
Concept explainers
(a)
Calculate the consolidation settlement inone year.
(a)
Answer to Problem 9.20CTP
The consolidation settlement in one year
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Consider the unit weight of water
Calculate the initial void ratio
Substitute
Calculate the saturated unit weight
Substitute
At the middle of the clay layer:
Calculate the effective overburden pressure
Substitute
Calculate the increase in vertical pressure
Substitute
Calculate the final primary consolidation settlement
Substitute
Calculate the time factor
Substitute
Refer Table 9.3 “Variation of Time Factor with Degree of consolidation” in the Text Book.
Take the value of Uas
Take the value of Uas
Calculate the value of U for the value
Calculate the final consolidation settlement
Substitute
Therefore, the consolidation settlement in one year is
(b)
Plot the in situ variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth for the clay layer.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water pressure
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water pressure
Substitute
Calculate the total stress
Substitute
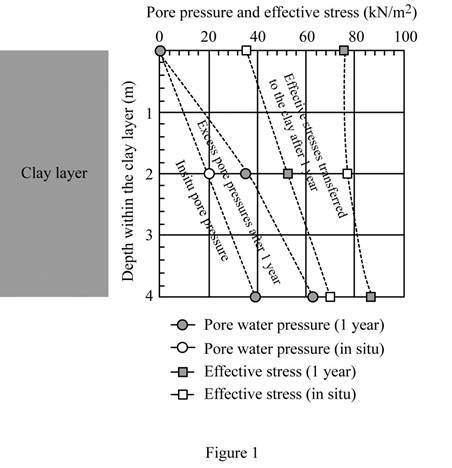
Show the variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth for the clay layer as in Figure 1.
(c)
Plot the variation of pore water pressure and effective stress with depth after on year.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The thickness of sand layer
The thickness of clay layer
The moisture content
The specific gravity of soil solids
The compression index
The coefficient of consolidation
The unit weight of sand is
The unit weight of fill
The depth of the compacted fill
Calculation:
Consider the degree of consolidation
Refer to part (a).
The time factor
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
Calculate the ratio of height of soil to the maximum drainage depth as shown below.
Substitute
Refer Figure 9.20 “Variation of
Take the value of
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
At the bottom of the clay layer, after one year:
Calculate the ratio of height of soil to the maximum drainage depth;
Substitute
Refer Figure 9.20 “Variation of
Take the value of
Calculate the effective stress
Substitute
Calculate the pore water
Substitute
Show the variation of the pore water pressure and the effective stress with depth as in Figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- 1. (20 Points) Determine the critical depth in the trapezoidal drainage ditch shown below. The slope of the ditch is 0.0016, the side slopes are 1V:2.5H, the bottom width is b = 14', and the design discharge is 500 cfs. At this discharge the depth is y = 4.25'. Also, determine the flow regime and calculate the Froude number. Ye= ? Z barrow_forward3. (20 Points) A broad crested weir, 10 feet high, will be constructed in a rectangular channel B feet wide. The weir crest extends a length of B = 120 feet between the banks with 2 - 4 foot wide, round nosed piers in the channel. The width of the weir crest is 8 feet. If H = 6', determine the design discharge for the weir.arrow_forwardParking Needs vs. Alternative Transportation Methods for presentation slides include images and graphsarrow_forward
- Please explain step by step and show formulararrow_forwardBeam ABD is supported and loaded as shown. The cross-section of the beam is also shown. The modulus of elasticity of the beam is 200 GPa. 6.0 kN/m Cross-section: 330 mm 4.5 kN 8.0 kNm 40 mm 2.5 m 1.5 m 20 mm Set up the discontinuity moment function in terms of x. List all the appropriate boundary conditions. Determine the slope function in terms of x. Determine the deflection function in terms of x. Determine the support reactions. Determine the maximum deflection. 290 mmarrow_forwardDraw the Shear Force Diagram and Bending Moment Diagram for the beam shown in Fig.1. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope Deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardText Book Problem 7.82 (page 261) Consider the total head-loss in the system forthis flow is 18.56 ft (head-losses in first and second pipe are 13.83 ft and 4.73 ftrespectively). Please show numerical values for EGL/HGL at the beginning/end/intermediatechange point. (Point distribution: elevation determination 5 points, EGL, HGL lines 4points).(I think we are just using the values provided for head losses to solve this problem)arrow_forwardCalculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the moment distribution method, and draw the Shear force diagram and Bending moment diagram for the beam shown. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forward
- Calculate the BMs (bending moments) at all the joints of the beam shown in Fig.1 using the Slope deflection method. The beam is subjected to an UDL of w=65m. L=4.5m L1= 1.8m. Assume the support at C is pinned, and A and B are roller supports. E = 200GPa, I = 250x106 mm4.arrow_forwardThank you for your help if you would also provide the equations used .arrow_forwardThe sectors are divided as follows:top right = 1, top left = 2, middle = 3, bottom = 4.(a) Determine the distance yˉ to the centroid of the beam’s cross-sectional area.Solve the next questions by building a table. (Table format Answers) (b) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the x′ axis. (c) Determine the second moment of area (moment of inertia) about the y-axis.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning



