
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780073511214
Author: Francis A Carey Dr., Robert M. Giuliano
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 9, Problem 37P
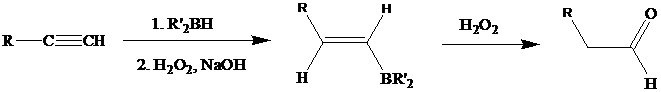
The oxidation step involves an enol intermediate. Using Mechanism
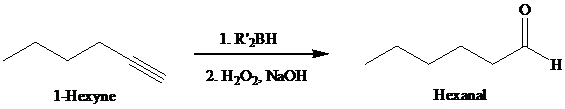
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Determine the change in Gibbs energy, entropy, and enthalpy at 25°C for the battery from which the data in the table were obtained.T (°C) 15 20 25 30 35Eo (mV) 227.13 224.38 221.87 219.37 216.59Data: n = 1, F = 96485 C mol–1
Indicate the correct options.1. The units of the transport number are Siemens per mole.2. The Siemens and the ohm are not equivalent.3. The Van't Hoff factor is dimensionless.4. Molar conductivity does not depend on the electrolyte concentration.
Ideally nonpolarizable electrodes can1. participate as reducers in reactions.2. be formed only with hydrogen.3. participate as oxidizers in reactions.4. form open and closed electrochemical systems.
Chapter 9 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
Ch. 9.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 9.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 9.4 - How do bond distances and bond strengths change...Ch. 9.5 - Complete each of the following equations to show...Ch. 9.6 - Prob. 5PCh. 9.6 - Which of the alkynes of molecular formula C5H8 can...Ch. 9.7 - Give the structures of three isomeric dibromides...Ch. 9.7 - Prob. 8PCh. 9.9 - Write a series of equations showing how you could...Ch. 9.9 - Write a series of equations showing how to prepare...
Ch. 9.10 - Prob. 11PCh. 9.11 - Give the structure of the enol formed by hydration...Ch. 9.11 - Prob. 13PCh. 9.13 - Prob. 14PCh. 9.14 - Prob. 15PCh. 9 - Provide the IUPAC name for each of the following...Ch. 9 - Prob. 17PCh. 9 - All compounds in Problem 9.17 are isomers except...Ch. 9 - Prob. 19PCh. 9 - Write structural formulas for all the alkynes of...Ch. 9 - Prob. 21PCh. 9 - Prob. 22PCh. 9 - The alkane formed by hydrogenation of...Ch. 9 - Write the structure of the major organic product...Ch. 9 - Write the structure of the major organic product...Ch. 9 - When 2-heptyne was treated with aqueous sulfuric...Ch. 9 - Prob. 27PCh. 9 - Prob. 28PCh. 9 - Prob. 29PCh. 9 - Show by writing appropriate chemical equations how...Ch. 9 - Show by writing appropriate chemical equations how...Ch. 9 - Diphenylacetylene can be synthesized by the double...Ch. 9 - (Z)-9-tricosene [ (Z)-CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)12CH3 ]...Ch. 9 - Prob. 34PCh. 9 - Prob. 35PCh. 9 - Prob. 36PCh. 9 - Alkynes undergo hydroboration to give...Ch. 9 - Prob. 38DSPCh. 9 - Prob. 39DSPCh. 9 - Prob. 40DSPCh. 9 - Prob. 41DSPCh. 9 - Thinking Mechanistically About Alkynes The...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Indicate the options for an electrified interface:1. Temperature has no influence on it.2. Not all theories that describe it include a well-defined electrical double layer.3. Under favorable conditions, its differential capacitance can be determined with the help of experimental measurements.4. A component with high electronic conductivity is involved in its formation.arrow_forwardTo describe the structure of the interface, there are theories or models that can be distinguished by:1. calculation of the charge density.2. distribution of ions in the solution.3. experimentally measured potential difference.4. external Helmoltz plane.arrow_forwardIndicate the correct options when referring to Luther's equation:1. It is not always easy to compare its results with experimental results.2. It depends on the number of electrons exchanged in the species involved.3. Its foundation is thermodynamic.4. The values calculated with it do not depend on temperature.arrow_forward
- Indicate which of the unit options correspond to a measurement of current density.1. A s m-22. mC s-1 m-23. Ω m-24. V J-1 m-2arrow_forwardIndicate the options that are true when referring to electrode membranes:1. The Donnan potential, in general, does not always intervene in membranes.2. There are several ways to classify the same membrane.3. Any membrane can be used to determine the pH of a solution.4. Only one solution and one membrane are needed to determine the pH of that solution.arrow_forwardCalculate the maximum volume of carbon dioxide gasarrow_forward
- In galvanic cells, their potential1. can be measured with a potentiometer2. does not depend on the equilibrium constant of the reaction occurring within them3. is only calculated from the normal potentials of the electrodes they comprise4. can sometimes be considered a variation in a potential differencearrow_forwardIf some molecules in an excited state collide with other molecules in a ground state, this process1. can occur in solution and in the gas phase.2. can be treated as a bimolecular process.3. always results in collisional deactivation.4. does not compete with any other process.arrow_forwardRadiation of frequency v is incident on molecules in their ground state. The expected outcome is that1. the molecules do not change their state.2. the molecules transition to an excited state.3. the molecules undergo a secondary process.4. collisional deactivation occurs.arrow_forward
- Predict the major product of the following reaction and then draw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 H₂SO heat : OH 90 Draw the structure of the major product. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 3arrow_forwardDraw a curved arrow mechanism for the reaction, adding steps as necessary. Be sure to include all electrons that are necessary to the mechanism and all nonzero formal charges. C Ö-H H + -S-OH .0. Add/Remove step X टे Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. You may need to re-draw structures to show certain bonds. Ensure that HSO is used as the base to deprotonate the ẞ carbon when necessary. C HO : OH HO: OH =s = + 1 Add/Remove step X Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Coenzymes and cofactors; Author: CH15 SWAYAM Prabha IIT Madras;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bubY2Nm7hVM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Aromaticity and Huckel's Rule; Author: Professor Dave Explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7-BguH4_WBQ;License: Standard Youtube License