
To describe: The signs of inflammation that came in the given statement.
Introduction: An inflammation is the sequence of events in response to the infections that would limit the effects of injury or any agent in the body. It is the biological response against the harmful stimuli to eliminate the initial cause of the healthy tissue injury or damage. Its main function is to act as a defense mechanism of the body to remove the injurious agents from the body to prevent infections.
Explanation of Solution
Given statement: While jogging in the surf, a person’s toes land on a jelly fish. The bottom of the toes becomes swollen, red, and warm to touch.
In the given case, the sting of the jellyfish causes inflammation that accompanies the visible signs such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain. The inflammation begins through a signal provided by the damage caused by the sting. The basic steps involved in the inflammation are caused by the sting of jelly fish as follows:
Basic steps involved:
- 1. Release of various chemicals: Numerous chemicals such as histamine, interleukins, tumor necrosis factors (TNFs), chemotactic factors, leukotriene, and prostaglandins are released by the damaged cells of injured tissues basophils, mast cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and infectious organisms to promote inflammation.
- 2. Vascular changes: The released chemical causes many local effects on the blood vessels such as:
- Increased vascular permeability
- Arteriolar vasodilation
- Leukocyte adhesion
- 3. Leukocyte recruitment:The movement of the leukocyte through the blood at the site of infection occurs by the following processes:
- a) Margination: The cell adhesion molecules (CAM) present on the surface of the leukocytes (first neutrophil and then macrophages) adhere to the endothelial capillaries present within the injured tissue.
- b) Diapedesis: Here, the cells migrate to the site of infection by exiting the blood through “squeezing out” between the vessel walls.
- c)
Chemotaxis : Chemotaxis is the movement of cells along a chemical gradient formed due to the chemicals release by the damaged cells, dead cells, or invading pathogens. Cytokines and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) are released to attract more macrophages to the site of infection. IL-1 released by macrophages induces fever in the body. - d) Delivery of plasma proteins: Several plasma proteins such as immunoglobulin’s complement, clotting proteins, and kinins are brought into the infection site that cause local effects such as increased vascular permeability, pain, heat, and swelling on the infected site.
- 4. Tissue repair and healing:Immune cells and their secretions process the pathogen and the newly formed lymph carries the pathogen with the unwanted dead cells and cell debris from the interstitial space of the tissue. The exudate (fluid and cellular/protein mix) is passed through the lymph nodes for monitoring, transported liver, and then, removed from the body.
- 1. Redness: Inflammation increases the vascular permeability which causes the flow of a large amount of blood toward the site of infection. Due to the increased blood flow, there will be redness at the site of infection.
- 2. Heat: The heat will be generated at the site of infection due to the increased blood flow as well as the increased
metabolic activity of cells within the area. - 3. Swelling: As a result of inflammation, a large amount of fluid is lost from capillaries into the interstitial space that causes swelling around the injured site.
- 4. Pain: Pain occurs when the pain receptors are stimulated due to the compression from the accumulation of interstitial fluid and by the irritation of the released microbial substances, kinins, or prostaglandins.
- 5. Loss of function: Loss of function occurs due to the pain and swelling.
The cardinal signs of inflammation are as follows:
Thus, several immune factors produced as a result of inflammation neutralize the toxin from the jellyfish.
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows the steps in the inflammatory response followed by bacterial invasion and activation of immune cells at the site of injury.
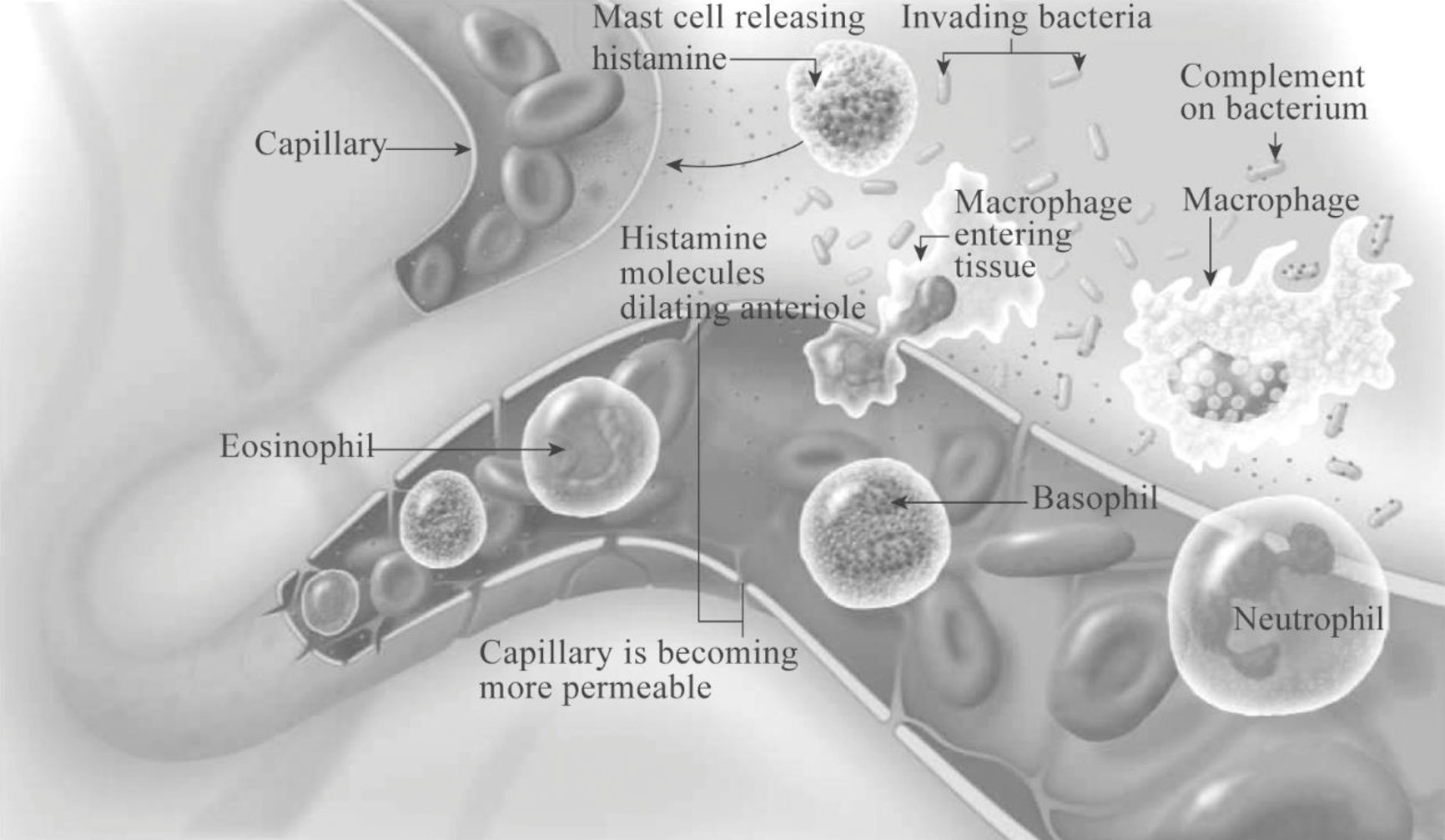
Fig.1: Basic steps in inflammatory response
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 9 Solutions
EBK HUMAN BIOLOGY
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





