
Concept explainers
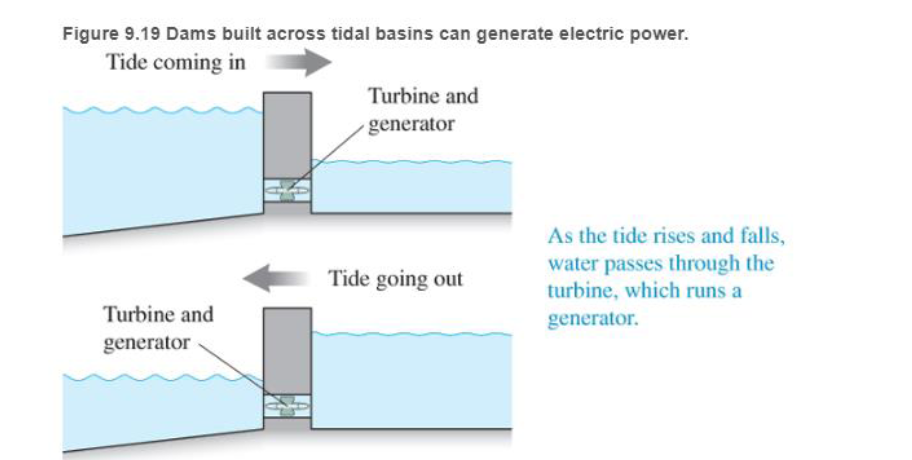
Tidal energy Tides are now used so gene-ate electric power in two ways. In the first, huge dams can be built. across the mouth of a river where it exits to the ocean. As the ocean tide moves in and out of this tidal bas in or estuary, the water flows through tunnels in the dam (see Figure 9.19). This flowing water turns turbines in the tunnels that run electric generators. Unfortunately, this technique works best with large increases in tides—a 5-m difference between high and low tide Such differences are found at only a small number of places Currently, France is the only country that successfully uses this power source A tidal basin plant in France, the Rance. Tidal Power Station. makes 240 megawatts of power—enough energy to power 240,000 homes. Damming tidal basins can have negative environmental effects because of reduced tidal flow and silt buildup. Another disadvantage is that they can only generate electricity when the tide is flowing in or out, for about 10 hours each day.
A second method for collecting energy from the tidal flow (as well as all water flow) is to place turbines directly in the water—like windmills in moving water instead of in moving air. These water turbines have the advantages that they are much cheaper to build, they do not have the environmental problems of a tidal basin, and there are many more suitable sites for such water flow energy farms. Also the energy density of flowing water is about 800 times the energy density of dry air flow. Verdant Power is developing turbine prototypes in the East River near New York City and in the Saint Lawrence Seaway in Canada, and they are looking at other sites in the Puget Sound and all over the world. The worldwide potential tor hydroelectric power is about
—enough to supply the world's energy needs.
If the Rance Tidal Power Station in France could produce power 24 hours a day, which answer below is closest to the daily amount of energy in joules that it could produce?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
Modified Mastering Physics with Pearson eText -- Access Card -- for College Physics: Explore and Apply (18-Weeks)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
- Can someone help me solve this thank you.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward1.62 On a training flight, a Figure P1.62 student pilot flies from Lincoln, Nebraska, to Clarinda, Iowa, next to St. Joseph, Missouri, and then to Manhattan, Kansas (Fig. P1.62). The directions are shown relative to north: 0° is north, 90° is east, 180° is south, and 270° is west. Use the method of components to find (a) the distance she has to fly from Manhattan to get back to Lincoln, and (b) the direction (relative to north) she must fly to get there. Illustrate your solutions with a vector diagram. IOWA 147 km Lincoln 85° Clarinda 106 km 167° St. Joseph NEBRASKA Manhattan 166 km 235° S KANSAS MISSOURIarrow_forward
- Plz no chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward3.19 • Win the Prize. In a carnival booth, you can win a stuffed gi- raffe if you toss a quarter into a small dish. The dish is on a shelf above the point where the quarter leaves your hand and is a horizontal dis- tance of 2.1 m from this point (Fig. E3.19). If you toss the coin with a velocity of 6.4 m/s at an angle of 60° above the horizontal, the coin will land in the dish. Ignore air resistance. (a) What is the height of the shelf above the point where the quarter leaves your hand? (b) What is the vertical component of the velocity of the quarter just before it lands in the dish? Figure E3.19 6.4 m/s 2.1arrow_forwardCan someone help me answer this thank you.arrow_forward
- 1.21 A postal employee drives a delivery truck along the route shown in Fig. E1.21. Determine the magnitude and direction of the resultant displacement by drawing a scale diagram. (See also Exercise 1.28 for a different approach.) Figure E1.21 START 2.6 km 4.0 km 3.1 km STOParrow_forwardhelp because i am so lost and it should look something like the picturearrow_forward3.31 A Ferris wheel with radius Figure E3.31 14.0 m is turning about a horizontal axis through its center (Fig. E3.31). The linear speed of a passenger on the rim is constant and equal to 6.00 m/s. What are the magnitude and direction of the passenger's acceleration as she passes through (a) the lowest point in her circular motion and (b) the high- est point in her circular motion? (c) How much time does it take the Ferris wheel to make one revolution?arrow_forward
- 1.56 ⚫. Three horizontal ropes pull on a large stone stuck in the ground, producing the vector forces A, B, and C shown in Fig. P1.56. Find the magnitude and direction of a fourth force on the stone that will make the vector sum of the four forces zero. Figure P1.56 B(80.0 N) 30.0 A (100.0 N) 53.0° C (40.0 N) 30.0°arrow_forward1.39 Given two vectors A = -2.00 +3.00 +4.00 and B=3.00 +1.00 -3.00k. (a) find the magnitude of each vector; (b) use unit vectors to write an expression for the vector difference A - B; and (c) find the magnitude of the vector difference A - B. Is this the same as the magnitude of B - Ä? Explain.arrow_forward5. The radius of a circle is 5.5 cm. (a) What is the circumference in meters? (b) What is its area in square meters? 6. Using the generic triangle below, solve the following: 0 = 55 and c = 32 m, solve for a and b. a = 250 m and b = 180 m, solve for the angle and c. b=104 cm and c = 65 cm, solve for a and the angle b a 7. Consider the figure below representing the Temperature (T in degrees Celsius) as a function of time t (in seconds) 4 12 20 (a) What is the area under the curve in the figure below? (b) The area under the graph can be calculated using integrals or derivatives? (c) During what interval is the derivative of temperature with respect to time equal to zero?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





