
Find the reactions and all bar forces for the truss.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The Young’s modulus E of the beam is
The area of all the bars is
Calculation:
Show the free body diagram of the truss as shown in Figure 1.
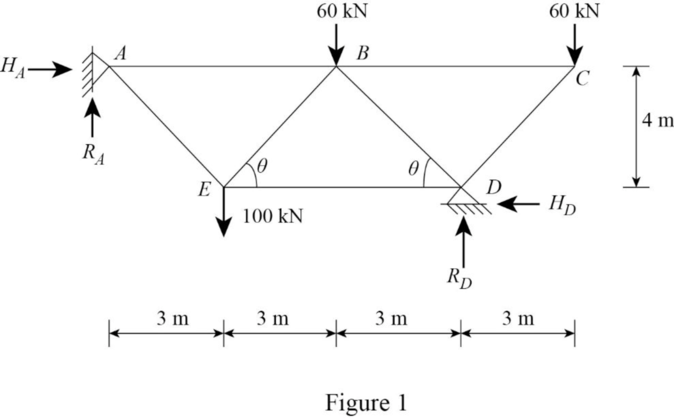
Refer Figure 1.
Find the length of the inclined members of the truss as follows:
Consider the length of the inclined members AE, EB, BD, DC is l.
By symmetry of truss,
Find the angle
Consider the horizontal reaction at D as the redundant.
Remove the redundant at D to get the released structure.
Show the released structure with applied load as shown in Figure 2.
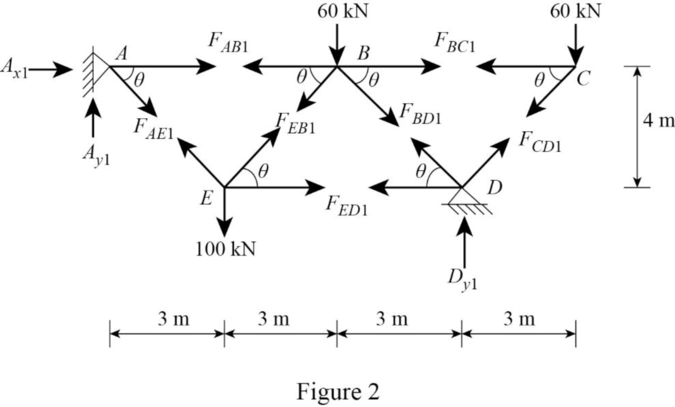
Refer Figure 2.
Find the reactions at A and D as follows:
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Find the forces
Refer Figure 2.
Consider Joint A.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Consider joint C.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Consider joint B.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Solve Equation (1) and (2).
Consider joint D.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Show the P forces in the members of the truss due to the applied load at D as shown in Table 1.
| Members | |
| AB | 50 (C) |
| BC | 45 (T) |
| CD | 75 (C) |
| DE | 25 (T) |
| EA | 83.3 (T) |
| BE | 41.7 (T) |
| BD | 116.7 (C) |
Table 1
Show the released structure loaded with unit horizontal load at D as shown in Figure 3.
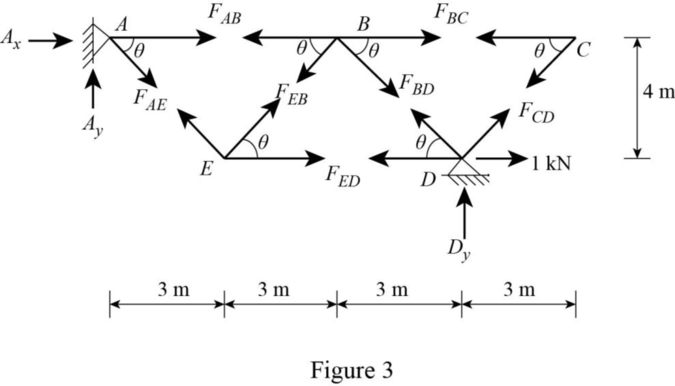
Refer Figure 3.
By symmetry of the truss,
Find the
Refer Figure 3.
Consider Joint A.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Consider joint C.
In a two member forces BC and CD, if both the members are not parallel and the no external loads or reactions acts at that joint. Then, the force in both the members is zero.
The forces in the member BC and CD is
Consider joint B.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Solve Equation (1) and (2).
Consider joint D.
Apply Equation of Equilibrium,
Show the Q forces in the members of the truss due to the unit load at D as shown in Table 1.
| Members | |
| AB | 0.667 (C) |
| BC | 0 |
| CD | 0 |
| DE | 0.667 (C) |
| EA | 0.556 (C) |
| BE | 0.556 (T) |
| BD | 0.556 (C) |
Table 2
Find the deflection
| Members | |||||
| AB | -50 | -0.667 | 6 | ||
| BC | 45 | 0 | 6 | 0 | |
| CD | -75 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| DE | 25 | -0.667 | 6 | ||
| EA | 83.3 | -0.556 | 5 | ||
| BE | 41.7 | 0.556 | 5 | ||
| BD | -116.7 | -0.556 | 5 |
Table 3
Refer Table 3.
Find the horizontal reaction at D as follows:
Thus, the horizontal reaction at D is
Find final forces in the truss as shown in Table 4.
| Members | ||||
| AB | -50 | -0.667 | -30.9 | -29.4 |
| BC | 45 | 0 | -30.9 | 45 |
| CD | -75 | 0 | -30.9 | -75 |
| DE | 25 | -0.667 | -30.9 | 45 |
| EA | 83.3 | -0.556 | -30.9 | 100.5 |
| BE | 41.7 | 0.556 | -30.9 | 24.5 |
| BD | -116.7 | -0.556 | -30.9 | -99.5 |
Table 4
Show the final support reaction as shown in Table 5.
| Support Reactions | ||||
| Members | ||||
| 0 | 1 | -30.9 | -30.9 | |
| 66.7 | -0.444 | -30.9 | 80.4 | |
| 153.3 | 0.444 | -30.9 | 139.6 | |
Table 5
Thus, the reactions and all bar forces for the truss is tabulate in table 4 and table 5.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
- Determine the minimum possible surface area of a secondary clarifier treating activated sludge with a design influent flow rate (Q) of 1,000 m³/d, a return activated sludge (RAS) recycling ratio of 25%, and a mixed liquor total suspended solids (MLSS) concentration of 4,000 mg/L, if the overflow rate must be less than 33 m/d and the solids loading rate must be less than 250 kg/m²/d. Express your answer in m² and round up to the next integer.arrow_forwardEstimate the required air flow rate for the new activated sludge plant at Pea Ridge (Problems 23-223-723-10, and 23-13). The flow rate is 8,450 m³/day, the concentration of bCOD going into the system (So) is 137 mg/L, the concentration of bCOD leaving the system (S) is 16.3 mg/L, and the mass of cells produced per day (Pxvss) is 277.4 kg/d. Use the following assumptions to estimate the required air flow rate: . Clean water correction, a = 0.50 . Salinity correction, B = 0.95 Fouling factor = 0.9 Wastewater temperature = 12°C Atmospheric pressure = 101.325 kPa .Elevation 500 m . Depth of aerator = 5.6 m Operating DO 2.0 mg/L Percent oxygen leaving aeration tank - 19% ■ Manufacturer's SOTR = 535 kg/d Manufacturer's air flow rate at standard conditions 50 m³/d - aerator Express your answer with the units of m³/d and round to the nearest integer.arrow_forwardDetermine the required solids retention time (SRT) of a completely mixed activated sludge aeration tank for a conventional activated sludge system treating a design flow rate of 34,560 m³/d, where the effluent standards are 30.0 mg/L for BODs and 30.0 mg/L for total suspended solids (TSS). Assume that the BOD5 of the effluent TSS is 70% of the TSS concentration. Assume the BODs concentration leaving the primary clarifier is 128 mg/L that the MLVSS concentration (X₂) is 2,500 mg/L. Assume the following values for the growth constants: Ks 100 mg/L BODS ⚫ Hm - 2.5 d 1 kd = 0.050 d 1 Y = 0.50 mg VSS/mg BODs removed Express your answer in days and round to the nearest 0.1.arrow_forward
- Q1: Figure below shows loaded beam with its cross-section area, (A) Draw shear force and bending moment diagrams, stating the main values, (B) Find central slope and deflection, (C) Sketch the distribution of shear stress at left support, (D) Find maximum tensile and compressive bending stresses set up in beam at right support. E-205GN/m² P1 P2 P3 W1 W2 Lin Lin # A Length in (m) and loads in kN 3a a 2a 2a (Cross-section area, All dimensions in (mm))arrow_forwardEstimate the mass of oxygen to be supplied for a new activated sludge plant at Pea Ridge to treat a flow rate of 8,450 m³/day. Assume that the concentration of bCOD going into the system (So) is 137 mg/L, that the bCOD leaving the system (S) is 16.3 mg/L, and that the mass of cells produced per day (Pxvss) is 277.4 kg/d. Express your answer in kg/day and round to the nearest integer.arrow_forward*10-4. Determine the internal moments at the supports A, B, and C, then draw the moment diagram. Assume A is pinned, and B and C are rollers. El is constant. 3 k/ft 8 ft- 8 ft -4 ft-arrow_forward
- Q2: Determine the change in dimensions in each section of the bar shown in figure. The portion AB is circular section and portion BC is rectangular section. E=115GN/m², v=0.33. L1 L2 P2+ P2 B Q3: A block is subjected to the stresses as shown in figure, find: principal stresses, shear stress with their directions and the normal and shear stresses on a plane inclined at 0. All stresses in MPa. (Confirm your answer by means of Mohr's stress circle). Txy 30 Note: (1) For all questions the student can choose any values of P1, P2, P3, W1, W2, a, σ (MPa), Txy (MPa), 0°, length and the dimensions of cross section area.arrow_forwardFor the gravity concrete dam shown in the figure, the following data are available: Unit weight of concrete (y)-2.4 ton/m Neglect Wave pressure, silt pressure, ice force and earth quake force) -0.65, (7)-1 ton/m Find factor of safety against sliding and overturning (F.Sa & FS), If heel and toe stresses (Pa & Pen) are 57.17ton/m² and 84.53 ton/m² respectively. w.s.l 83m Solve and sketch on paper 10m 80m 8marrow_forwardNeed assistance with d.arrow_forward
- 2. A series of gears are mounted on a 40mm diameter steel shaft. Take G = 75 GPa. (i) Draw the torque load diagram. (ii) Determine the angle of twist of gear B relative to gear A. (iii) Determine the maximum shear stress and it's location along the shaft. 600 N-m 900 N-m 200 mm 200 mm 200 mm 500 Nm 300 N·m 200 mm 500 N-marrow_forward1. The figure below shows a circular shaft with three sections. The length of each section is 50mm. (E 500 MPa). = (i) Draw the axial load diagram of the circular shaft. (ii) Determine the average normal stress at points A, B and C. (iii) Determine the maximum deformation and it's location along the shaft. 10 mm 5 mm 5 mm B 300 N A 900 N 800 N C 200 Narrow_forward02: For the gravity concrete dam shown in the figure, (the vertical stresses at toe and heel ((Pmax & Pmin) are 199 and 52 ton/m respectively. following data are available:- -Unit weight of concrete (ycone)-24 ton/m³ -Neglect Wave pressure, silt pressure, ice force and earth quake force. #-0.65 Find factor of safety against sliding and overturning (F.Sslid & F.Sover) AS 115 m 8 m 120 m Solve with sketch on paperarrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





