
Introduction:
Elements combine to form compounds. Compounds have unique characteristics. They are formed from specific combination of elements in a fixed ratio. The force that holds the atoms together in a molecule of a compound is called
Answer to Problem 1STP
Correct answer :
The correct answer is option C. CF4
Explanation of Solution
Explanation/justification for the correct answer:
Option C. CF4−Carbon has four electrons in its outermost shell and fluorine has seven electrons in its outermost shell. Onecarbon atom can share electrons with four different fluorine atoms to complete its outer energy level. It forms four covalent bonds, one with each fluorine atom.Hence one carbon atom can combine with four fluorine atoms to form a compound CF4.
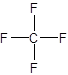
Hence this is the correct option.
Explanation for incorrect answer:
Option A. CF2−One carbon atom can share electrons with four different fluorine atoms to complete its outer energy level. It forms four covalent bonds, one with each fluorine atom. Hence one carbon atom can combine with four fluorine atoms to form a compound CF4. Carbon cannot satisfy outer energy level with only two fluorine atoms.
Hence this is not the correct option.
Option B. CF3- One carbon atom can share electrons with four different fluorine atoms to complete its outer energy level. It forms four covalent bonds, one with each fluorine atom. Hence one carbon atom can combine with four fluorine atoms to form a compound CF4. Carbon cannot satisfy outer energy level with only three fluorine atoms.
Hence this is not the correct option.
Option D. CF5- One carbon atom can share electrons with four different fluorine atoms to complete its outer energy level. It forms four covalent bonds, one with each fluorine atom. Hence one carbon atom can combine with four fluorine atoms to form a compound CF4. Carbon cannot combine with five fluorine atoms.
Hence this is not the correct option.
Chapter 9 Solutions
EP BIOLOGY 2012-STUDENTWORKS ONLINE
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Chemistry
Human Anatomy & Physiology (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
- students in a science class investiged the conditions under which corn seeds would germinate most successfully. BAsed on the results which of these factors appears most important for successful corn seed germination.arrow_forwardI want to write the given physician orders in the kardex formarrow_forwardAmino Acid Coclow TABle 3' Gly Phe Leu (G) (F) (L) 3- Val (V) Arg (R) Ser (S) Ala (A) Lys (K) CAG G Glu Asp (E) (D) Ser (S) CCCAGUCAGUCAGUCAG 0204 C U A G C Asn (N) G 4 A AGU C GU (5) AC C UGA A G5 C CUGACUGACUGACUGAC Thr (T) Met (M) lle £€ (1) U 4 G Tyr Σε (Y) U Cys (C) C A G Trp (W) 3' U C A Leu בוט His Pro (P) ££ (H) Gin (Q) Arg 흐름 (R) (L) Start Stop 8. Transcription and Translation Practice: (Video 10-1 and 10-2) A. Below is the sense strand of a DNA gene. Using the sense strand, create the antisense DNA strand and label the 5' and 3' ends. B. Use the antisense strand that you create in part A as a template to create the mRNA transcript of the gene and label the 5' and 3' ends. C. Translate the mRNA you produced in part B into the polypeptide sequence making sure to follow all the rules of translation. 5'-AGCATGACTAATAGTTGTTGAGCTGTC-3' (sense strand) 4arrow_forward
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





