
Find the moment and product of inertia of the area with respect to x and y axes about through
Answer to Problem 9.192RP
The moment of inertia of the area with respect to x about through
The moment of inertia of the area with respect to y about through
The product of inertia of the area with respect to x and y axes about through
Explanation of Solution
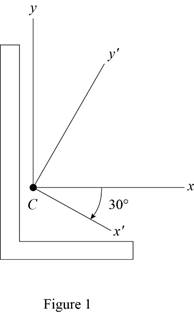
Sketch the cross section as shown in Figure 1.
Refer to Figure 9.13.
The moment of inertia
The moment of inertia
Refer to Problem 9.191.
Sketch the cross section as shown in Figure 2.
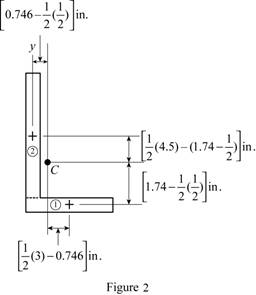
Express the product of inertia as shown below:
Here,
Applying parallel axis theorem,
When the x and y axis is symmetry.
Refer to Figure 1.
Find the area of semicircle section 1 as shown below:
Here,
Substitute
Find the area of rectangle section 2 as shown below:
Here,
Substitute
Find the centroid for section 1 about x axis
Find the centroid for section 1 about x axis
Find the centroid for section 1 about y axis
Find the centroid for section 2 about x axis
Find the product of inertia of the area with respect to x and y axes by using parallel axis theorem as shown below:
Substitute
The Mohr circle is defined by the diameter XY, where
Find the average moment of inertia
Here,
Substitute
Find the radius (R) using the relation as shown below:
Here, R is radius and
Substitute
Sketch the Mohr circle as shown in Figure 3.
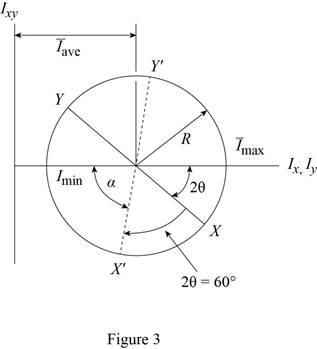
Refer to Figure 2.
Substitute
Find the angle
Find the moment of inertia of the area with respect to x about through
Here,
Substitute
Thus, the moment of inertia of the area with respect to x about through
Find the moment of inertia of the area with respect to y about through
Substitute
Thus, the moment of inertia of the area with respect to y about through
Find the product of inertia of the area with respect to y about through
Substitute
Thus, the product of inertia of the area with respect to x and y axes about through
(b)
Find the orientation of the principal axes through the centroid and corresponding values.
(b)
Answer to Problem 9.192RP
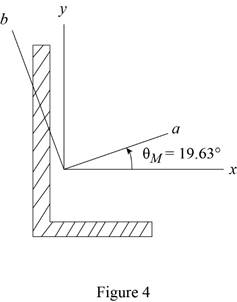
The orientation of the principal axes at the origin is
The maximum moment of inertia is
The minimum moment of inertia is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Find the orientation of the principal axes through at origin as shown below.
Refer part a.
Thus, the orientation of the principal axes at the origin is
Sketch the orientation axis as shown in Figure 4.
Find the maximum moment
Substitute
Thus, the maximum moment of inertia is
Find the minimum moment
Substitute
Thus, the minimum moment of inertia is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK VECTOR MECHANICS FOR ENGINEERS: STA
- MY ID#016948724 please solve the problem step by spetarrow_forward1 8 4 For the table with 4×4 rows and columns as shown Add numbers so that the sum of any row or column equals .30 Use only these numbers: .1.2.3.4.5.6.10.11.12.12.13.14.14arrow_forwardMY ID# 016948724 please solve this problem step by steparrow_forward
- The pickup truck weighs 3220 Ib and reaches a speed of 30 mi/hr from rest in a distance of 200 ft up the 10-percent incline with constant acceleration. Calculate the normal force under each pair of wheels and the friction force under the rear driving wheels. The effective coefficient of friction between the tires and the road is known to be at least 0.8.arrow_forward1. The figure shows a car jack to support 400kg (W=400kg). In the drawing, the angle (0) varies between 15 and 70 °. The links are machined from AISI 1020 hot-rolled steel bars with a minimum yield strength of 380MPa. Each link consists of two bars, one on each side of the central bearings. The bars are 300mm in length (/) and 25 mm in width (w). The pinned ends have the buckling constant (C) of 1.4 for out of plane buckling. The design factor (nd) is 2.5. (1) Find the thickness (t) of the bars and the factor of safety (n). (2) Check if the bar is an Euler beam. Darrow_forward(Read image)arrow_forward
- UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL DE SAN ANTONIO ABAD DEL CUSCO PRIMER EXAMEN PARCIAL DE MECÁNICA DE FLUIDOS I ............ Cusco, 23 de setiembre de 2024 AP. Y NOMBRES: ........ 1.- Para el tanque de la figura: a) Calcule la profundidad de la hidrolina si la profundidad del agua es de 2.8 m y el medidor del fondo del tanque da una lectura de 52.3kPa. b) Calcule la profundidad del agua si la profundidad de la hidrolina es 6.90 m y el medidor de la parte inferior del tanque registra una lectura de 125.3 kPa. Hidrolina Sp=0.90 Abertura Agua sup suge to but amulor quit y 2.- Calcule la magnitud de la fuerza resultante sobre el área A-B y la ubicación del centro de presión. Señale la fuerza resultante sobre el área y dimensione su ubicación con claridad. 3.5 ft 12 in: Oil (38-0.93) 14 in 8 inarrow_forwardplease solve this problem and give me the correct answer step by steparrow_forwardplease solve this problem step by step and show the best way that can be explainedarrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





