
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
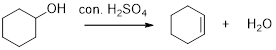
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(b)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
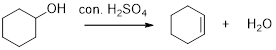
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the alkene product. Thus the removal of water molecule occurs in the dehydration process and the major product of the acid-catalysed dehydration reaction will be the more substituted product.
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
(c)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
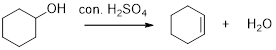
E2 dehydration of primary alcohols:
Due to the unstability of the primary carbocation, the dehydration of primary alcohol is an E2 reaction.
In the E2 reaction, protonation of the most basic atom occurs and then base will remove a proton from the beta carbon.
(d)
Interpretation:
The major elimination product obtained when the given alcohol is heated in the presence of sulphuric acid has to be has to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Dehydration reaction:
Removal of water molecule from the reaction of alcohol with strong acid like sulfuric acid is known as dehydration reaction.
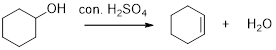
E1 dehydration reaction of secondary and tertiary alcohols:
The alcohols react with acids like hydrochloric acid or hydrobromic which yield the corresponding stable carbocation intermediate. The elimination of hydrogen from the beta carbon results in the alkene product. Thus the removal of water molecule occurs in the dehydration process and the major product of the acid-catalysed dehydration reaction will be the more substituted product.
Carbocation: It is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
The increasing stability order of carbocation is as follows,
Primary carbocation < secondary carbocation < tertiary carbocation
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
