
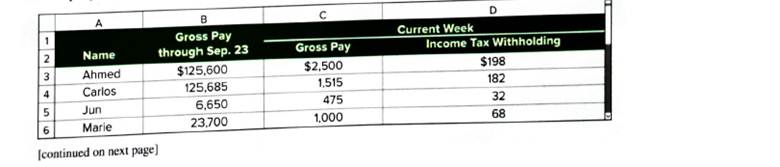
Fishing Guides Co. has four employees. FICA Social Security taxes are 6.2% of the first $127,200 paid to each Problem employee, and FICA Medicare taxes are 1.45% of gross pay. Also, for the first $7,000 paid to each employee, the Company’s FUTA taxes are 0.6% and SUTA taxes are 1.75%. The company is preparing its payroll calculations for the week ended September 30. Payroll records show the following information for the company's four employees.
In addition to gross pay, the company must pay two-thirds of the 60% of the $50 per employee weekly health insurance; each employee pays the remaining 40%. The company also contributes an extra 5% of each employee’s gross pay (at no cost to employees) to a pension fund.
Required
Compute the following for the week ended September30 (Round amounts to the nearest cent):
- Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Social Security.
- Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
- Employer’s FICA taxes for Social Security.
- Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
- Employer’s FUTA taxes.
- Employer’s SUTA taxes.
- Each employee’s net (take-home) pay.
- Employer’s total payroll-related expenses for each employee.
1.
Introduction: FICA withholdings for social security is a payroll deduction done by the employers and paid to the government. It is the withholding done to secure retirement and disabilities.
To compute: Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Social Security.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s FICA withholdings for social security.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person A | |
| Maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,600 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $1,600 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,500 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $1,600 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.20% |
| FICA social security tax | $99.20 |
| Person C | |
| The maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,685 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $1,515 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,515 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $1,515 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.20% |
| FICA social security tax | $93.93 |
| Person J | |
| The maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $6,650 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $120,550 |
| Gross pay for the current week(B) | $475 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $475 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.20% |
| FICA social security tax | $29.45 |
| Person M | |
| The maximum limit for FICA Social security tax | $127,200 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $23,700 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $103,500 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $1,000 |
| FICA social security tax rate | 6.20% |
| FICA social security tax | $62 |
2.
Introduction: FICA withholdings for Medicare is a payroll deduction done by the employers and paid to the Internal Revenue Service. It is the withholding done to secure an employee from the financial distress of an unexpected medical emergency.
To compute: Each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s FICA withholdings for Medicare.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person A | |
| Gross pay of current week | $2,500 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $36.25 |
| Person C | |
| Gross pay of current week | $1,515 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $21.97 |
| Person J | |
| Gross pay of current week | $475 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $6.89 |
| Person M | |
| Gross pay of current week | $1,000 |
| FICA Medicare tax rate | 1.45% |
| FICA Medicare tax | $14.50 |
3.
Introduction: Employer’s FICA taxes for social security is the contribution made by the employer for the employee’s retirement benefits and future survivorship.
To compute: Employer’s FICA taxes for Social Security.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FICA taxes for social security.
| Particular | Amount |
| FICA social security tax of person A | $99.20 |
| FICA social security tax of person C | $93.93 |
| FICA social security tax of person J | $29.45 |
| FICA social security tax of person M | $62 |
| Total employer’s FICA taxes for social security | $284.58 |
4.
Introduction: Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare is the contribution made by the employer for the employee’s medical expenses. It is like a medical insurance premium of an employee.
To compute: Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare.
| Particular | Amount |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of person A | $36.25 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of person C | $21.97 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of person J | $6.89 |
| FICA taxes for Medicare of person M | $14.50 |
| Total employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare | $79.61 |
5.
Introduction: Federal unemployment tax act (FUTA) is a law applicable on employers. Under this act, tax is imposed on employer’s payroll expense to collect funds for the scheme made for removing unemployment.
To compute: Employer’s FUTA taxes.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s FUTA taxes.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person A | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,600 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,500 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| FUTA tax rate | 0.60% |
| FUTA tax | $0 |
| Person C | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,685 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,515 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| FUTA tax rate | 0.60% |
| FUTA tax | $0 |
| Person J | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $6,650 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $350 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $475 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $350 |
| FUTA tax rate | 0.6% |
| FUTA tax | $2.10 |
| Person M | |
| Maximum limit of Gross pay for FUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $23,700 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| FUTA tax rate | 0.6% |
| FUTA tax | $0 |
| Total FUTA tax of Employer | $2.10 |
6.
Introduction: State unemployment tax act (SUTA) is a law made to impose a tax on employers. The employers pay this amount to the state unemployment fund, established by the state government to remove unemployment.
To compute: Employer’s SUTA taxes.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of Employer’s SUTA taxes.
| Particular | Amount |
| Person A | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for SUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,600 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $2,500 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| SUTA tax rate | 1.75% |
| SUTA tax | $0 |
| Person C | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for SUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $125,685 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,515 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| SUTA tax rate | 1.75% |
| SUTA tax | $0 |
| Person J | |
| Maximum limit of gross pay for SUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $6,650 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $350 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $475 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $350 |
| SUTA tax rate | 1.75% |
| SUTA tax | $6.13 |
| Person M | |
| Maximum limit of Gross pay for SUTA taxes | $7,000 |
| Gross pay till September 23 | $23,700 |
| Remaining limit(A) | $0 |
| Gross pay for current week(B) | $1,000 |
| Gross pay on which tax has to be deducted(Lower of A & B) | $0 |
| SUTA tax rate | 1.75% |
| SUTA tax | $0 |
| Total SUTA tax of Employer | $6.13 |
7.
Introduction: Take-home pay to an employee means the amount paid to an employee against their salary after deducting all the voluntary contributions and withholdings for which the employee is liable.
To compute: Each employee’s net (take-home) pay.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of each employee’s net (take home) pay.
| Particular | Person A | Person C | Person J | Person M |
| Gross Pay | $2,500 | $1,515 | $475 | $1,000 |
| Less: Income Tax Withholding | ($198) | ($182) | ($32) | ($68) |
| Less: FICA social security tax | ($99.20) | ($93.93) | ($29.45) | ($62) |
| Less: FICA taxes for Medicare | ($36.25) | ($21.97) | ($6.89) | ($14.50) |
| Less: Weekly health insurance | ($20) | ($20) | ($20) | ($20) |
| Net (take home) pay | $2,146.55 | $1197.1 | $386.66 | $835.5 |
8.
Introduction: Payroll related expense are the expense related to the employees of the company which is incurred due to providing employment. All the payment made to employees, government and any other fund is included in it.
To compute:Employer’s total payroll-related expense for each employee.
Explanation of Solution
Computation of employer’s total payroll-related expense for each employee.
| Particular | Person A | Person C | Person J | Person M |
| Gross pay | $2,500 | $1,515 | $475 | $1,000 |
| Employer’s FICA taxes for social security | $99.2 | $93.93 | $29.45 | $62 |
| Employer’s FICA taxes for Medicare | $36.25 | $21.97 | $6.89 | $14.50 |
| Employer’s FUTA taxes | $0 | $0 | $2.10 | $0 |
| Employer’s SUTA taxes | $0 | $0 | $6.13 | $0 |
| Employee weekly health insurance | $30 | $30 | $30 | $30 |
| Total payroll-related expense | $2,665.45 | $1,660.90 | $549.57 | $1,106.50 |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Connect Access Card for Financial Accounting: Information and Decisions
- QS 15-18 (Algo) Computing and recording over- or underapplied overhead LO P4 A company applies overhead at a rate of 170% of direct labor cost. Actual overhead cost for the current period is $1,081,900, and direct labor cost is $627,000. 1. Compute the under- or overapplied overhead. 2. Prepare the journal entry to close over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Compute the under- or overapplied overhead.arrow_forwardQuestion 6 During 2019, Bitsincoins Corporation had EBIT of $100,000, a change in net fixed assets of $400,000, an increase in net current assets of $100,000, an increase in spontaneous current liabilities of $400,000, a depreciation expense of $50,000, and a tax rate of 30%. Based on this information, what is Bitsincoin's free cash flow? (3 marks)arrow_forwardQuestion 4 Waterfront Inc. wishes to borrow on a short-term basis without reducing its current ratio below 1.25. At present its current assets and current liabilities are $1,600 and $1,000 respectively. How much can Waterfront Inc. borrow? (5 marks)arrow_forward
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





