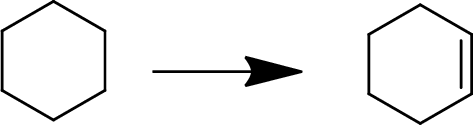
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
(i)
Interpretation:
The conversion of given starting material into the desired product has to be shown.
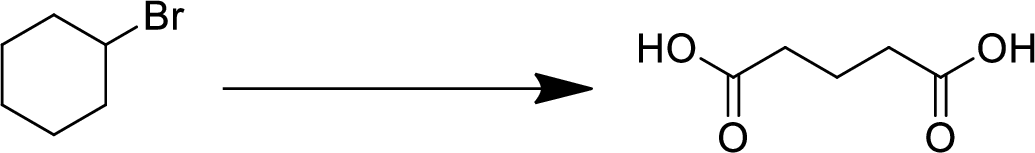
Concept Introduction:
Elimination:
An atom or group are removed from saturated compound to give unsaturated alkene is known as elimination reaction.
In elimination, the removal of halogen ion forms a carbocation followed by removal of hydrogen ion forms an alkene is known as E1 reaction.
The abstraction of proton and removal of leaving group takes simultaneously means it is E2 reaction because the rate of reaction depends on both base and substrate.
E1 elimination fallows Zaitsev rule (more substituted alkene is formed).
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Loose-leaf Version
- Using what we have learned in CHEM 2310 and up through class on 1/31, propose a series of reaction steps to achieve the transformation below. Be sure to show all reagents and intermediates for full credit. You do not need to draw mechanism arrows, but you do need to include charges where appropriate. If you do not put your group name, you will get half credit at most. ? Brarrow_forwardDraw a mechanism for the formation of 2-bromovanillin using bromonium ion as the reactive electrophile.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
