
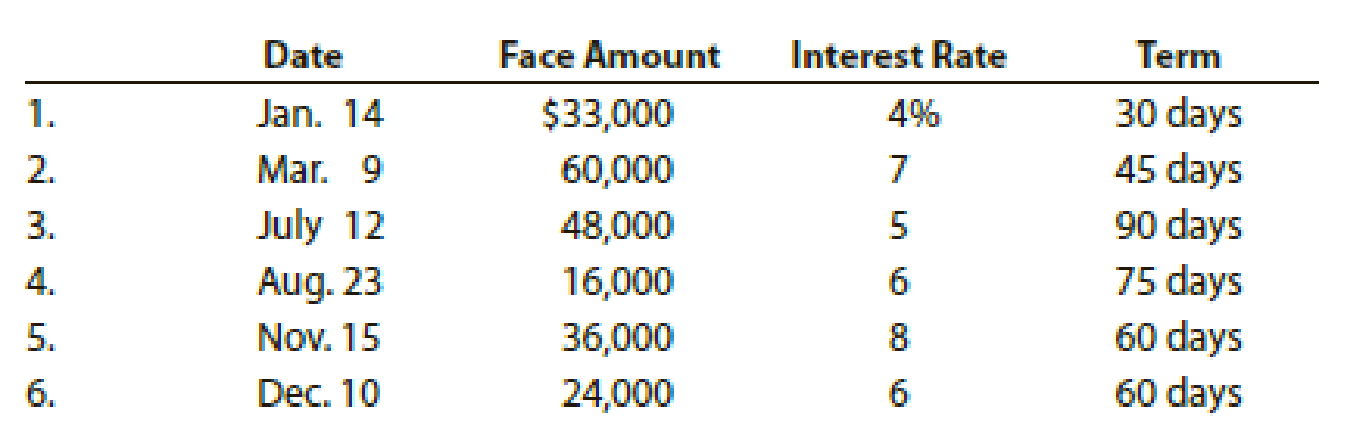
Gen-X Ads Co. produces advertising videos. During the current fiscal year, Gen-X Ads Co. received the following notes:
Instructions
- 1. Determine for each note (a) the due date and (b) the amount of interest due at maturity, identifying each note by number.
- 2.
Journalize the entry to record the dishonor of Note (3) on its due date. - 3. Journalize the
adjusting entry to record the accrued interest on Notes (5) and (6) on December 31. - 4. Journalize the entries to record the receipt of the amounts due on Notes (5) and (6) in January and February.
(1)
Calculate (a) the due date and (b) the amount of interest due at maturity.
Explanation of Solution
Note receivable: Note receivable refers to a written promise received by the creditor from the debtor in formal, for the amounts to be settled within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to the lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business. Notes receivable often used for the credit periods of more than 60 days.
Due date: Due date is the maturity date on note, on due date the borrower is supposed to repay the face value of the note along with interest.
Interest on note: Interest on note is the amount charged on the principal value of note for the privilege of borrowing money. Interest is to be paid by the borrower and to be received by the lender.
Determine (a) the due date and (b) the amount of interest due at maturity.
| Due date | Amount of interest due at maturity | |
| 1. | February 13 | $110 (1) |
| 2. | April 23 | $525 (2) |
| 3. | October10 | $600 (3) |
| 4. | November 6 | $200 (4) |
| 5. | January 14 | $480 (5) |
| 6. | February 8 | $240 (6) |
Table (1)
Working note (1):
For note 1:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Working note (2):
For note 2:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Working note (3):
For note 3:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Working note (4):
For note 4:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Working note (5):
For note 5:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Working note (6):
For note 6:
Calculate the amount of interest due at maturity.
Note:
Due date has been identified by omitting the date of note received but including the due date.
(2)
Journalize the dishonor of Note (3) on its due date.
Explanation of Solution
Dishonored note: Note receivable refers to a written promise by the debtor for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. Note is otherwise known as promissory note. If this promissory note is not settled by the debtor at its maturity date, then it became is known as dishonored note.
