
(a)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
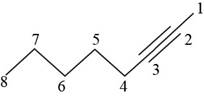
Figure 1
The structural formula for
(b)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
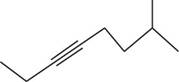
Figure 2
The structural formula for
(c)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(c)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
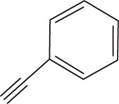
Figure 3
The structural formula for
(d)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(d)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
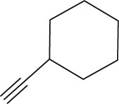
Figure 4
The structural formula for
(e)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(e)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
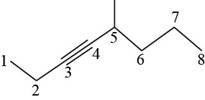
Figure 5
It is conferred form the above structure that the structural formula for
(f)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(f)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
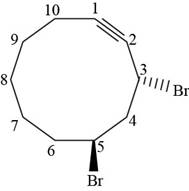
Figure 6
The stereochemistry along with structural formula for
(g)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(g)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
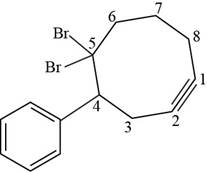
Figure 7
The structural formula for
(h)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(h)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
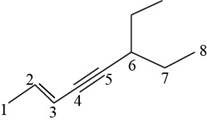
Figure 8
The structural formula for
(i)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(i)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
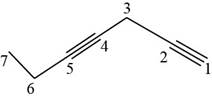
Figure 9
The structural formula for
(j)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(j)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
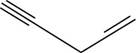
Figure 10
The structural formula for
(k)
To determine: The structural formula for
Interpretation: The structural formula for
Concept introduction: Structural formulas are used to describe the arrangement of atoms, groups or substituents in a molecule, whereas molecular formula describes the total number and the type of atoms present in a molecule. The chemical structures are described by IUPAC name or common names. IUPAC names are totally different from common names because IUPAC names are applied at international level and it comprises suffix, prefix, numbers and other priority rules.
(k)
Answer to Problem 9.26SP
The structural formula for
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula for
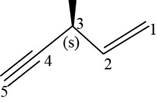
Figure 11
The structural formula for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Plus Masteringchemistry With Pearson Etext, Global Edition
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. N S S HgCl2, H2SO4 く 8 W X Parrow_forwardtab esc く Drawing the After running various experiments, you determine that the mechanism for the following reaction occurs in a step-wise fashion. Br + OH + Using this information, draw the correct mechanism in the space below. 1 Explanation Check F2 F1 @2 Q W A os lock control option T S # 3 80 F3 Br $ 4 0105 % OH2 + Br Add/Remove step X C F5 F6 6 R E T Y 29 & 7 F D G H Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce A F7 DII F8 C Ո 8 * 9 4 F10 F C J K L C V Z X B N M H command P ge Coarrow_forwardIndicate compound A that must react with ethylbenzene to obtain 4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid. 3-bromo-4-ethylbenzene-1-sulfonic acid.arrow_forward
- Part 1 of 2 Draw the structure of A, the minor E1 product of the reaction. esc I Skip Part Check H₂O, D 2 A + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. -0- F1 F2 1 2 # 3 Q A 80 F3 W E S D F4 $ 4 % 5 F5 ㅇ F6 R T Y F G X 5 & 7 + Save 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. DII F7 F8 H * C 80 J Z X C V B N 4 F9 6arrow_forwardFile Preview The following is a total synthesis of the pheromone of the western pine beetle. Such syntheses are interesting both because of the organic chemistry, and because of the possibility of using species specific insecticides, rather than broad band insecticides. Provide the reagents for each step. There is some chemistry from our most recent chapter in this synthesis, but other steps are review from earlier chapters. (8 points) COOEt COOEt A C COOEt COOEt COOH B OH OTS CN D E See the last homework set F for assistance on this one. H+, H₂O G OH OH The last step is just nucleophilic addition reactions, taking the ketone to an acetal, intramolecularly. But it is hard to visualize the three dimensional shape as it occurs. Frontalin, pheromone of the western pine beetlearrow_forwardFor the reaction below: 1. Draw all reasonable elimination products to the right of the arrow. 2. In the box below the reaction, redraw any product you expect to be a major product. C Major Product: Check + ◎ + X ง © Cl I F2 80 F3 I σ F4 I F5 NaOH Click and drawing F6 A 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights E F7 F8 $ # % & 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Q W E R T Y U A S D F G H Jarrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this graph. If you can show exactly where it needs to pass through.arrow_forwardN Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. D 1. H₂O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up V P W X DE CO e C Larrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. N O' 1. H2O, pyridine 2. neutralizing work-up く 8 W aarrow_forward
- Ideal Gas Law Practice Name If you need a refresher on Ideal Gas Law, go back to your Ideal Gas Law Reading Assignment from last week! On all of the following, you'll need to make sure to convert pressures to atm and convert temperatures to Kelvin in order to be able to use the R gas constant on your equation sheet! Given: Ideal Gas Law = then P= pressure V = volume R= ideal gas consent PV=nRT namount of substance n=PV/TR P=nRT/V I = temperature V=nRT/P T=PV/nR R=PV/nT 1. What pressure is required to contain 0.023 moles of nitrogen gas in a 4.2 L container at a temperature of 20.°C? 2. Oxygen gas is collected at a pressure of 123 kPa in a container which has a volume of 10.0 L. What temperature must be maintained on 0.500 moles of this gas in order to maintain this pressure? Express the temperature in degrees Celsius. 3. How many moles of chlorine gas would occupy a volume of 35.5 L at a pressure of 100.0 kPa and a temperature of 100. °C? After determining the number of moles,…arrow_forward1. The following conversion includes chemistry we have covered very recently, some chemistry from last term, and chemistry from the first chapter of this unit. Provide curly arrows and an explanation for this mechanism. Use the reagents in the order given. You do not need any other reagents. 1. NaOEt OEt 2.arrow_forwardCOOEt COOEt Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 COOEt COOEt COOH Step 6 OH Step 4 Step 7 (racemic) cyclizes under conditions (8) OTS Step 5 Step 8 ОН OH (racemic) Frontalin (racemic) Shown above are the steps in one of the several published syntheses of Frontalin, a pheromone of the western pine beetle. From the choices provided, show the reagents and conditions by which step 3 of this synthesis might be accomplished. List the reagent(s) in order that will accomplish this transformation. No more than 4 steps are required. List your answer as a single letter (single-step transformation) or a series of letters (multi-step transformation) with no commas separating them. For example, "ab" corresponds to: 1. Eto Na+ 2. NaOH, H₂O NOTE: The order in which you list your letters matters! Reagents: a. Eto Na* g. NaCN b. NaOH, H₂O h. SOCI₂ c. H3O+, heat i. (CH3)2CuLi, ether, -78°C d. LiAlH4 j. H₂O e. p-TsCI, pyridine k. RCO3H f. Br I. H3O+ 1,024arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





