
Concept explainers
Predict the bond angles for the following molecules:
Interpretation:
The bond angles of the given molecules are to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electron domain is the number of bonds and lone pair of electrons around the central atom.
According to VSEPR, the electron domains repel each other and arrange themselves as far apart as possible in space.
Molecular geometry represents the arrangement of bonded atoms. If no lone pairs are present, then the molecular geometry is the same as the electron domain geometry.
The repulsion in lone pair–lone pair is greater than that in lone pair–bond pair, which in turn is greater than that in bond pair–bond pair. The repulsion due to a double bond is more than that due to single bonds.
Answer to Problem 75AP
Solution:
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
f) Less than
g) Less than
h)
Explanation of Solution
a)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
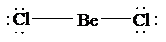
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to two chlorine atoms by single bonds, and there is no lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, two electron domains are arranged on opposite sides to give a linear shape, with a bond angle of
b)
The Lewis structure of
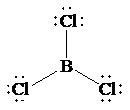
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to three chlorine atoms by single bonds, and there is no lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, three electron domains are arranged in a trigonal planar shape with a bond angle of
c)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
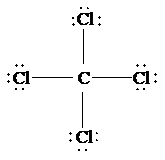
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to four chlorine atoms by single bonds, and there is no lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, four electron domains are arranged in a tetrahedral shape with a bond angle of
d)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
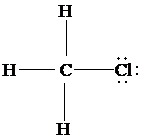
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to three hydrogen atoms and one chlorine atom by single bonds, and there is no lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, four electron domains are arranged in a tetrahedral shape with a bond angle of
e)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
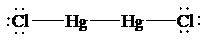
In this structure, each
atom is bonded to one chorine atom, and to each other. Thus, there are two electron domains around each
atom. Thus, the shape is linear with a bond angle of
f)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
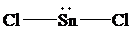
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to two chlorine atoms by single bonds, and there is a lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, three electron domains are arranged in a trigonal planar shape with a bond angle of
atom, the shape of
is bent with a bond angle less than
g)
The Lewis structure of
is as follows:
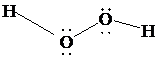
In this structure, each
atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom, and to each other. There are two lone pairs on each oxygen atom. Thus, there are four electron domains around each oxygen atom. According to VSEPR, four electron domains have a tetrahedral shape. Due to the presence of two lone pairs, the shape is bent with a bond angle less than
h)
The Lewis structure is as follows:
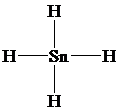
In this structure, the
atom is bonded to four chlorine atoms by single bonds, and there is no lone pair on
atom. According to VSEPR, four electron domains are arranged in a tetrahedral shape with a bond angle of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Chemistry
- If 10 mL of a commercial sodium silicate solution is added, the water required to obtain a 20% solids solution (SiO2+Na2O) is added. Indicate the final grams of Na2SiO3.arrow_forwardPlease help me figure out the mechanism with arrows of the following reactionarrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of acetal hydrolysis termine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H* H* + H₂O Y ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X, Y, and Z. You may draw that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure Explanation Check @2 W Click and drag to start drawing a structure. #4 # 3 LU E % 67 olo 5 66 R T Y & 7 AcGraw Hill LLC. All Rights R Xarrow_forward
- 8. (16 pts) Provide the stepwise mechanism for the synthesis of the following compound via an enaminearrow_forwardDraw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forward
- Predict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaH (20°C) 2. CH3Br ? Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. G Crarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LDA (-78°C) ? 2. Br Some notes: • Draw only the major product, or products. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. . • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds where necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. • If there are no products, just check the box under the drawing area. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forward
- Please draw the structuresarrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediates 1 and 2, plus the final product 3, of this synthesis: 0 1. Eto 1. Eto- 1 2 2. MeBr 2. EtBr H3O+ A 3 You can draw the three structures in any arrangement you like. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw the missing intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this synthesis: 1. MeO- H3O+ 1 2 2. PrBr Δ You can draw the two structures in any arrangement you like. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning




