
Concept explainers
JOURNALIZING AND POSTING PAYROLL ENTRIES Cascade Company has four employees. All are paid on a monthly basis. The fiscal year of the business is June 1 to May 31.
The accounts kept by Cascade include the following:
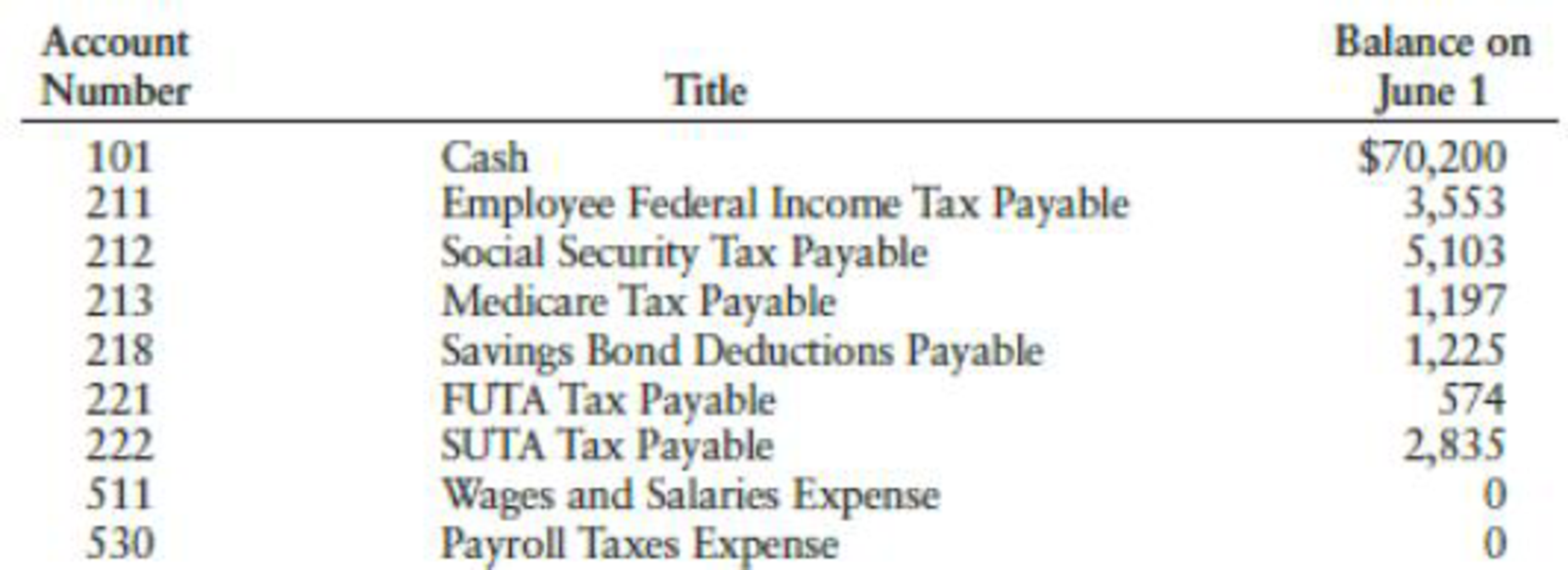
The following transactions relating to payrolls and payroll taxes occurred during June and July:
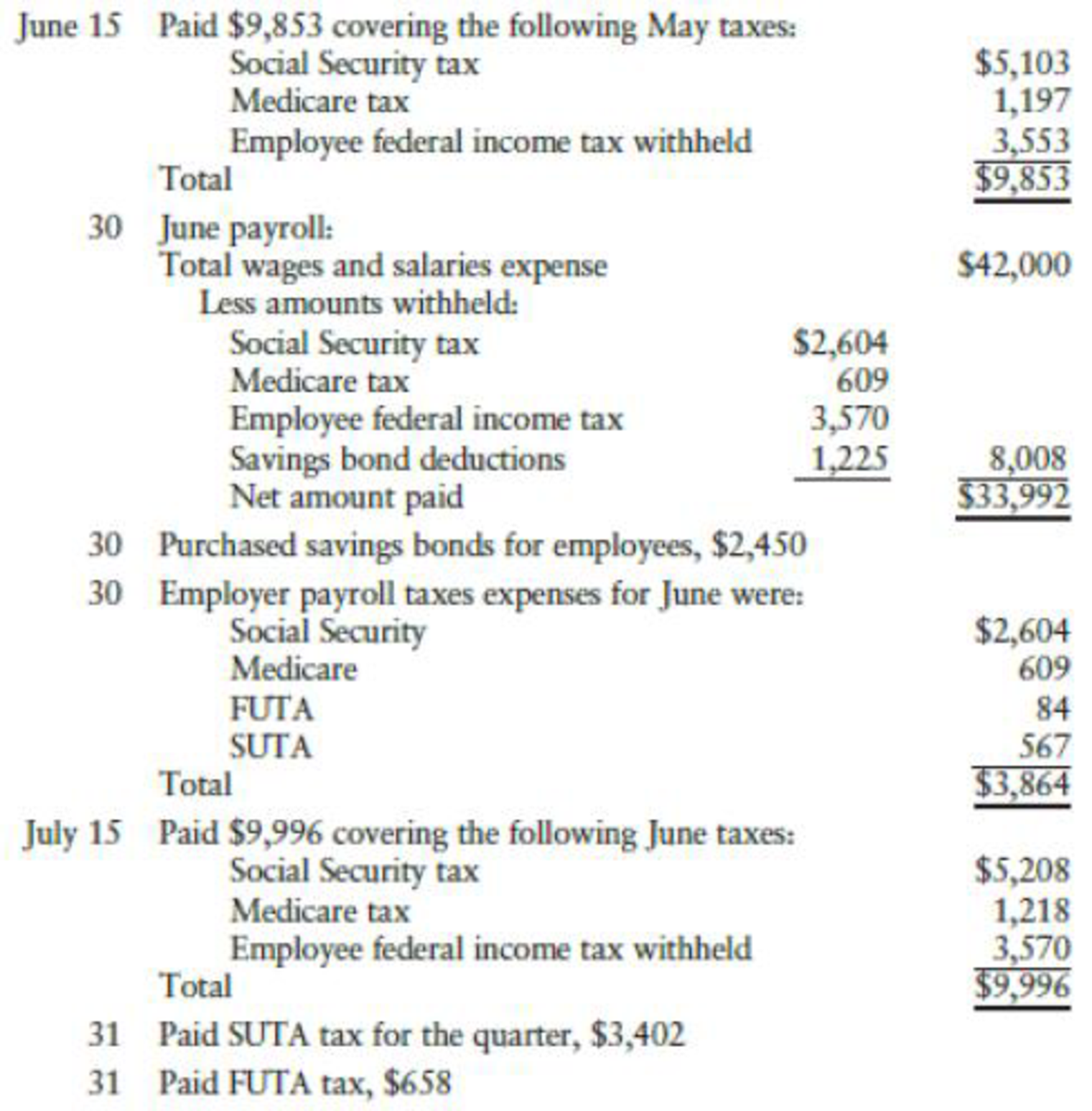
REQUIRED
- 1. Journalize the preceding transactions using a general journal.
- 2. Open Τ accounts for the payroll expenses and liabilities. Enter the beginning balances and post the transactions recorded in the journal.
1.
Prepare journal entry to record the given transactions.
Explanation of Solution
Payroll tax:
Payroll tax refers to the tax that are equally contributed by employees and employer based on the salary and wages of an employee. Payroll tax includes taxes like federal tax, local income tax, state tax, social security tax and federal and state unemployment tax.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of payroll tax of May on June 15.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| June 15 | Employee Federal income tax payable | 211 | 3,553 | |
| FICA-Social Security taxes payable | 212 | 5,103 | ||
| FICA-Medicare Taxes payable | 213 | 1,197 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 9,853 | ||
| (To record the deposit of employee federal income tax and Social security and Medicare taxes) |
Table (1)
- Employee federal income tax payable is a liability and it is decreased. Hence, debit employee federal income tax payable by $3,553.
- FICA tax – social and security tax payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA tax – social and security tax payable by $5,103.
- FICA tax – medical tax payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA tax – medical tax payable by $1,197.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $9,853.
Prepare journal entry to record the June payroll.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| June 30 | Wages and Salaries expense | 511 | 42,000 | |
| Employee federal income tax payable | 211 | 3,570 | ||
| FICA-Social Security taxes payable | 212 | 2,604 | ||
| FICA-Medicare Taxes payable | 213 | 609 | ||
| Savings bonds deductions payable | 218 | 1,225 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 33,992 | ||
| (To record the payroll for the week ended June 30) |
Table (2)
- Wages and Salaries expense is an expense account and it is increased. Hence, debit wages and salaries expense with $42,000
- Employee Federal income tax payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the employee Federal income tax payable by $3,570.
- FICA tax – social and security tax payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA tax – social and security tax payable by $2,604.
- FICA tax – medical tax payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA tax – medical tax payable by $609.
- Savings bonds deductions payable is a liability and it is increased. Hence, credit savings bonds deductions payable by $1,225.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $33,992.
Prepare journal entry to record the purchase of bonds for employees.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| June 30 | Savings bonds deductions payable | 218 | 2,450 | |
| Cash | 101 | 2,450 | ||
| (To record the purchase of U.S savings bonds for employees.) |
Table (3)
- Savings bonds deductions payable is a liability and it is decreased. Hence, debit savings bonds deductions payable by $2,450.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $2,450.
Prepare journal entry to record the employer payroll tax expense.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| June 30 | Payroll tax expense | 530 | 3,864 | |
| FICA-Social Security taxes payable | 212 | 2,604 | ||
| FICA-Medicare Taxes payable | 213 | 609 | ||
| FUTA tax payable | 221 | 84 | ||
| SUTA tax payable | 222 | 567 | ||
| (To record the employer payroll taxes expense) |
Table (4)
- Payroll taxes expense is an expense account and it is increased. Hence, debit payroll taxes expense with $3,864.
- FICA tax – social and security tax payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA tax – social and security tax payable by $2,604.
- FICA tax – medical tax payable is a liability and there is an increase in the value of liability. Hence, credit the FICA tax – medical tax payable by $609.
- FUTA tax payable is a liability and it is increased. Hence, credit FUTA tax payable by $84.
- SUTA tax payable is a liability and it is increased. Hence, credit SUTA tax payable by $567.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of June taxes.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 15 | Employee Federal income tax payable | 211 | 3,570 | |
| FICA-Social Security taxes payable | 212 | 5,208 | ||
| FICA-Medicare Taxes payable | 213 | 1,218 | ||
| Cash | 101 | 9,996 | ||
| (To record the deposit of employee federal income tax and Social security and Medicare taxes) |
Table (5)
- Employee federal income tax payable is a liability and it is decreased. Hence, debit employee federal income tax payable by $3,570.
- FICA tax – social and security tax payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA tax – social and security tax payable by $5,208.
- FICA tax – medical tax payable is a liability and there is a decrease in the value of liability. Hence, debit the FICA tax – medical tax payable by $1,218.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $9,996.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of SUTA tax.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | SUTA tax payable | 222 | 3,402 | |
| Cash | 101 | 3,402 | ||
| (To record the payment of SUTA tax) |
Table (6)
- SUTA tax payable is a liability and it is decreased. Hence, debit SUTA tax payable by $3,402.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $3,402.
Prepare journal entry to record the payment of FUTA tax.
| Date | Account Title and explanation | Post. ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | FUTA tax payable | 221 | 658 | |
| Cash | 101 | 658 | ||
| (To record the payment of FUTA tax) |
Table (7)
- FUTA tax payable is a liability and it is decreased. Hence, debit FUTA tax payable by $658.
- Cash is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the cash by $658.