Journalize the dishonor of Note (3) on its due date.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| October 10 | Accounts receivable | 48,600 | |
| Notes receivable | 48,000 | ||
| Interest revenue (3) | 600 | ||
| (To record dishonor of Note 3) |
Table (1)
Note 3 have been dishonored on its due date. To record the dishonor on note, full value of note and accrued interest on note must be recorded as accounts receivable at the date of maturity. To record the defaulted note, accounts receivable and interest revenue should be increased and notes receivable should be eliminated. Hence,
- • An increase in accounts receivable (asset account) is debited with $48,600,
- • A decrease in notes receivable (asset account) is credited with $48,000, and
- • An increase in interest revenue (stockholders’ equity account) is credited with $600.
(3)
Journalize the adjusting entry to record the accrued interest on Notes (5) and (6) on December 31.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize adjusting entry to record the accrued interest on Notes (5) and (6) on December 31.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Interest receivable | 452 | |
| Interest revenue (9) | 452 | ||
| (To record the interest revenue accrued on the Note 5and Note 6 ) |
Working note (7):
Calculate the amount of interest revenue accrued on Note 5 as on December 31.
Working note (8):
Calculate the amount of interest revenue accrued on Note 6 as on December 31.
Working note (9):
Calculate the total amount of interest revenue accrued on Note 5 and Note 6.
On December 31, company has to record its accrued interest revenue on its note receivable, as December 31 is the accounting year end date of the company. This accrued interest revenue has to be recognized by increasing interest receivable and by increasing interest revenue of $452. Hence,
- • An increase in interest receivable (asset account) is debited with $452(9), and
- • An increase in interest revenue (stockholders’ equity account) is credited with $452 (9).
(4)
Journalize the entries to record the receipt of the amounts due on Notes (5) and (6) in January.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the entries to record the receipt of the amounts due on Notes (5) and (6) in January.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 14 | Cash | 36,480 | |
| Notes receivable | 36,000 | ||
| Interest receivable (7) | 368 | ||
| Interest revenue (10) | 112 | ||
| (To record the collection of cash on note 5 in full) |
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 29 | Cash | 24,240 | |
| Notes receivable | 24,000 | ||
| Interest receivable (8) | 84 | ||
| Interest revenue (11) | 156 | ||
| (To record the collection of cash on note 6 in full) |
Working note (10):
Calculate the amount of interest revenue earned on Note 5 from January 1 to January 14.
Working note (11):
Calculate the amount of interest revenue earned on Note 6 from January 1 to February 8.
On January 14, company has collected cash on note along with interest on its note receivable on Note 5. When a notes receivable is matured, it has to be cancelled by decreasing the note receivable account.
- • To decrease the (asset account) note receivable, credit the note receivable account with $36,000.
- • Interest receivable has been collected at maturity. Hence, it has to be cancelled by decreasing the interest receivable account. To decrease the (asset account) interest receivable, credit the interest receivable account with $368(7).
- • Interest revenue earned for last 28 days has to be recognized at maturity date. Hence, to increase the interest revenue balance, credit the interest revenueaccount with $112(10).
- • Collection of cash on note increases cash. Hence, to increase the cash account balance, debit the cash account with $36,480.
On February 8, company has collected cash on note along with interest on its note receivable on Note 6. When a notes receivable is matured, it has to be cancelled by decreasing the note receivable account.
- • To decrease the (asset account) note receivable, credit the note receivable account with $24,000.
- • Interest receivable has been collected at maturity. Hence, it has to be cancelled by decreasing the interest receivable account. To decrease the (asset account) interest receivable, credit the interest receivable account with $84(8).
- • Interest revenue earned for last 28 days has to be recognized at maturity date. Hence, to increase the interest revenue balance, credit the interest revenueaccount with $156(11).
- • Collection of cash on note increases cash. Hence, to increase the cash account balance, debit the cash account with $24,240.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- I am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward
- Can you explain the correct methodology to solve this financial accounting problem?arrow_forwardWhy does sustainability impact measurement require special approaches? a. Standard measures capture all impacts b. Environmental factors remain irrelevant c. Traditional methods work fine d. Long-term environmental effects demand unique valuation methodsarrow_forwardPlease show me the correct approach to solving this financial accounting question with proper techniques.arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





