
Concept explainers
Ethylene oxide is an intermediate in the manufacture or ethylene glycol (antifreeze) and polyester
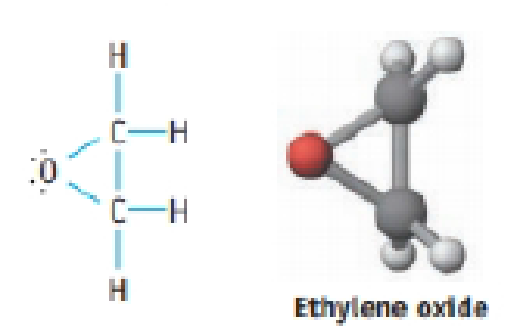
(a) What are the bond angles in the ring? Comment on the relation between the bond angles expected based on hybridization an d the bond angles expected for a three-member ring.
(b) Is the molecule polar? Based on the electrostatic poten1ial map shown below. where do the neg-alive and positive charges lie in the molecule?
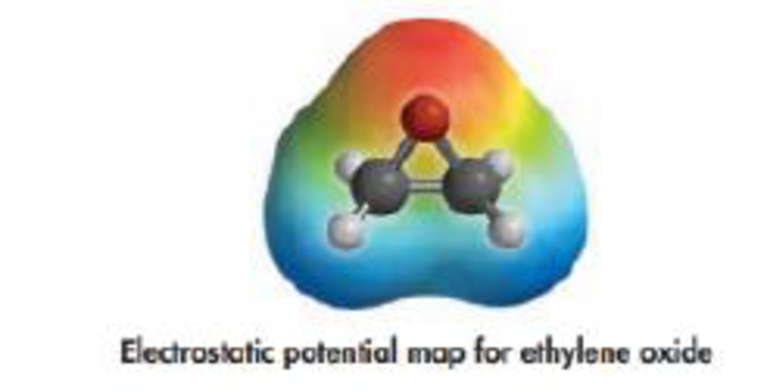
Polarity: It is a well separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or chemical compounds having an electrical dipole moment. Generally the polar molecules must contain polar bonds due to a different in electronegative between the bonded atoms.
The electrostatic potential map clearly to explain, the oxygen atom has more negative (δ–) charge and other side has less positive (δ–) charge, so this molecule is a more polar nature.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 9 Solutions
Owlv2 With Ebook, 1 Term (6 Months) Printed Access Card For Kotz/treichel/townsend/treichel's Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, 10th
- Part I. Problem solving. Include all necessary calculations 13 provide plots and graphs. Complexation wl diphenyl carbazide (OPC) in acidic media is another type of sensitive photometric method used for the analysis of aqueous. hexavalent chromium. At 540nm the cherry-red complex as a result of DPC reaction w/ chromium can be photometrically measured. at this wavelength. - a 25mL The UV-vis analysis for the determination of nexavalent chromium in ground water sample is given below. The experiment was based on external calibration method w/ each measurement sample prepared are as follows lab sample analysis contained the standard 100 ppb croy cor groundwater sample, volumes used as indicated below), 12.50 mL of 0.02 M H2Soy and 5.50 ml of 100 ppm DPC (wi water to adjust final volume to 25-ml). The main stripping method was square wave voltammetry, following the conditions set in the main ASV experiment. Standard 100 Volumetric Groundwater H2SO4 0.20 M, flask Sample, mL ppb CrO4*, 100…arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forwardPredict the products of the following reactions. Draw mechanism arrows for each step for a, b, and c. a.) HBr b.) HI H₂O H2SO4 d.) C12 HO H2SO4 1.) BH3 2.) H2O2, NaOHarrow_forward
- K for the following reaction is 0.11 at constant temperature. If the equilibrium concentration of HCl is 0.5 M, what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3. NH4CI(s) ⇌ NH3(g) + HCI(g)arrow_forwardplease help by Draw the following structures (Lewis or line-angle drawing).arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forward
- Consider the reaction: 2 A (aq) ⇌ B(aq) Given the following KC values and starting with the initial concentration of A = 4.00 M, complete ICE diagram(s)and find the equilibrium concentrations for A and B.A) KC = 4.00B) KC = 200C) KC = 8.00 x10-3arrow_forward5) Consider the reaction: Cl2 (g) + F2 (g) ⟷ 2 ClF (g) KP=? The partial pressure of 203 kPa for Cl2 and a partial pressure of 405 kPa for F2. Upon reaching equilibrium, thepartial pressure of ClF is 180 kPa. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations and then find the value for KP.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- (9 Pts) In one of the two Rare Earth element rows of the periodic table, identify an exception tothe general ionization energy (IE) trend. For the two elements involved, answer the followingquestions. Be sure to cite sources for all physical data that you use.a. (2 pts) Identify the two elements and write their electronic configurations.b. (2 pts) Based on their configurations, propose a reason for the IE trend exception.c. (5 pts) Calculate effective nuclear charges for the last electron in each element and theAllred-Rochow electronegativity values for the two elements. Can any of these valuesexplain the IE trend exception? Explain how (not) – include a description of how IErelates to electronegativity.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't use AIarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