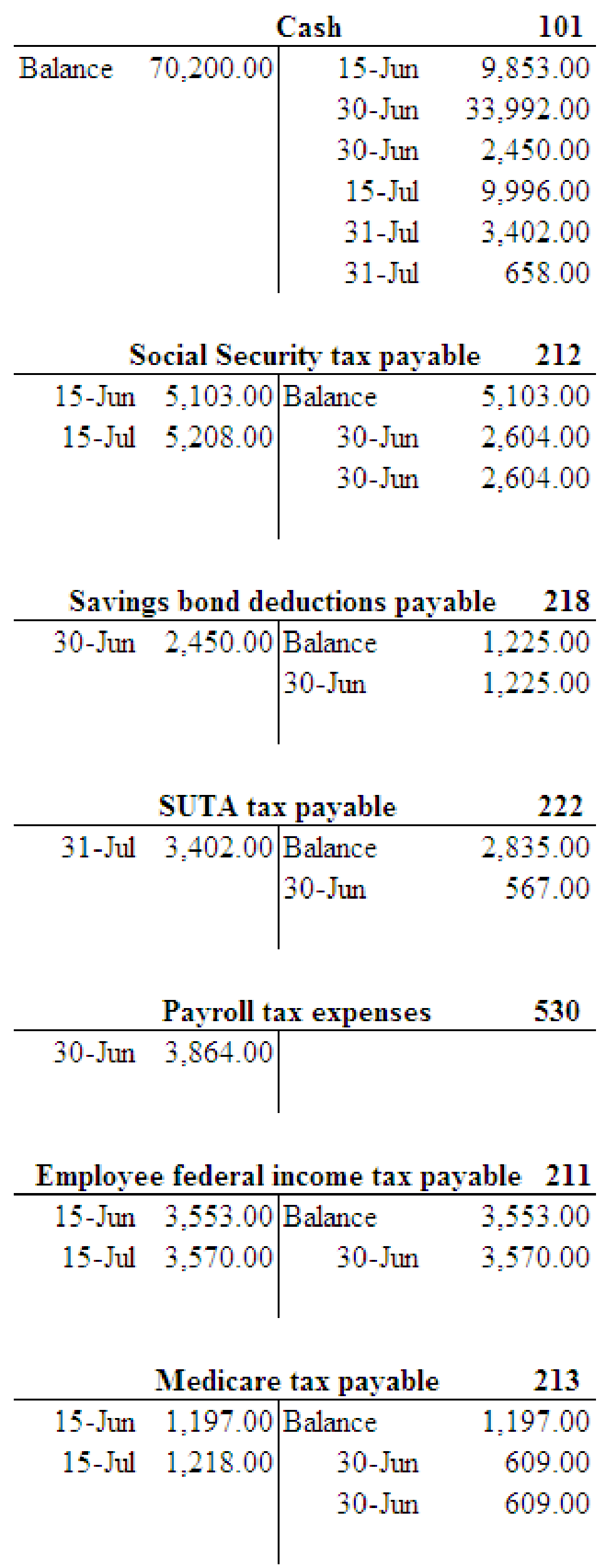
2.
Prepare T-Account for the payroll expenses and liabilities.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare T-Account for the payroll expenses and liabilities.
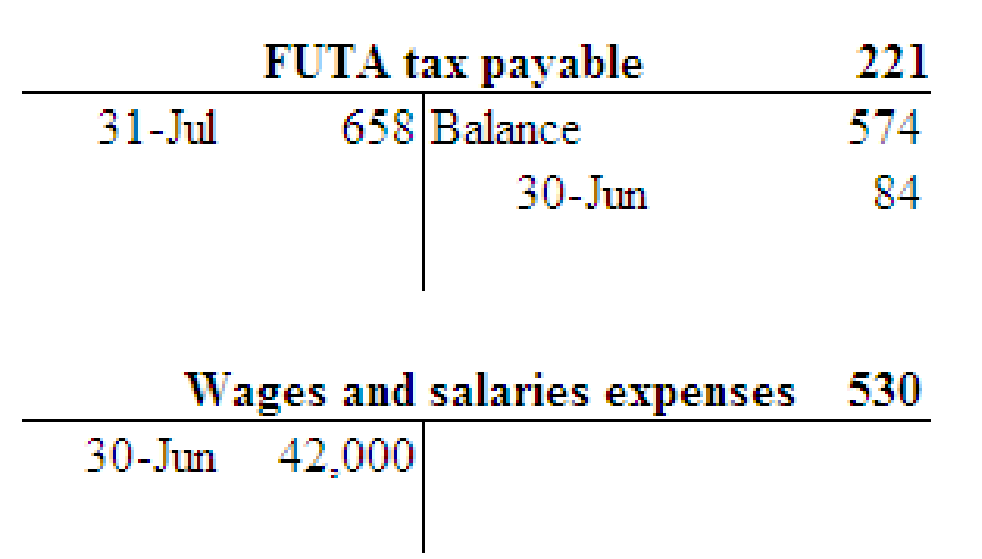
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Bundle: College Accounting, Chapters 1-27, Loose-leaf Version, 22nd + Cengagenowv2™, 2 Terms Printed Access Card For Heintz/parry's College ... Set For College Accounting, 22nd + Cenga
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub





