
What are the common and systematic names of the following ethers?
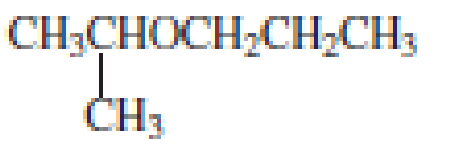
- a. CH3CH2CH2CH2OCH2CH3
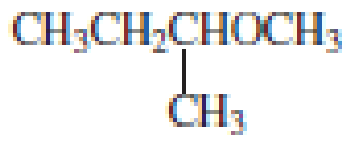
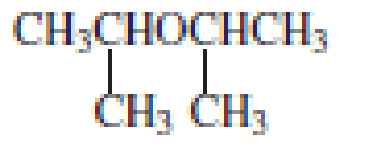
(a)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether have to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
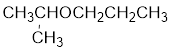
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with three carbons in the parent chain. Hence, the parent chain will be propane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
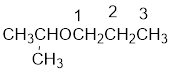
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen is the isopropyl group.
Therefore, systematic name of the compound is given below:
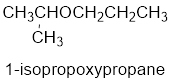
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one iso propyl group and one propyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
Propyl isopropyl ether
(b)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
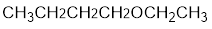
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with four carbons in the parent chain. Thus the parent chain will be butane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
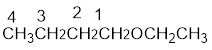
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen that is in the first carbon is the ethyl group and therefore, the prefix will be “ethoxy”.
Therefore, the systematic name of the compound is given below:
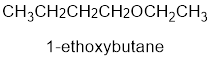
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one ethyl group and one butyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
butyl ethyl ether.
(c)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
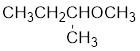
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with four carbons in the parent chain. Thus the parent chain will be butane. The numbering of the longest chain will be in such a way to get the carbon atom attached to the oxygen the possible lowest number.
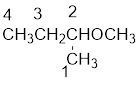
The oxygen is attached to the second carbon.
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen is the methyl group and therefore, the prefix will be “methoxy”.
Therefore, the systematic name of the compound is given below:
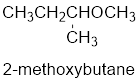
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, one sec-butyl group and one methyl group is attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
Sec-butyl methyl ether.
(d)
Interpretation:
The systematic name and the common name of the given ether has to be given.
Concept introduction:
IUPAC naming of Ether compounds:
An ether group consists of oxygen atom attached between two carbon chains. The shorter of two chains becomes the first part of the name with ‘ane’ changes to ‘oxy’ and the longer alkane becomes the suffix of the name of the ether.
When the Oxygen is not at the terminal position of main chain of alkane, then the shorter alkyl group and the ether group together are treated as a side chain and prefixed with its position of bonding on the main chain.
Common name for ether compounds:
- The name of the groups attached to the oxygen has to be given in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the compound is given below:
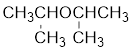
From the structure of the compound, it is understood that the compound is an ether with three carbons in the parent chain. Hence, the parent chain will be propane.
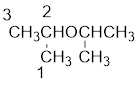
The shorter alkyl group attached to the oxygen that is in the second carbon is the isopropyl group and therefore, the prefix of the name will be “isopropoxy”.
Therefore, systematic name of the compound is given below:
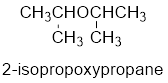
The common name of the compound can be identified by naming the alkyl groups attached to the oxygen followed by the word ether. In the given compound, diisopropyl groups are attached to oxygen.
Therefore, common name of the compound is given below:
disopropyl ether.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- help me solve this HWarrow_forwardMolecules of the form AH2 can exist in two potential geometries: linear or bent. Construct molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent CH2. Identify the relevant point group, include all of the appropriate symmetry labels and pictures, and fill in the electrons. Which geometry would you predict to be more stable, and why? (Please draw out the diagram and explain)arrow_forwardIndicate the variation in conductivity with concentration in solutions of strong electrolytes and weak electrolytes.arrow_forward
- The molar conductivity of a very dilute solution of NaCl has been determined. If it is diluted to one-fourth of the initial concentration, qualitatively explain how the molar conductivity of the new solution will compare with the first.arrow_forwardWhat does the phrase mean, if instead of 1 Faraday of electricity, Q coulombs (Q/F Faradays) pass through?arrow_forwardWhat characteristics should an interface that forms an electrode have?arrow_forward
- For a weak acid AcH, calculate the dissociated fraction (alpha), if its concentration is 1.540 mol L-1 and the concentration [H+] is 5.01x10-4 mol L-1.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardIf the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forward
- If the molar conductivity at infinite dilution of HAC is A0 = 390.5 S cm² mol¹. Calculate the Arrhenius conductivity of a 9.3% by weight solution of HAc with a pH of 3.3. Data: molecular weight of HAC is 60.05 g/mol and the density of the solution is 1 g/cm³.arrow_forwardDetermine the distance between the metal and the OHP layer using the Helm- holtz model when the electrode's differential capacitance is 145 μF cm². DATA: dielectric constant of the medium for the interfacial zone &r= lectric constant of the vacuum &0 = 8.85-10-12 F m-1 = 50, die-arrow_forwardDescribe a sequence of photophysical processes that can be followed by radiation adsorbed by a molecule in the ground state to give rise to phosphorescent emission.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning


