
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305632134
Author: J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 9.34P
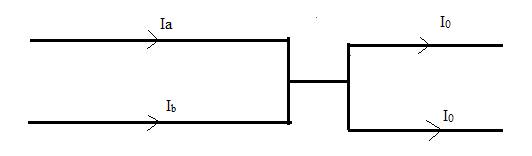
At the general three-phase bus shown in Figure 9.7(a) of the text, consider a simultaneous single line-to-ground fault on phase a and line-to-line fault between phases b and c, with no fault impedances. Obtain the sequence-network interconnection satisfying the current and voltage constraints.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
please help with the question and the following attached with the question. This is a homework practice help please
Pls show neat and whole solution
Pls show neat and whole solution.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course List)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Section 15-3 reversing motors using magnetic starters.Section 15-3Use data sheet B on page 383 to draw the wiring diagram. Note: use only the number of contacts required. First 1. Wire the motor to operate in forward and reverse at 115 VAC.arrow_forwardPlease solutionarrow_forwardUse data sheet B on page 383 to draw the wiring diagram. Note: use only the number of contacts required. First 1. Wire the motor to operate in forward and reverse at 115 VAC.arrow_forward
- B:A 20 MVA transformer which may be called upon to operate at 30% overload, feeds 11 KV busbars through a circuit breaker: other circuit breakers supply outgoing feeders. The transformer circuit breaker is equipped with 1000/5 A CTS and the feeder circuit breakers with 400/5 A CTS and all sets of CTs feed induction type over current relays. The relays on the feeder circuits breakers have a 125% plug setting, and 0.3 time setting. If 3 ph fault current of 5000 A flows from the transformer to one of the feeders, find the operating time of the feeder relay, the minimum plug setting of the transformer relay and its time setting assuming a discrimination time margin of 0.5 sec. Relays having the following characteristics for TMS=1 PSM T in sec. 2 3.6 5 10 15 20 10 6 3.9 2.8 2.2 2.1arrow_forward10.34 Determine the power readings of the two wattmetersshown in the circuit of Fig. P10.34 given that ZY = (15− j5) Warrow_forward10.29 A 208-V (rms) balanced three-phase source supports twoloads connected in parallel. Each load is itself a balanced threephaseload. Determine the line current, given that load 1 is 12 kVAat pf 1 = 0.7 leading and load 2 is 18 kVA at pf 2 = 0.9 lagging.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...Electrical EngineeringISBN:9781305632134Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. SarmaPublisher:Cengage Learning

Power System Analysis and Design (MindTap Course ...
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781305632134
Author:J. Duncan Glover, Thomas Overbye, Mulukutla S. Sarma
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Fault Analysis in Power Systems part 1a; Author: GeneralPAC: Power System Tutorials;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g8itg4MOjok;License: Standard youtube license