
Concept explainers
Absorption, variable, and throughput costing. Tesla Motors assembles the fully electric Model S-85 automobile at its Fremont, California, plant. The standard variable
| Direct materials | $36,000 |
| Direct manufacturing labor | $10,800 |
| Variable manufacturing |
$12,000 |
Variable manufacturing overhead is allocated to vehicles on the basis of assembly time. The standard assembly time per vehicle is 20 hours.
The Fremont plant is highly automated and has a practical capacity of 4,000 vehicles per month. The budgeted monthly fixed manufacturing overhead is $45 million. Fixed manufacturing overhead is allocated on the basis of the standard assembly time for the budgeted normal capacity utilization of the plant. For 2017, the budgeted normal capacity utilization is 3,000 vehicles per month.
Tesla started production of the Model S-85 in 2017. The actual production and sales figures for the first three months of the year are:
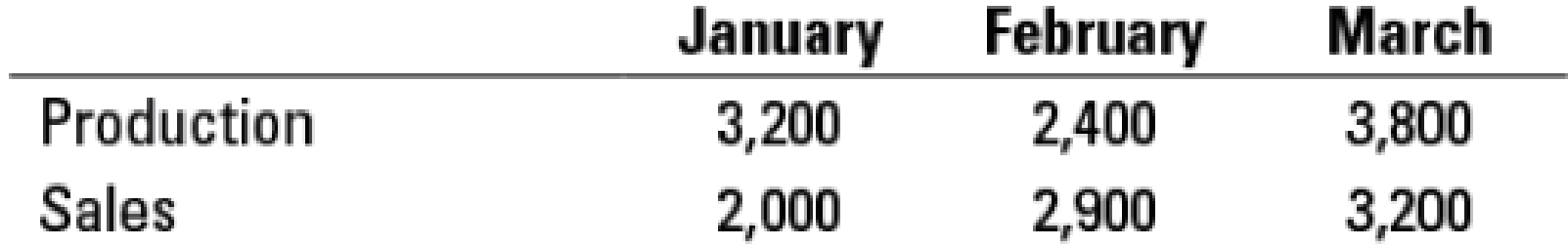
Franz Holzhausen is SVP of Tesla and director of the Fremont plant. His compensation includes a bonus that is 0.25% of monthly operating income, calculated using absorption costing. Tesla prepares absorption-costing income statements monthly, which include an adjustment for the production-volume variance occurring in that month. There are no variable cost variances or fixed overhead spending variances in the first three months of 2017.
The Fremont plant is credited with revenue (net of marketing costs) of $96,000 for the sale of each Tesla S-85 vehicle.
- 1. Compute (a) the fixed manufacturing cost per unit and (b) the total manufacturing cost per unit.
- 2. Compute the monthly operating income for January, February, and March under absorption costing. What amount of bonus is paid each month to Franz Holzhausen?
- 3. How much would the use of variable costing change Holzhausen’s bonus each month if the same 0.25% figure were applied to variable-costing operating income?
- 4. Explain the differences in Holzhausen’s bonuses in requirements 2 and 3.
- 5. How much would the use of throughput costing change Holzhausen’s bonus each month if the same 0. 25% figure were applied to throughput-costing operating income?
- 6. What are the different approaches Tesla Motors could take to reduce possible undesirable behavior associated with the use of absorption costing at its Fremont plant?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Operations Management
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Corporate Finance (4th Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance) - Standalone book
Financial Accounting (12th Edition) (What's New in Accounting)
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

